Abstract
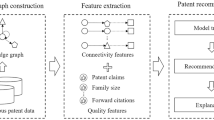
We show how a deep neural network can be designed to learn meaningful representations from high-dimensional and heterogeneous categorical features in patent data using self-supervised learning. Based on each firm’s technology portfolio and each patent’s co-classification information, we propose a novel recommendation system for firms seeking new convergence opportunities through representations of convergence items and firms. The results of this work are expected to recommend convergence opportunities in multiple technology fields by considering the target firm’s potential preference. First, we create a technology portfolio consisting of a set of patents owned by each firm. Then, we train a neural network to extract latent representations of firms and technology convergence items. Despite a lack of indicators related to a firm’s latent preference for a convergence item, a self-supervised neural network can capture the similarity with semantic information of firm’s latent preference that is implicitly present in patent’s co-classification information in each firm’s technology portfolio. We then calculate the similarity between the vector of a target firm and convergence items for recommendation. The top N similar convergence items that have the highest scores are recommended as the new convergence items for the target firm. We apply our framework to the dataset of patents granted by the United States Patent and Trademark Office between 2011 and 2015. The results indicate that the recent development in theories and empirical studies of deep representation learning can shed new light on extracting valuable information from the structured part of patent data.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achille, A., & Soatto, S. (2018). Emergence of invariance and disentanglement in deep representations. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 19(1), 1947–1980.
Allarakhia, M., & Walsh, S. (2012). Analyzing and organizing nanotechnology development: Application of the institutional analysis development framework to nanotechnology consortia. Technovation, 32(3–4), 216–226.
An, J., Kim, K., Mortara, L., & Lee, S. (2018). Deriving technology intelligence from patents: Preposition-based semantic analysis. Journal of Informetrics, 12(1), 217–236.
Arora, S., Khandeparkar, H., Khodak, M., Plevrakis, O., & Saunshi N. (2019). A theoretical analysis of contrastive unsupervised representation learning. In International Conference on Machine Learning, (pp. 5628–5637).
Bengio, Y. (2009). Learning deep architectures for AI. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 2(1), 1–127.
Bengio, Y., Lamblin, P., Popovici, D., & Larochelle, H. (2007). Greedy layer-wise training of deep networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 153–160).
Bengio, Y., Courville, A., & Vincent, P. (2013). Representation learning: A review and new perspectives. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 35(8), 1798–1828.
Bigliardi, B., Ivo Dormio, A., & Galati, F. (2012). The adoption of open innovation within the telecommunication industry. European Journal of Innovation Management, 15(1), 27–54.
Breschi, S., Lissoni, F., & Malerba, F. (2003). Knowledge-relatedness in firm technological diversification. Research policy, 32(1), 69–87.
Caviggioli, F. (2016). Technology fusion: Identification and analysis of the drivers of technology convergence using patent data. Technovation, 55, 22–32.
Cerda, P., Varoquaux, G., & Kégl, B. (2018). Similarity encoding for learning with dirty categorical variables. Machine Learning, 107(8–10), 1477–1494.
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., & Hinton, G. (2020). A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.05709.
Cheng, H. T., Koc, L., Harmsen, J., Shaked, T., Chandra, T., Aradhye, H., & Anil, R. (2016, September). Wide & deep learning for recommender systems. In Proceedings of the 1st workshop on deep learning for recommender systems, (pp. 7–10).
Cho, C., Yoon, B., Coh, B. Y., & Lee, S. (2016). An empirical analysis on purposes, drivers and activities of technology opportunity discovery: The case of Korean SMEs in the manufacturing sector. R&D Management, 46(1), 13–35.
Choi, C., Kim, S., & Park, Y. (2007). A patent-based cross impact analysis for quantitative estimation of technological impact: The case of information and communication technology. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 74(8), 1296–1314.
