Abstract
Model-driven engineering (MDE) is believed to have a significant impact in software quality. However, researchers and practitioners may have a hard time locating consolidated evidence on this impact, as the available information is scattered in several different publications. Our goal is to aggregate consolidated findings on quality in MDE, facilitating the work of researchers and practitioners in learning about the coverage and main findings of existing work as well as identifying relatively unexplored niches of research that need further attention. We performed a tertiary study on quality in MDE, in order to gain a better understanding of its most prominent findings and existing challenges, as reported in the literature. We identified 22 systematic literature reviews and mapping studies and the most relevant quality attributes addressed by each of those studies, in the context of MDE. Maintainability is clearly the most often studied and reported quality attribute impacted by MDE. Eighty out of 83 research questions in the selected secondary studies have a structure that is more often associated with mapping existing research than with answering more concrete research questions (e.g., comparing two alternative MDE approaches with respect to their impact on a specific quality attribute). We briefly outline the main contributions of each of the selected literature reviews. In the collected studies, we observed a broad coverage of software product quality, although frequently accompanied by notes on how much more empirical research is needed to further validate existing claims. Relatively, little attention seems to be devoted to the impact of MDE on the quality in use of products developed using MDE.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The DARE criteria are based on those used by the Center for Reviews and Dissemination of the University of York, for assessing the eligibility of systematic reviews to be included in their Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE). http://www.crd.york.ac.uk/CRDWeb/.
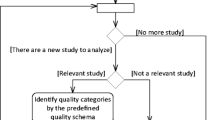
Although Genero et al. (2011) published as a SLR, its 5 research questions are of a mapping nature. Under these circumstances, the quality classifications, which can be seen as adequacy for inclusion classifications, can be less strict.
References
Agner, L. T. W., Soares, I. W., Stadzisz, P. C., & Simão, J. M. (2013). A Brazilian survey on UML and model-driven practices for embedded software development. Journal of Systems and Software, 86(4), 997–1005. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2012.11.023.
Ameller, D., Franch, X., Gómez, C., Araujo, J., Svensson, R. B., Biffl, S., Cabot, J., Cortellessa, V., Daneva, M., Fernández, D. M., Moreira, A., Muccini, H., Vallecillo, A., Wimmer, M., Amaral, V., Brunelièrek, H., Burgueño, L., Goulão, M., Schätz, B., & Teufl, S. (2015) Handling non-functional requirements in model-driven development: An ongoing industrial survey. In 23rd IEEE international requirements engineering conference (RE 2015).
Badreddin, O., Lethbridge, T. C., & Elassar, M. (2013). Modeling practices in open source software. In Open source software: Quality verification (pp. 127–139). Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-38928-3_9.
Badreddin, O., Sturm, A., Hamou-Lhadj, A., Lethbridge, T., Dixon, W., & Simmons, R. (2015). The effects of education on students’ perception of modeling in software engineering. In First International workshop on human factors in modeling (HuFaMo 2015), CEUR workshop proceedings
Biolchini, J., Mian, P. G., Natali, A. C. C., & Travassos, G. H. (2005). Systematic review in software engineering. Tech. Rep. RT–ES 679/05, System engineering and computer science department COPPE/UFRJ. http://www.cin.ufpe.br/~in1037/leitura/systematicReviewSE-COPPE.pdf.
Brereton, P., Kitchenham, B. A., Budgen, D., Turner, M., & Khalil, M. (2007). Lessons from applying the systematic literature review process within the software engineering domain. Journal of Systems and Software, 80(4), 571–583. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2006.07.009.
Budgen, D., Kitchenham, B. A., Charters, S. M., Turner, M., Brereton, P., & Linkman, S. G. (2008). Presenting software engineering results using structured abstracts: A randomised experiment. Empirical Software Engineering, 13(4), 435–468. doi:10.1007/s10664-008-9075-7.
Cruzes, D. S., & Dybå, T. (2011). Research synthesis in software engineering: A tertiary study. Information and Software Technology, 53(5), 440–455. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2011.01.004.
