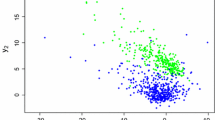
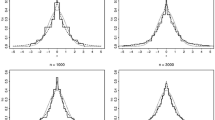
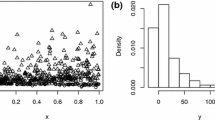
Abstract
It may sometimes be clear from background knowledge that a population under investigation proportionally consists of a known number of subpopulations, whose distributions belong to the same, yet unknown, family. While a parametric family is commonly used in practice, one can also consider some nonparametric families to avoid distributional misspecification. In this article, we propose a solution using a mixture-based nonparametric family for the component distribution in a finite mixture model as opposed to some recent research that utilizes a kernel-based approach. In particular, we present a semiparametric maximum likelihood estimation procedure for the model parameters and tackle the bandwidth parameter selection problem via some popular means for model selection. Empirical comparisons through simulation studies and three real data sets suggest that estimators based on our mixture-based approach are more efficient than those based on the kernel-based approach, in terms of both parameter estimation and overall density estimation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartolucci, F.: Clustering univariate observations via mixtures of unimodal normal mixtures. J. Classif. 22, 203–219 (2005)
Benaglia, T., Chauveau, D., Hunter, D.R.: An EM-like algorithm for semi- and nonparametric estimation in multivariate mixtures. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 18, 505–526 (2009)
Bordes, L., Mottelet, S., Vandekerkhove, P.: Semiparametric estimation of a two-component mixture model. Ann. Stat. 34, 1204–1232 (2006)
Bordes, L., Chauveau, D., Vandekerkhove, P.: A stochastic EM algorithm for a semiparametric mixture model. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 51, 5429–5443 (2007)
Bowman, A.W.: An alternative method of cross-validation for the smoothing of density estimates. Biometrika 71, 353–360 (1984)
Burnham, K.P., Anderson, D.R.: Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2002)
Charnigo, R., Pilla, R.S.: Semiparametric mixtures of generalized exponential families. Scand. J. Stat. 34, 535–551 (2007)
Cook, R.D., Weisberg, S.: An Introduction to Regression Graphics. Wiley, New York (1994)
Frühwirth-Schnatter, S.: Finite Mixture and Markov Switching Models. Springer, New York (2006)
Heinz, G., Peterson, L.J., Johnson, R.W., Kerk, C.J.: Exploring relationships in body dimensions. J. Stat. Edu. 11 (2003)
Hubert, L., Arabie, P.: Comparing partitions. J. Classif. 2, 193–218 (1985)
Hunter, D.R., Wang, S., Hettmansperger, T.P.: Inference for mixtures of symmetric distributions. Ann. Stat. 35, 224–251 (2007)
Hurvich, C.M., Tsai, C.-L.: Regression and time series model selection in small samples. Biometrika 76, 297–307 (1989)
Kottas, A., Fellingham, G.W.: Bayesian semiparametric modeling and inference with mixtures of symmetric distributions. Stat. Comput. 22, 93–106 (2012)
Laird, N.M.: Nonparametric maximum likelihood estimation of a mixing distribution. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 73, 805–811 (1978)
Lindsay, B.G.: The geometry of mixture likelihoods: A general theory. Ann. Stat. 11, 86–94 (1983a)
Lindsay, B.G.: The geometry of mixture likelihoods, Part II: The exponential family. Ann. Stat. 11, 783–792 (1983b)
Lindsay, B.G.: Mixture Models: Theory, Geometry and Applications. NSF-CBMS Regional Conference Series in Probability and Statistics, vol. 5. Institute of Mathematical Statistics, Hayward (1995)
Lindsay, B.G., Lesperance, M.L.: A review of semiparametric mixture models. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 47, 29–39 (1995)
McLachlan, G., Peel, D.: Finite Mixture Models. Wiley, New York (2000)
Miloslavsky, M., van der Laan, M.J.: Fitting of mixtures with unspecified number of components using cross validation distance estimate. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 41, 413–428 (2003)
R Development Core Team: R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna (2010)
Roeder, K.: Density estimation with confidence sets exemplified by superclusters and voids in the galaxies. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 85, 617–624 (1990)
Scott, D.W., Terrell, G.R.: Biased and unbiased cross-validation in density estimation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 82, 1131–1146 (1987)
Sheather, S.J., Jones, M.C.: A reliable data-based bandwidth selection method for kernel density estimation. J. R. Stat. Soc., Ser. B, Stat. Methodol. 53, 683–690 (1991)
Silverman, B.W.: Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis. Chapman & Hall, London (1986)
Smyth, P.: Model selection for probabilistic clustering using cross-validated likelihood. Stat. Comput. 10, 63–72 (2000)
Sugiura, N.: Further analysts of the data by Akaike’s information criterion and the finite corrections. Commun. Stat., Theory Methods 7, 13–26 (1978)
Wang, Y.: Maximum likelihood computation for fitting semiparametric mixture models. Stat. Comput. 20, 75–86 (2010)
Wang, Y., Chee, C.-S.: Density estimation using nonparametric and semiparametric mixtures. Stat. Model. (2012, to appear)
Young, D.S., Benaglia, T., Chauveau, D., Elmore, R.T., Hettmansperger, T.P., Hunter, D.R., Thomas, H., Xuan, F.: mixtools: Tools for Analyzing Finite Mixture Models. R package version 0.4.1 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chee, CS., Wang, Y. Estimation of finite mixtures with symmetric components. Stat Comput 23, 233–249 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-011-9305-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-011-9305-5