Choromanska, A., Henaff, M., Mathieu, M., Arous, G. B., & LeCun, Y. (2015, February). The loss surfaces of multilayer networks. In Artificial intelligence and statistics, (pp. 192–204).
Chung, P., & Sohn, S. Y. (2020). Early detection of valuable patents using a deep learning model: Case of semiconductor industry. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 158, 120146.
Covington, P., Adams, J., & Sargin, E. (2016, September). Deep neural networks for Youtube recommendations. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM conference on recommender systems (pp. 191–198).
Curran, C. S., & Leker, J. (2011). Patent indicators for monitoring convergence–examples from NFF and ICT. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 78(2), 256–273.
Dai, A. M., Olah, C., & Le, Q. V. (2015). Document embedding with paragraph vectors. arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.07998.
Dean, J., Corrado, G., Monga, R., Chen, K., Devin, M., Mao, M., & Le, Q. V. (2012). Large scale distributed deep networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 1223–1231).
Devlin, J., Chang, M. W., Lee, K., & Toutanova, K. (2018). Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805.
Dosovitskiy, A., Fischer, P., Springenberg, J. T., Riedmiller, M., & Brox, T. (2015). Discriminative unsupervised feature learning with exemplar convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 38(9), 1734–1747.
Gambardella, A., & Torrisi, S. (1998). Does technology convergence imply convergence in markets? Evidence from the electronics industry. Research Policy, 27(5), 445–463.
Ganin, Y., Ustinova, E., Ajakan, H., Germain, P., Larochelle, H., Laviolette, F., et al. (2016). Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 17(1), 2096–2030.
Gidaris, S., Singh, P., & Komodakis, N. (2018). Unsupervised representation learning by predicting image rotations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.07728.
Glorot, X., Bordes, A., & Bengio, Y. (2011, January). Domain adaptation for large-scale sentiment classification: A deep learning approach. In ICML.
Goodfellow, I., Lee, H., Le, Q. V., Saxe, A., & Ng, A. Y. (2009). Measuring invariances in deep networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 646–654).
Goyal, P., Mahajan, D., Gupta, A., & Misra, I. (2019). Scaling and benchmarking self-supervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 6391–6400).
Guo, C., & Berkhahn, F. (2016). Entity embeddings of categorical variables. arXiv preprint arXiv:1604.06737.
Hacklin, F., Raurich, V., & Marxt, C. (2004, October). How incremental innovation becomes disruptive: The case of technology convergence. In Engineering Management Conference, Proceedings. 2004 IEEE International (Vol. 1, pp. 32–36).
Han, E. J., & Sohn, S. Y. (2016). Technology convergence in standards for information and communication technologies. Technological forecasting and social change, 106, 1–10.
He, J., Zhuo, H. H., & Law, J. (2017). Distributed-representation based hybrid recommender system with short item descriptions. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.04854.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 770–778).
He, X., Liao, L., Zhang, H., Nie, L., Hu, X., & Chua, T. S. (2017). Neural collaborative filtering. In Proceedings of the 26th international conference on world wide web (pp. 173–182).
Hinton, G. E. (1989). Deterministic Boltzmann learning performs steepest descent in weight-space. Neural computation, 1(1), 143–150.
Hinton, G. E., & Salakhutdinov, R. R. (2006). Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science, 313(5786), 504–507.
Hsieh, C. K., Yang, L., Cui, Y., Lin, T. Y., Belongie, S., & Estrin, D. (2017, April). Collaborative metric learning. In Proceedings of the 26th international conference on world wide web (pp. 193–201).
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Van Der Maaten, L., & Weinberger, K. Q. (2017). Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 4700–4708).
Hwang, I. (2020). The effect of collaborative innovation on ICT-based technology convergence: A patent-based analysis. PLoS ONE, 15(2), e0228616.
Jaffe, A. B. (1986). Technological opportunity and spillovers of R&D: evidence from firms' patents, profits and market value (No. w1815). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Jeong, S., & Lee, S. (2015). What drives technology convergence? Exploring the influence of technological and resource allocation contexts. Journal of Engineering and Technology Management, 36, 78–96.
