Abstract
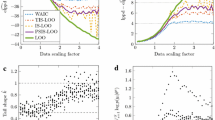
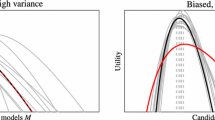
The predictive loss of Bayesian models can be estimated using a sample from the full-data posterior by evaluating the Watanabe-Akaike information criterion (WAIC) or using an importance sampling (ISCVL) approximation to leave-one-out cross-validation loss. With hierarchical models the loss can be specified at different levels of the hierarchy, and in the published literature, it is routine for these estimators to use the conditional likelihood provided by the lowest level of model hierarchy. However, the regularity conditions underlying these estimators may not hold at this level, and the behaviour of conditional-level WAIC as an estimator of conditional-level predictive loss must be determined on a case-by-case basis. Conditional-level ISCVL does not target conditional-level predictive loss and instead is an estimator of marginal-level predictive loss. Using examples for analysis of over-dispersed count data, it is shown that conditional-level WAIC does not provide a reliable estimator of its target loss, and simulations show that it can favour the incorrect model. Moreover, conditional-level ISCVL is numerically unstable compared to marginal-level ISCVL. It is recommended that WAIC and ISCVL be evaluated using the marginalized likelihood where practicable and that the reliability of these estimators always be checked using appropriate diagnostics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, W.-Y., Vasilev, G., Lee, S.-H., Busemeyer, J.R., Kruschke, J.K., Bechra, A., Vassileva, J.: Decision-making in stimulant and opiate addicts in protracted abstinence: evidence from computational modeling with pure users. Front. Psychol. 5, 15 (2014). doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00849
Alderman, D.L., Powers, D.E.: The effects of special preparation on SAT-verbal scores. Am. Edu. Res. J. 17, 239–251 (1980)
Anderson, M.J., Millar, R.B.: Spatial variation and effects of habitat on temperate reef fish assemblages in northeastern New Zealand. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 305, 191–221 (2004)
Burman, P.: A comparative study of ordinary cross-validation, \(v\)-fold cross-validation and the repeated learning-testing methods. Biometrika 76, 503–514 (1989)
Geisser, S., Eddy, W.F.: A predictive approach to model selection. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 74, 153–160 (1979)
Gelfand, A.E., Dey, D.K.: Bayesian model choice: Asymptotics and exact calculations. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 56, 501–514 (1994)
Gelman, A., Hwang, J., Vehtari, A.: Understanding predictive information criteria for Bayesian models. Stat. Comput. 24, 997–1016 (2013)
Gelman, A., Meng, X.-L.: Simulating normalizing constants: from importance sampling to bridge sampling to path sampling. Stat. Sci. 13, 163–185 (1998)
Geweke, J.: Evaluating the accuracy of sampling-based approaches to calculating posterior moments. In: Bernado, J., Berger, J., Dawid, A., Smith, A. (eds.) Bayesian Statistics 4. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1992)
Ionides, E.L.: Truncated importance sampling. J. Comput. Gr. Stat. 17, 295–311 (2008)
Kadane, J.B., Lazar, N.A.: Methods and criteria for model selection. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 99, 279–290 (2004)
Li, L., Qiu, S., Zhang, B., Feng, C.X.: Approximating cross-validatory predictive evaluation in Bayesian latent variable models with integrated IS and WAIC. Stat. Comput. 26, 881–897 (2016)
Li, Y., Ansari, A.: A Bayesian approach for endogeneity and heterogeneity in choice models. Manag. Sci. 60, 1161–1179 (2014)
Millar, R.B.: Assessment of locally influential observations in Bayesian models. Bayesian Anal. 2, 365–384 (2007)
Millar, R.B., Stewart, W.S.: Assessment of locally influential observations in Bayesian models. Bayesian Anal. 2, 365–384 (2007)
Onogi, A., Ideta, O., Yoshioka, T., Ebana, K., Yamasaki, M., Iwata, H.: Uncovering a nuisance influence of a phenological trait of plants using a nonlinear structural equation: Application to days to heading and culm length in Asian cultivated rice ( Oryza Sativa L). PloS One (2016). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0148609
Roever, C.L., Beyer, H.L., Chase, M.J., van Aarde, R.J.: The pitfalls of ignoring behaviour when quantifying habitat selection. Divers. Distrib. 20, 322–333 (2014)
Sekar, N., Giam, X., Sharma, N.P., Sukumar, R.: How much dillenia indica seed predation occurs from asian elephant dung? Acta Oecol. 70, 53–59 (2016)
Spiegelhalter, D.J., Best, N.G., Carlin, B.R., van der Linde, A.: Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit (with Discussion). J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 64, 583–616 (2002)
Vehtari, A., Gelman, A., Gabry, J.: Practical Bayesian model evaluation using leave-one-out cross-validation and WAIC. Comput. Stat. (2016). doi:10.1007/s11222-016-9696-4
Vehtari, A., Lampinen, J.: Bayesian model assessment and comparison using cross-validation predictive densities. Neural Comput. 14, 2439–2468 (2002)
Vehtari, A., Mononen, T., Tolvanen, V., Sivula, T., Winther, O.: Bayesian leave-one-out cross-validation approximations for Gaussian latent variable models. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 17, 1–38 (2016)
Vehtari, A., Ojanen, J.: A survey of bayesian predictive methods for model assessment, selection and comparison. Stat. Surv. 6, 142–228 (2012)
Watanabe, S.: Algebraic analysis for singular statistical estimation. In: Watanabe, O., Yokomori, T., (eds.) Algorithmic Learning Theory. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol 1720. Spring, Berlin Heidelberg, (1999)
Watanabe, S.: Algebraic Geometry and Statistical Learning Theory. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2009)
Watanabe, S.: Asymptotic equivalence of Bayes cross validation and widely applicable information criterion in singular learning theory. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 11, 3571–3594 (2010a)
Watanabe, S.: Asymptotic learning curve and renormalizable condition in statistical learning theory. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 233, 012014 (2010b)
Watanabe, S.: Equations of state in singular statistical estimation. Neural Netw. 23, 20–34 (2010c)
Watanabe, S.: Equations of states in statistical learning for a nonparametrizable and regular case. IEICE Trans. E 93A(3), 617–626 (2010d)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Millar, R.B. Conditional vs marginal estimation of the predictive loss of hierarchical models using WAIC and cross-validation. Stat Comput 28, 375–385 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-017-9736-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-017-9736-8