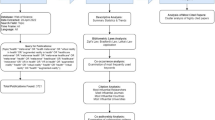
Abstract
The purpose of our study is to investigate the genealogy of the literature on digital pathology (DP) by evaluating the “upstream” (source papers in the field), “midstream” (outstanding papers in the field), and “downstream” (latest papers in the field) of the research field. All analyses are carried out on a complete database, on which we performed cocitation analysis, bibliographic coupling and double-cluster analysis. Our research reveals the integral knowledge structure of DP, which will help researchers understand the trend of DP, accounting for academic prospects regarding the application of DP in clinic. In addition, as a methodological contribution, we propose a two-dimensional bibliometric approach.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acs, B., & Hartman, J. (2020). Next generation pathology: Artificial intelligence enhances histopathology practice. Journal of Pathology, 250(1), 7–8.
Acs, B., & Rimm, D. L. (2018). Not Just Digital Pathology, Intelligent Digital Pathology. Jama Oncology, 4(3), 403–404.
Aeffner, F., Wilson, K., Bolon, B., Kanaly, S., Mahrt, C. R., Rudmann, D., Elaine Charles, G., & Young, D. (2016). Commentary: Roles for pathologists in a high-throughput image analysis team. Toxicologic Pathology, 44(6), 825–834.
Al-Janabi, S., Huisman, A., & Van Diest, P. J. (2012). Digital pathology: Current status and future perspectives. Histopathology, 61(1), 1–9.
Bacopoulou, F., Landis, G. N., Pałasz, A., Tsitsika, A., Vlachakis, D., Tsarouhas, K., Tsitsimpikou, C., Stefanaki, C., Kouretas, D., & Efthymiou, V. (2020). Identifying early abdominal obesity risk in adolescents by telemedicine: A cross-sectional study in Greece. Food and Chemical Toxicology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2020.111532
Beck, A. H., Sangoi, A. R., Leung, S., Marinelli, R. J., Nielsen, T. O., van de Vijver, M. J., West, R. B., van de Rijn, M., & Koller, D. (2011). Systematic analysis of breast cancer morphology uncovers stromal features associated with survival. Science Translational Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3002564
Bera, K., Schalper, K. A., Rimm, D. L., Velcheti, V., & Madabhushi, A. (2019). Artificial intelligence in digital pathology — new tools for diagnosis and precision oncology. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncolog, 16(11), 703–715.
Cheng, W. C., Saleheen, F., & Badano, A. (2019). Assessing color performance of whole-slide imaging scanners for digital pathology. Color Research and Application, 44(3), 322–334.
Cooper, I. D. (2015). Bibliometrics basics. Journal of the Medical Library Association, 103(4), 217–218.
Cooper, L. A. D., Demicco, E. G., Saltz, J. H., Powell, R. T., Rao, A., & Lazar, A. (2018). PanCancer insights from the cancer genome atlas: The pathologist’s perspective. The Journal of Pathology. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.5028
Dunn, B. E., Choi, H., Almagro, U. A., Recla, D. L., Krupinski, E. A., & Weinstein, R. S. (1999). Routine surgical telepathology in the department of veterans affairs: Experience-related improvements in pathologist performance in 2200 cases. Telemedicine Journal, 5(4), 323–337.
Falzarano, S. M., Zhou, M., Hernandez, A. V., Klein, E. A., Rubin, M. A., & Magi-Galluzzi, C. (2011). Single focus prostate cancer: Pathological features and ERG fusion status. Journal of Urology, 185(2), 489–494.
Farris, A. B., Moghe, I., Simon, W., Hogan, J., Cornell, L. D., Alexander, M. P., Kers, J., Demetris, A. J., Levenson, R. M., Tomaszewski, J., Barisoni, L., Yagi, Y., & Solez, K. (2020). Banff digital pathology working group: Going digital in transplant pathology. American Journal of Transplantation. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.15850
Gilbertson, J. R., Ho, J., Anthony, L., Jukic, D. M., Yagi, Y., & Parwani, A. V. (2006). Primary histologic diagnosis using automated whole slide imaging: A validation study. BMC clinical pathology, 6(1), 1–19.