Cuadrado, J. S., Molina, J. G., & Tortosa, M. M. (2006). Rubytl: A practical, extensible transformation language. In A. Rensink & J. Warmer (Eds.), Model driven architecture–Foundations and applications (pp. 158–172). Bilbao, Spain: Springer.
Cuadrado, J. S., Izquierdo, J. L. C., & Molina, J. G. (2014). Applying model-driven engineering in small software enterprises. Science of Computer Programming, 89, 176–198. doi:10.1016/j.scico.2013.04.007.
Dybå, T., & Dingsøyr, T. (2008). Strength of evidence in systematic reviews in software engineering. In Proceedings of the second acm-ieee international symposium on empirical software engineering and measurement (pp. 178–187), ACM. doi:10.1145/1414004.1414034.
Fernández-Sáez, A. M., Genero, M., Caivano, D., & Chaudron, M. R. V. (2015). On the use of UML documentation in software maintenance: Results from a survey in industry. In ACM/IEEE 18th International conference on model driven engineering languages and systems (MODELS 2015) (pp. 292–301). ACM/IEEE.
Forward, A., Lethbridge, T., & Badreddin, O. (2010). Problems and opportunities for model-centric vs code-centric development: A survey of software professionals. In 5th Workshop “From code centric to model centric: Evaluating the effectiveness of MDD (C2M: EEMDD)”, University Pierre & Marie Curie, Paris.
Hirsch, J. E. (2005). An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(46), 16,569–16,572. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507655102.
Hutchinson, J., Whittle, J., Rouncefield, M., & Kristoffersen, S. (2011). Empirical assessment of MDE in industry. In Proceedings of the 33rd international conference on software engineering (pp. 471–480). ACM, New York, NY, USA, ICSE ’11. doi:10.1145/1985793.1985858.
Hutchinson, J., Whittle, J., & Rouncefield, M. (2014). Model-driven engineering practices in industry: Social, organizational and managerial factors that lead to success or failure. Science of Computer Programming, 89, 144–161. doi:10.1016/j.scico.2013.03.017.
ISO/IEC. (2011). IEC25010:2011 Systems and software engineering–Systems and software Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE)–System and software quality models. International Organization for Standardization, 34.
Kitchenham, B., & Charters, S. (2007). Guidelines for performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering. In Technical report, Version 2.3 EBSE technical report. EBSE, Keele University and Durham University Joint Report. http://www.dur.ac.uk/ebse/resources/Systematic-reviews-5-8.pdf.
Kitchenham, B., Brereton, O. P., Budgen, D., Turner, M., Bailey, J., & Linkman, S. (2009). Systematic literature reviews in software engineering-a systematic literature review. Information and Software Technology, 51(1), 7–15. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2008.09.009.
Kitchenham, B., Pretorius, R., Budgen, D., Brereton, O. P., Turner, M., Niazi, M., et al. (2010). Systematic literature reviews in software engineering-a tertiary study. Information and Software Technology, 52(8), 792–805. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2010.03.006.
Kitchenham, B. A., Dyba, T., & Jorgensen, M. (2004). Evidence-based software engineering. In Proceedings of the 26th international conference on software engineering (pp. 273–281). IEEE Computer Society. doi:10.1109/ICSE.2004.1317449.
Kitchenham, B. A., Budgen, D., & Brereton, O. P. (2011). Using mapping studies as the basis for further research-a participant-observer case study. Information and Software Technology, 53(6), 638–651. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2010.12.011.
Mohagheghi, P., & Conradi, R. (2007). Quality, productivity and economic benefits of software reuse: A review of industrial studies. Empirical Software Engineering, 12(5), 471–516. doi:10.1007/s10664-007-9040-x.
Mohagheghi, P., Gilani, W., Stefanescu, A., & Fernandez, M. A. (2013). An empirical study of the state of the practice and acceptance of model-driven engineering in four industrial cases. Empirical Software Engineering, 18(1), 89–116. doi:10.1007/s10664-012-9196-x.
OMG (2015). OMG unified modeling language ™(OMG UML). Tech. Rep. formal/2015-03-01, Object Management Group. http://www.omg.org/spec/UML/2.5.