Jin, J. H., Park, S. C., & Pyon, C. U. (2011). Finding research trend of convergence technology based on Korean R&D network. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(12), 15159–15171.
Jing, L., & Tian, Y. (2020). Self-supervised visual feature learning with deep neural networks: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence.
Karvonen, M., & Kässi, T. (2013). Patent citations as a tool for analysing the early stages of convergence. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 80(6), 1094–1107.
Kim, B., Gazzola, G., Lee, J. M., Kim, D., Kim, K., & Jeong, M. K. (2014). Inter-cluster connectivity analysis for technology opportunity discovery. Scientometrics, 98(3), 1811–1825.
Kim, M. S., & Kim, C. (2012). On a patent analysis method for technology convergence. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 40, 657–663.
Kim, D. H., Lee, H., & Kwak, J. (2017). Standards as a driving force that influences emerging technological trajectories in the converging world of the Internet and things: An investigation of the M2M/IoT patent network. Research Policy, 46(7), 1234–1254.
Kim, J., Kim, S., & Lee, C. (2019). Anticipating technology convergence: Link prediction using Wikipedia hyperlinks. Technovation, 79, 25–34.
Kim, K., Jung, S., & Hwang, J. (2019). Technology convergence capability and firm innovation in the manufacturing sector: An approach based on patent network analysis. R&D Management, 49(4), 595–606.
Kim, N., Lee, H., Kim, W., Lee, H., & Suh, J. H. (2015). Dynamic patterns of industry convergence: Evidence from a large amount of unstructured data. Research Policy, 44(9), 1734–1748.
Kim, T. S., & Sohn, S. Y. (2020). (2020) Machine-learning-based deep semantic analysis approach for forecasting new technology convergence. Technological Forecasting & Social Change, 157, 1–10.
Klevorick, A. K., Levin, R. C., Nelson, R. R., & Winter, S. G. (1995). On the sources and significance of interindustry differences in technological opportunities. Research Policy, 24(2), 185–205.
Ko, N., Yoon, J., & Seo, W. (2014). Analyzing interdisciplinarity of technology fusion using knowledge flows of patents. Expert Systems with Applications, 41(4), 1955–1963.
Kodama, F. (1986). Japanese innovation in mechatronics technology. Science and Public Policy, 13(1), 44–51.
Kolesnikov, A., Zhai, X., & Beyer, L. (2019). Revisiting self-supervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 1920–1929).
Kose, T., & Sakata, I. (2019). Identifying technology convergence in the field of robotics research. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 146, 751–766.
Kwon, Y. I., & Jeong, D. H. (2014). Technology relevance analysis between wind power energy-fuel cell-green car using network analysis, IPC map. Collnet Journal of Scientometrics and Information Management, 8(1), 109–121.
Le, Q. V., Marc’Aurelio Ranzato, R. M., Devin, M., Chen, K., Corrado, G. S., Dean, J., & Ng, A. Y. (2012). Building high-level features using large scale unsupervised learning'. In International Conference on Machine Learning.
Le, Q., & Mikolov, T. (2014, January). Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In International Conference on Machine Learning (pp. 1188–1196).
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., & Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learning. Nature, 521(7553), 436–444.
Lee, C., Kogler, D. F., & Lee, D. (2019). Capturing information on technology convergence, international collaboration, and knowledge flow from patent documents: A case of information and communication technology. Information Processing & Management, 56(4), 1576–1591.
Lee, H., Ekanadham, C., & Ng, A. Y. (2008). Sparse deep belief net model for visual area V2. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 873–880).
Lee, H., Ge, R., Ma, T., Risteski, A., & Arora, S. (2017). On the ability of neural nets to express distributions. arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.07028.