Goldenberg, S. L., Nir, G., & Salcudean, S. E. (2019). A new era: Artificial intelligence and machine learning in prostate cancer. Nature Reviews Urology, 16(7), 391–403.
Halliday, B. E., Bhattacharyya, A. K., Graham, A. R., Davis, J. R., Anne Leavitt, S., Nagle, R. B., Mclaughlin, W. J., Rivas, R. A., Martinez, R., Krupinski, E. A., & Weinstein, R. S. (1997). Diagnostic accuracy of an international static-imaging telepathology consultation service. Human Pathology, 28(1), 17–21.
Hamza, S. H., & Reddy, V. V. B. (2004). Digital image acquisition using a consumer-type digital camera in the anatomic pathology setting. Advances in Anatomic Pathology, 11(2), 94–100.
Herwig-Carl, M. C., & Loeffler, K. U. (2020). Ophthalmic Pathology - Still the Gold Standard? Klinische Monatsblatter Fur Augenheilkunde, 237(07), 867–878.
Ho, J., Parwani, A. V., Jukic, D. M., Yagi, Y., Anthony, L., & Gilbertson, J. R. (2006). Use of whole slide imaging in surgical pathology quality assurance: Design and pilot validation studies. Human pathology, 37(3), 322–331.
Hui, G., Cheng, Z., Ran, H., Ziwei, W., & Fang, D. (2020). A pooled study of angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion gene polymorphism in relation to risk, pathology and prognosis of childhood immunoglobulin a vasculitis nephritis. Biochemical Genetics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-020-09999-2
Kaplan, K. J., Burgess, J. R., Sandberg, G. D., Myers, C. P., Bigott, T. R., & Greenspan, R. B. (2002). Use of robotic telepathology for frozen-section diagnosis: A retrospective trial of a telepathology system for intraoperative consultation. Modern Pathology, 15(11), 1197–1204.
Klughammer, J., Kiesel, B., Roetzer, T., Fortelny, N., Nemc, A., Nenning, K.-H., Furtner, J., Sheffield, N. C., Datlinger, P., Peter, N., Nowosielski, M., Augustin, M., Mischkulnig, M., Ströbel, T., Alpar, D., Ergüner, B., Senekowitsch, M., Moser, P., Freyschlag, C. F., … Bock, C. (2018). The DNA methylation landscape of glioblastoma disease progression shows extensive heterogeneity in time and space. Nature Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0156-x
Koohbanani, N. A., Jahanifar, M., Tajadin, N. Z., & Rajpoot, N. (2020). NuClick: A deep learning framework for interactive segmentation of microscopic images. Medical Image Analysis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2020.101771
Kwak, J. T., & Hewitt, S. M. (2017). Multiview boosting digital pathology analysis of prostate cancer. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 142, 91–99.
Lei, C. (2008). Development of a text mining system based on the co-occurrence of bibliographic items in literature databases. New Technology of Library and Information Service, 24(8), 70–5.
Leong, F.J.W.-M., & McGee, J. . O. ’D. (2001). Automated complete slide digitization: A medium for simultaneous viewing by multiple pathologists. The Journal of Pathology. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.972
Lorbach, S. K., Hokamp, J. A., Quimby, J. M., & Cianciolo, R. E. (2020). Clinicopathologic characteristics, pathology, and prognosis of 77 dogs with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 34(5), 1948–1956.
Mittal, S., Kevin Yeh, L., Leslie, S., Kenkel, S., Kajdacsy-Balla, A., & Bhargava, R. (2018). PNAS plus: Simultaneous cancer and tumor microenvironment subtyping using confocal infrared microscopy for all-digital molecular histopathology. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1719551115
Mobadersany P, Yousefi S, Amgad M, Gutman DA, Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Vega JEV, Brat DJ, Cooper LAD (2018). Predicting cancer outcomes from histology and genomics using convolutional networks. 201717139.
