Abstract
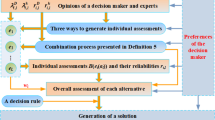
The evaluation of scientific research projects is a multi-expert decision-making problem under incomplete information environment. Whether evaluation results are reasonable or not depends on the expression of experts’ opinions, the reliability of experts and the aggregation method of experts’ opinions. From the perspective of expert reliability, this paper proposes a data-driven evidential reasoning method based on two-dimensional frames of discernment. In the proposed method, project evaluation information and experts’ characteristics information are used as two-dimensional evidence to represent decision information and decision quality information respectively, and belief distribution is used to express these two kinds of information. Experts’ characteristics information is used to measure the reliability of experts to modify project evaluation information given by experts. The discounted project evaluation information is aggregated by using evidential reasoning analysis algorithm to complete the evaluation of scientific research projects. In addition, a learning optimisation model is constructed to determine the relevant parameter values of the proposed method in a data-driven manner using historical evaluation data of projects. The empirical analysis of the National Nature Science Foundation of China verifies the validity and applicability of the proposed method.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayrulu, B., & Barshan, B. (2002). Reliability measure assignment to sonar for robust target differentiation. Pattern Recognition, 35(6), 1403–1419.
Beg, I., & Rashid, T. (2014). Hesitant intuitionistic fuzzy linguistic term sets. Notes on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets, 20(3), 53–64.
Brown, N. D., Quevedo, J. G., & Montolio, D. (2012). Assessing the assignation of public subsidies: Do the experts choose the most efficient R&D projects? World Review of Science, Technology and Sustainable Development, 9(2–4), 149–168.
Chen, Z. S., Chin, K. S., Li, Y. L., & Yang, Y. (2016). Proportional hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set for multiple criteria group decision making. Information Sciences, 357, 61–87.
Dempster, A. P. (1967). Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multi-valued mapping. Annual Mathematical Statistics, 38(2), 325–339.
Du, Y. W., Yang, N., Zhou, W., & Li, C. X. (2018). A reliability-based consensus model for multiattribute group decision-making with analytically evidential reasoning approach. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2018, 1–14.
Gong, K. X., & Chen, C. F. (2019). A programming-based algorithm for probabilistic uncertain linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy group decision-making. Symmetry, 11(2).
Guo, H. W., Shi, W. K., & Deng, Y. (2006). Evaluating sensor reliability in classification problems based on evidence theory. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics—Part B: Cybernetics, 36(5), 970–981
Guo, M., Yang, J. B., Chin, K. S., Wang, H. W., & Liu, X. B. (2009). Evidential reasoning approach for multiattribute decision analysis under both fuzzy and interval uncertainty. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 17(3), 683–697.
Guo, W. T., Huynh, V. N., & Sriboonchitta, S. (2017). A proportional linguistic distribution based model for multiple attribute decision making under linguistic uncertainty. Annals of Operations Research, 256(2), 305–328.
Herrera, F., Herrera-Viedma, E., & Martínez, L. (2000). A fusion approach for managing multi-granularity linguistic term sets in decision-making. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 114(1), 43–58.
Jiang, W., Xie, C. H., Zhuang, M. Y., Shou, Y. H. & Tang, Y. C. (2016a). Sensor data fusion with Z-numbers and its application in fault diagnosis. Sensors, 16(9).
Jiang, W., Xie, C. H., Wei, B. Y., & Zhou, D. Y. (2016b). A modified method for risk evaluation in failure modes and effects analysis of aircraft turbine rotor blades. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 8(4), 1–16.
Koksalmis, E., & Kabak, Ö. (2020). Sensor fusion based on Dempster-Shafer theory of evidence using a large scale group decision making approach. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 35(7), 1126–1162.
Kong, G., Xu, D. L., Yang, J. B., & Ma, X. M. (2015). Combined medical quality assessment using the evidential reasoning approach. Expert Systems with Applications, 42(13), 5522–5530.
Lawry, J. (2004). A framework for linguistic modelling. Artificial Intelligence, 155(1–2), 1–39.
Lee, C. J., Sugimoto, C. R., Zhang, G., & Cronin, B. (2013). Bias in peer review. Journal of the American Society for Information Science & Technology, 64(1), 2–17.
Lin, M. W., Xu, Z. S., Zhai, Y. L., & Yao, Z. Q. (2017). Multi-attribute group decision-making under probabilistic uncertain linguistic environment. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 69(2), 157–170.
Liu, S., Yu, W., Liu, L., & Hu, Y. N. (2019). Variable weights theory and its application to multi-attribute group decision making with intuitionistic fuzzy numbers on determining decision maker's weights. Plos One, 14(3).
Liu, F., Zhu, W. D., Chen, Y. W., Xu, D. L., & Yang, J. B. (2017). Evaluation, ranking and selection of R&D projects by multiple experts: An evidential reasoning rule based approach. Scientometrics, 111(3), 1501–1519.
Liu, S., Chan, F. T. S., & Ran, W. X. (2013). Multi-attribute group decision-making with multi-granularity linguistic assessment information: An improved approach based on deviation and TOPSIS. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 37(24), 10129–10140.
Ma, Z. Z., Ponnambalam, K., Zhu, J. J., & Zhang, S. T. (2018). Dynamic hesitant fuzzy linguistic group decision-making from a reliability perspective. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 29(5), 1009–1021.