Lee, J., & Sohn, S. Y. (2017). What makes the first forward citation of a patent occur earlier? Scientometrics, 113(1), 279–298.
Lee, M., & Lee, S. (2017). Identifying new business opportunities from competitor intelligence: An integrated use of patent and trademark databases. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 119, 170–183.
Lee, W. S., Han, E. J., & Sohn, S. Y. (2015). Predicting the pattern of technology convergence using big-data technology on large-scale triadic patents. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 100, 317–329.
Lee, Y., Kim, S. Y., Song, I., Park, Y., & Shin, J. (2014). Technology opportunity identification customized to the technological capability of SMEs through two-stage patent analysis. Scientometrics, 100(1), 227–244.
Liu, X., Zhang, F., Hou, Z., Wang, Z., Mian, L., Zhang, J., & Tang, J. (2020). Self-supervised Learning: Generative or Contrastive. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.08218.
Martin, B. R., Nightingale, P., & Yegros-Yegros, A. (2012). Science and technology studies: Exploring the knowledge base. Research Policy, 41(7), 1182–1204.
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., & Dean, J. (2013). Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv preprint arXiv:1301.3781.
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G. S., & Dean, J. (2013). Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 3111–3119).
Montúfar, G. F., & Morton, J. (2015). When does a mixture of products contain a product of mixtures? SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics, 29(1), 321–347.
Montúfar, G. F., Pascanu, R., Cho, K., & Bengio, Y. (2014). On the number of linear regions of deep neural networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 2924–2932).
Nemet, G. F., & Johnson, E. (2012). Do important inventions benefit from knowledge originating in other technological domains? Research Policy, 41(1), 190–200.
Noroozi, M., Vinjimoor, A., Favaro, P., & Pirsiavash, H. (2018). Boosting self-supervised learning via knowledge transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 9359–9367).
Olsson, O. (2005). Technological opportunity and growth. Journal of Economic Growth, 10(1), 31–53.
Oord, A. V. D., Li, Y., & Vinyals, O. (2018). Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.03748.
Park, C., Lee, J., & Sohn, S. Y. (2019). Recommendation of feeder bus routes using neural network embedding-based optimization. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 126, 329–341.
Park, I., & Yoon, B. (2018). Technological opportunity discovery for technology convergence based on the prediction of technology knowledge flow in a citation network. Journal of Informetrics, 12(4), 1199–1222.
Park, Y., & Yoon, J. (2017). Application technology opportunity discovery from technology portfolios: Use of patent classification and collaborative filtering. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 118, 170–183.
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., & Sun, J. (2015). Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 91–99).
Ridder, H. G. (2017). The theory contribution of case study research designs. Business Research, 10(2), 281–305.
Riesenhuber, M., & Poggio, T. (1999). Hierarchical models of object recognition in cortex. Nature Neuroscience, 2(11), 1019–1025.
Rosenberg, N. (1963). Technological change in the machine tool industry 1840-1910. Journal of Economic History. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022050700109155.
Schoen, A., Villard, L., Laurens, P., Cointet, J. P., Heimeriks, G., & Alkemade, F. (2012, September). The network structure of technological developments; Technological distance as a walk on the technology map. In Science & Technology Indicators (STI) Conference.
Schumpeter, J. (1934). The theory of economic development. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Seo, W., Yoon, J., Park, H., Coh, B. Y., Lee, J. M., & Kwon, O. J. (2016). Product opportunity identification based on internal capabilities using text mining and association rule mining. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 105, 94–104.
Shin, D. H. (2005). Technology convergence and regulatory challenge: A case from Korean digital media broadcasting. Info, 7(3), 47–58.
Song, C. H., Elvers, D., & Leker, J. (2017). Anticipation of converging technology areas—A refined approach for the identification of attractive fields of innovation. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 116, 98–115.