Molnar, B. (2003). Digital slide and virtual microscopy based routine and telepathology evaluation of routine gastrointestinal biopsy specimens. Journal of Clinical Pathology. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.56.6.433
Mukhopadhyay, S., Feldman, M. D., Abels, E., Ashfaq, R., Beltaifa, S., Cacciabeve, N. G., Cathro, H. P., Cheng, L., Cooper, K., Dickey, G. E., Gill, R. M., Heaton, R. P., Kerstens, R., Lindberg, G. M., Malhotra, R. K., Mandell, J. W., Manlucu, E. D., Mills, A. M., Mills, S. E., … Taylor, C. R. (2018). Whole slide imaging versus microscopy for primary diagnosis in surgical pathology: A multicenter blinded randomized noninferiority study of 1992 cases (pivotal study). American Journal of Surgical Pathology, 42(1), 39.
Nam, S., Chong, Y., Jung, C. K., Kwak, T.-Y., Lee, J. Y., Park, J., Rho, M. J., & Go, H. (2020). Introduction to digital pathology and computer-aided pathology. Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine, 54(2), 125–134.
Nordrum, I., Engum, B., Rinde, E., Finseth, A., Ericsson, H., Kearney, M., & Eide, T. J. (1991). Remote frozen section service: A telepathology project in northern Norway. Human pathology, 22(6), 514–518.
Orazem, M., Oblak, I., Spanic, T., & Ratosa, I. (2020). Telemedicine in radiation oncology post-COVID-19 pandemic: There is no turning back. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics, 108(2), 411–415.
Pantanowitz, L., Evans, A. J., Pfeifer, J. D., Collins, L. C., Valenstein, P. N., Kaplan, K. J., Wilbur, D. C., & Colgan, T. J. (2011). Review of the current state of whole slide imaging in pathology. Journal of Pathology Informatics. https://doi.org/10.4103/2153-3539.83746
Pantanowitz, L., Sinard, J. H., Henricks, W. H., Fatheree, L. A., Carter, A. B., Contis, L., & Parwani, A. V. (2013). Validating whole slide imaging for diagnostic purposes in pathology: Guideline from the College of American Pathologists Pathology and Laboratory Quality Center. Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, 137(12), 1710–1722.
Park, S., Pantanowitz, L., & Parwani, A. V. (2012). Digital imaging in pathology. Clinics in Laboratory Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cll.2012.07.006
Pierga, J.-Y., Bonneton, C., Vincent-Salomon, A., de Cremoux, P., Nos, C., Blin, N., Pouillart, P., Thiery, J.-P., & Magdelénat, H. (2004). Clinical significance of immunocytochemical detection of tumor cells using digital microscopy in peripheral blood and bone marrow of breast cancer patients. Clinical Cancer Research, 10(4), 1392–1400.
Potts, S. J. (2009). Digital pathology in drug discovery and development: Multisite integration. Drug Discovery Today, 14(19–20), 935–941.
Robertson, S., Azizpour, H., Smith, K., & Hartman, J. (2018). Digital image analysis in breast pathology—from image processing techniques to artificial intelligence. Translational Research, 194, 19–35.
Ruifrok, A. C., & Johnston, D. A. (2001). Quantification of histochemical staining by color deconvolution. Analytical and quantitative cytology and histology, 23(4), 291–299.
Scolyer, R. A. (2017). Is pathology the gold standard for diagnosing melanocytic tumors: Does it always glitter? Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 31, 11–11.
Steel, M., Rao, S., Ho, J., Donnellan, F., Yang, H.-M., & Schaeffer, D. F. (2019). Cytohistological diagnosis of pancreatic serous cystadenoma: A multimodal approach. Journal of Clinical Pathology, 72(9), 615–621.