Petersen, K., Feldt, R., Mujtaba, S., & Mattsson, M. (2008). Systematic mapping studies in software engineering. In 12th international conference on evaluation and assessment in software engineering
Petre, M. (2013). Uml in practice. In D. Notkin, B. H. C. Cheng, & K. Pohl (Eds.), Proceedings of the 2013 international conference on software engineering (pp. 722–731). San Francisco, CA: IEEE Press. doi:10.1109/ICSE.2013.6606618.
Petticrew, M., & Roberts, H. (2008). Systematic reviews in the social sciences: A practical guide. New York: Wiley.
Schmidt, D. C. (2006). Guest editor’s introduction: Model-driven engineering. Computer, 39(2), 0025–31. doi:10.1109/MC.2006.58.
da Silva, A. R. (2015). Model-driven engineering: A survey supported by the unified conceptual model. Computer Languages, Systems and Structures, 43, 139–155. doi:10.1016/j.cl.2015.06.001.
Torchiano, M., Tomassetti, F., Ricca, F., Tiso, A., & Reggio, G. (2013). Relevance, benefits, and problems of software modelling and model driven techniques-a survey in the Italian industry. Journal of Systems and Software, 86(8), 2110–2126. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2013.03.084.
Whittle, J., Hutchinson, J., Rouncefield, M., Burden, H., & Heldal, R. (2015). A taxonomy of tool-related issues affecting the adoption of model-driven engineering. Software and Systems Modeling, pp. 1–19. doi:10.1007/s10270-015-0487-8.
Wohlin, C. (2014). Guidelines for snowballing in systematic literature studies and a replication in software engineering. In Proceedings of the 18th international conference on evaluation and assessment in software engineering (pp. 38:1–38:10). ACM, New York, NY, USA, EASE ’14. doi:10.1145/2601248.2601268.
Zhou, Y., Zhang, H., Huang, X., Yang, S., Babar, M. A., Tang, H. (2015). Quality assessment of systematic reviews in software engineering: A tertiary study. In Proceedings of the 19th international conference on evaluation and assessment in software engineering (pp. 14:1–14:14). ACM, New York, NY, USA, EASE ’15. doi:10.1145/2745802.2745815.
Included Secondary Studies
Budgen, D., Burn, A. J., Brereton, O. P., Kitchenham, B. A., & Pretorius, R. (2011). Empirical evidence about the UML: A systematic literature review. Software: Practice and Experience, 41(4), 363–392. doi:10.1002/spe.1009.
Delgado, A., Ruiz, F., de Guzmán, I. G. R., & Piattini, M. (2013). Main principles on the integration of SOC and MDD paradigms to business processes: A systematic review. In J. Cordeiro, M. Virvou, & B. Shishkov (Eds.), Software and Data Technologies (pp. 88–108). Athens, Greece: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-29578-2_6.
Domínguez, E., Pérez, B., Rubio, Á. L., & Zapata, M. A. (2012). A systematic review of code generation proposals from state machine specifications. Information and Software Technology, 54(10), 1045–1066. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2012.04.008.
Genero, M., Fernández-Saez, A. M., Nelson, H. J., Poels, G., & Piattini, M. (2011). A systematic literature review on the quality of UML models. Journal of Database Management, 22(3), 46–70. doi:10.4018/978-1-4666-2044-5.ch012.
Giachetti, G., Valverde, F., & Marín, B. (2012). Interoperability for model-driven development: Current state and future challenges. In Sixth international conference on research challenges in information science (RCIS 2012) (pp. 1–10). IEEE. doi:10.1109/RCIS.2012.6240445.
Giraldo, F. D., España, S., & Pastor, O. (2014). Analysing the concept of quality in model-driven engineering literature: A systematic review. In Eighth international conference on research challenges in information science (RCIS 2014), (pp. 1–12). IEEE. doi:10.1109/RCIS.2014.6861030.
Giraldo, F. D., España, S., Giraldo, W. J., & Pastor, O. (2015). Modelling language quality evaluation in model-driven information systems engineering: a roadmap. In 9th International conference on research challenges in information science (RCIS 2015) (pp. 64–69). IEEE. doi:10.1109/RCIS.2015.7128864.