Ma, Z. Z., Zhu, J. J., & Chen, Y. (2020). A probabilistic linguistic group decision-making method from a reliability perspective based on evidential reasoning. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics Systems, 50(7), 2421–2435.
Malik, M. G. A., Bashir, Z., Rashid, T. & Ali, J. (2018). Probabilistic hesitant intuitionistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Symmetry, 10(9).
Meng, F. Y., Chen, X. H., & Zhang, Q. (2014). Some intervalvalued intuitionistic uncertain linguistic Choquet operators and their application to multi-attribute group decision-making. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 38(9–10), 2543–2557.
Murphy, C. K. (2000). Combining belief functions when evidence conflicts. Decision Support Systems, 29(1), 1–9.
Pang, Q., Wang, H., & Xu, Z. S. (2016). Probabilistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Information Sciences, 369(10), 128–143.
Rodríguez, R. M., Martínez, L., & Herrera, F. (2011). Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. In Foundations of intelligent systems (pp. 287–295). IEEE.
Shafer, G. (1976). A mathematical theory of evidence. Princeton University Press.
Shi, M. H., Xiao, Y. W., & Wan, Q. (2019). Extended heronian mean based on hesitant fuzzy linguistic information for multiple attribute group decision-making. Complexity.
Simon, C., Weber, P., & Evsukoff, A. (2008). Bayesian networks inference algorithm to implement Dempster-Shafer theory in reliability analysis. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 93(7), 950–963.
Tang, Y. C., & Zheng, J. C. (2006). Linguistic modelling based on semantic similarity relation among linguistic labels. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 157(12), 1662–1673.
Wan, S.-P., & Xu, J. (2017). A method for multi-attribute group decision-making with triangular intuitionistic fuzzy numbers application to trustworthy service selection. Scientia Iranica, 24(2), 794–807.
Wang, Y. M., Yang, J. B., & Xu, D. L.(2006). Environmental impact assessment using the evidential reasoning approach. European Journal of Operational Research, 174(3), 1885–1913.
Wang, G. A., Jiao, J., Abrahams, A. S., Fan, W. G., & Zhang, Z. J. (2013). Expert Rank: A topic-aware expert finding algorithm for online knowledge communities. Decision Support Systems, 54(3), 1442–1451.
Wang, H. (2015). Extended hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and their aggregation in group decision making. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 8(1), 14–33.
Wang, J. H., & Hao, J. (2006). A new version of 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model for computing with words. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 14(3), 435–445.
Wang, X. D., & Song, Y. F. (2018). Uncertainty measure in evidence theory with its applications. Applied Intelligence, 48(7), 1672–1688.
Wu, Y. Z., Dong, Y. C., Qin, J. D., & Pedrycz, W. (2019). Flexible linguistic expressions and consensus reaching with accurate constraints in group decision-making. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 50(6), 2488–2501.
Wu, Z. B., & Xu, J. P. (2016). Possibility distribution-based approach for MAGDM with hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 46(3), 694–705.
Xu, J., Dong, J. Y., Wan, S. P., Yang, D. Y., & Zeng, Y. F. (2019). A heterogeneous multiattribute group decision-making method based on intuitionistic triangular fuzzy information. Complexity.
Xu, Z. S. (2007). A method for multiple attribute decision making with incomplete weight information in linguistic setting. Knowledge-Based Systems, 20(8), 719–725.
Yager, R. R. (2004). On the determination of strength of belief for decision support under uncertainty—Part I: Generating strengths of belief. Fuzzy Set and Systems, 142(1), 117–128.
Yang, J. B. (2001). Rule and utility based evidential reasoning approach for multiple attribute decision analysis under uncertainty. European Journal of Operational Research, 31(1), 31–61.
Yang, J. B., & Xu, D. L. (2002). On the evidential reasoning algorithm for multiple attribute decision analysis under uncertainty. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics-Part A, 32(3), 289–304.
Yang, J. B., & Xu, D. L. (2013). Evidential reasoning rule for evidence combination. Artificial Intelligence, 205, 1–29.
Zhang, G. Q., Dong, Y. C., & Xu, Y. F. (2014). Consistency and consensus measures for linguistic preference relations based on distribution assessments. Information Fusion, 17, 46–55.
Zhu, J. J., Wang, H. H., Chen, Y., & Qin, L. (2015a). Project evaluation method using non-formatted text information based on multi-granular linguistic labels. Information Fusion, 24, 93–107.
Zhu, W. D., Ku, Q., Wu, Y., Zhang, H. T., Sun, Y. B., & Zhang, C. (2018). A research into the evidence reasoning theory of two-dimensional framework and its application. Kybernetes, 47(5), 873–887.
Zhu, W. D., Li, S. R., Ku, Q., & Zhang, C. (2020). Evaluation information fusion of scientific research project based on evidential reasoning approach under two-dimensional frames of discernment. IEEE Access, 8, 8087–8100.
Zhu, W. D., Liu, F., Chen, Y. W., Yang, J. B., Xu, D. L., & Wang, D. P. (2015b). Research project evaluation and selection: An evidential reasoning rule-based method for aggregating peer review information with reliabilities. Scientometrics, 105(3), 1469–1490.
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.71774047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, W., Li, S., Zhang, H. et al. Evaluation of scientific research projects on the basis of evidential reasoning approach under the perspective of expert reliability. Scientometrics 127, 275–298 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-021-04201-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-021-04201-9