Steinberg, D. M., & Ali, S. Z. J. D. C. (2001). Application of virtual microscopy in clinical cytopathology. Diagnostic Cytopathology. https://doi.org/10.1002/dc.10021
Steiner, D. F., MacDonald, R., Liu, Y., Truszkowski, P., Hipp, J. D., Gammage, C., Thng, F., Peng, L., & Stumpe, M. C. (2018). Impact of deep learning assistance on the histopathologic review of lymph nodes for metastatic breast cancer. American Journal of Surgical Pathology. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0000000000001151
Ting, D. S., Peng, L., Varadarajan, A. V., Keane, P. A., Burlina, P. M., Chiang, M. F., & Wong, T. Y. (2019). Deep learning in ophthalmology: The technical and clinical considerations. Progress in retinal and eye research, 72, 100759.
Vamathevan, J., Clark, D., Czodrowski, P., Dunham, I., Ferran, E., Lee, G., & Zhao, S. (2019). Applications of machine learning in drug discovery and development. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 18(6), 463–477.
Wake, R. W., Hollabaugh, R. S., & Bon, K. H. (1996). Cryosurgical ablation of the prostate for localized adenocarcinoma: A preliminary experience. Journal of Urology, 155(5), 1663–1666.
Wang, S., Yang, D. M., Rong, R., Zhan, X., Fujimoto, J., Liu, H., & Xiao, G. (2019). Artificial intelligence in lung cancer pathology image analysis. Cancers, 11(11), 16.
Weinstein, R. S., Bhattacharyya, A. K., Graham, A. R., & Davis, J. R. (1997). Telepathology: A ten-year progress report. Human Pathology, 28(1), 1–7.
Weinstein, R. S., Bloom, K. J., & Rozek, L. S. (1987). Telepathology and the networking of pathology diagnostic services. Archives of pathology & laboratory medicine, 111(7), 646–652.
Weinstein, R. S., Descour, M. R., Liang, C., Barker, G., Scott, K. M., Richter, L., & Bartels, P. H. (2004). An array microscope for ultrarapid virtual slide processing and telepathology. Design, fabrication, and validation study. Human pathology, 35(11), 1303–1314.
Weinstein, R. S., Descour, M. R., Liang, C., Bhattacharyya, A. K., Graham, A. R., Davis, J. R., & Dunn, B. E. (2001). Telepathology Overview: From Concept to Implementation. Human pathology, 32(12), 1283–1299.
Wilbur, D. C., Madi, K., Colvin, R. B., Duncan, L. M., Faquin, W. C., Ferry, J. A., Frosch, M. P., Houser, S. L., Kradin, R. L., Lauwers, G. Y., Louis, D. N., Mark, E. J., Mino-Kenudson, M., Misdraji, J., Nielsen, G. P., Pitman, M. B., Rosenberg, A. E., Neal Smith, R., Sohani, A. R., … Klietmann, W. (2009). Whole-slide imaging digital pathology as a platform for teleconsultation: a pilot study using paired subspecialist correlations. Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, 133(12), 1949–1953.
Williams, S., Henricks, W. H., Becich, M. J., Toscano, M., & Carter, A. B. (2010). Telepathology for patient care: What am i getting myself into. Advances in Anatomic Pathology, 17(2), 130–149.
Yang, Y., Wang, J., Ng, C. W., Ma, Y., Mo, S., Fong, E. L. S., Xing, J., Song, Z., Xie, Y., Si, K., Wee, A., Welsch, R. E., So, P. T. C., & Hanry, Y. (2018). Deep learning enables automated scoring of liver fibrosis stages. Scientific Reports. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34300-2
Zarei, N., Bakhtiari, A., Korbelik, J., Carraro, A., Keyes, M., & MacAulay, C. (2017). Introducing an interactive method to improve digital pathology image segmentation case study on prostate cancer. Analytical and Quantitative Cytopathology and Histopathology, 39(1), 1–16.
Acknowledgements
This work received financial support from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (N171904006, N171902001, N172410006-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, D., Wang, C., Zheng, S. et al. Investigating the genealogy of the literature on digital pathology: a two-dimensional bibliometric approach. Scientometrics 127, 785–801 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-021-04224-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-021-04224-2