González, C. A., & Cabot, J. (2014). Formal verification of static software models in mde: A systematic review. Information and Software Technology, 56(8), 821–838. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2014.03.003.
Hansson, S., Zhao, Y., & Burden, H. (2014). How MAD are we? empirical evidence for model-driven agile development. In 3rd Workshop on Extreme Modeling, XM 2014, CEUR Workshop Proceedings (pp. 2–11). vol 1239. URL http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1239/XM2014#page=9.
Jensen, J., & Jaatun, M. G. (2011) Security in model driven development: A survey. In Availability, reliability and security (ARES), 2011 Sixth International conference on (pp. 704–709). IEEE. doi:10.1109/ARES.2011.110.
Loniewski, G., Insfran, E., & Abrahão, S. (2010). A systematic review of the use of requirements engineering techniques in model-driven development. In Model driven engineering languages and systems (pp. 213–227). Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-16129-216.
Lucas, F. J., Molina, F., & Toval, A. (2009). A systematic review of UML model consistency management. Information and Software Technology, 51(12), 1631–1645. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2009.04.009.
Malavolta, I., & Muccini, H. (2014). A study on MDE approaches for engineering wireless sensor networks. In Software engineering and advanced applications (SEAA), 2014 40th EUROMICRO conference on (pp. 149–157). IEEE. doi:10.1109/SEAA.2014.61.
Mehmood, A., & Jawawi, D. N. (2013). Aspect-oriented model-driven code generation: A systematic mapping study. Information and Software Technology, 55(2), 395–411. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2012.09.003.
Misbhauddin, M., & Alshayeb, M. (2015). Uml model refactoring: A systematic literature review. Empirical Software Engineering, 20(1), 206–251. doi:10.1007/s10664-013-9283-7.
Mohagheghi, P., & Dehlen, V. (2008). Where is the proof?—a review of experiences from applying mde in industry. In Schieferdecker, I., Hartman, A. (eds) Model driven architecture—foundations and applications, Lecture notes in computer Science (pp. 432–443). vol 5095, Springer, Berlin. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-69100-631.
Mohagheghi, P., Dehlen, V., & Neple, T. (2009). Definitions and approaches to model quality in model-based software development—A review of literature. Information and Software Technology, 51(12), 1646–1669. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2009.04.004.
Neto, V. V. G., Guessi, M., Oliveira, L. B. R., Oquendo, F., & Nakagawa, E. Y. (2014). Investigating the model-driven development for systems-of-systems. In Proceedings of the 2014 European Conference on software architecture workshops (pp. 22:1–22:8). ACM, New York, NY, USA, ECSAW ’14. doi:10.1145/2642803.2642825.
Nguyen, P. H., Klein, J., le Traon, Y., & Kramer, M. E. (2013) A systematic review of model-driven security. In 20th Asia–Pacific software engineering conference (APSEC 2013) (pp. 432–441). vol 1. doi:10.1109/APSEC.2013.64.
Santiago, I., Jiménez, Á., Vara, J. M., De Castro, V., Bollati, V. A., & Marcos, E. (2012). Model-driven engineering as a new landscape for traceability management: A systematic literature review. Information and Software Technology, 54(12), 1340–1356. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2012.07.008.
Szvetits, M., & Zdun, U. (2013). Systematic literature review of the objectives, techniques, kinds, and architectures of models at runtime. Software and Systems Modeling, pp. 1–39. doi:10.1007/s10270-013-0394-9.
Yue, T., Briand, L. C., & Labiche, Y. (2011). A systematic review of transformation approaches between user requirements and analysis models. Requirements Engineering, 16(2), 75–99. doi:10.1007/s00766-010-0111-y.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank FCT/MEC NOVA LINCS PEst UID/ CEC/04516/ 2013 for the financial support to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goulão, M., Amaral, V. & Mernik, M. Quality in model-driven engineering: a tertiary study. Software Qual J 24, 601–633 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11219-016-9324-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11219-016-9324-8