Song, G., Huang, X., Cao, G., Liu, W., Zhang, J., & Yang, L. (2019, May). Enhanced deep feature representation for patent image classification. In Tenth International Conference on Graphics and Image Processing (ICGIP 2018) (Vol. 11069, p. 110690P). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
Sutskever, I., Vinyals, O., & Le, Q. V. (2014). Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 3104–3112).
Tan, M., & Le, Q. (2019, May). EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In International Conference on Machine Learning (pp. 6105–6114).
Tang, Y., Lou, X., Chen, Z., & Zhang, C. (2020). A Study on dynamic patterns of technology convergence with IPC co-occurrence-based analysis: The case of 3D printing. Sustainability, 12(7), 2655.
Trappey, A. J., Trappey, C. V., Govindarajan, U. H., & Sun, J. J. (2019). Patent value analysis using deep learning models—the case of iot technology mining for the manufacturing industry. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management.
Tsai, Y. H. H., Wu, Y., Salakhutdinov, R., & Morency, L. P. (2020). Demystifying self-supervised learning: An information-theoretical framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.05576.
van Zeebroeck, N., & van de la Pottelsberghe Potterie, B. (2011). The vulnerability of patent value determinants. Economics of innovation and new technology, 20(3), 283–308.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., & Polosukhin, I. (2017). Attention is all you need. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 5998–6008).
Wang, P., Li, S., & Pan, R. (2018, April). Incorporating GAN for negative sampling in knowledge representation learning. In Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence.
Xia, B., Baoan, L. I., & Lv, X. (2016, November). Research on patent document classification based on deep learning. In 2016 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Industrial Engineering (AIIE 2016). Atlantis Press.
Yang, Y., Akers, L., Klose, T., & Yang, C. B. (2008). Text mining and visualization tools–impressions of emerging capabilities. World Patent Information, 30(4), 280–293.
Yang, Z., Dai, Z., Yang, Y., Carbonell, J., Salakhutdinov, R. R., & Le, Q. V. (2019). Xlnet: Generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 5753–5763).
Yasunaga, Y., Watanabe, M., & Korenaga, M. (2009). Application of technology roadmaps to governmental innovation policy for promoting technology convergence. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 76(1), 61–79.
Yoon, J., & Kim, K. (2011). Identifying rapidly evolving technological trends for R&D planning using SAO-based semantic patent networks. Scientometrics, 88(1), 213–228.
Yoon, J., Park, H., & Kim, K. (2013). Identifying technological competition trends for R&D planning using dynamic patent maps: SAO-based content analysis. Scientometrics, 94(1), 313–331.
Yoon, J., Park, H., Seo, W., Lee, J. M., Coh, B. Y., & Kim, J. (2015). Technology opportunity discovery (TOD) from existing technologies and products: A function-based TOD framework. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 100, 153–167.
Zhai, X., Oliver, A., Kolesnikov, A., & Beyer, L. (2019). S4l: Self-supervised semi-supervised learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 1476–1485).
Zhang, S., Yao, L., Sun, A., & Tay, Y. (2019). Deep learning-based recommender system: A survey and new perspectives. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 52(1), 1–38.
Zhang, Y., Shang, L., Huang, L., Porter, A. L., Zhang, G., Lu, J., et al. (2016). A hybrid similarity measure method for patent portfolio analysis. Journal of Infometrics, 10(4), 1108–1130.
Zhong, G., Wang, L. N., Ling, X., & Dong, J. (2016). An overview on data representation learning: From traditional feature learning to recent deep learning. The Journal of Finance and Data Science, 2(4), 265–278.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (2016R1A2A1A05005270) and (MSIT) (2020R1A2C2005026). Jungpyo Lee is currently working as an AI Research Engineer in Mobigen, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Sohn, S.Y. Recommendation system for technology convergence opportunities based on self-supervised representation learning. Scientometrics 126, 1–25 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03731-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03731-y
Keywords
- Deep representation learning
- Recommendation system
- Technology convergence
- Technology opportunity discovery
- Self-supervised learning