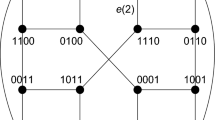
Abstract
Partitioned Optimal Passive Stars network, POPS(d,g), is an optical interconnection network of N processors (N=dg) with g 2 optical passive star couplers. In this network, there are g groups of d processors each and the g 2 couplers are used for connecting each group with each of the groups, including itself. In this paper, we present a technique for optimally simulating a frequently arising hypercube communication pattern on this network for all combinations of values of d and g. Specifically, we show that one-hop movements on the hypercube along the same dimension can be simulated on the POPS(d,g) network in \(\lceil \frac{d}{g}\rceil\) slots for d≠g and in 2 slots for d=g.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li K, Pan Y, Zheng SQ (1998) Parallel computing using optical interconnections. Kluwer, Boston
Gravenstreter G, Melhem RG, Chiarulli D, Levitan S, Teza J (1995) The partitioned optical passive stars (POPS) topology. In: Proceedings of the ninth international parallel processing symposium, pp 4–10
Gravenstreter G, Melhem RG (1998) Realizing common communication patterns in partitioned optical passive stars (POPS) networks. IEEE Trans Comput 47(9):998–1013
Melhem RG, Gravenstreter G, Chiarulli D, Levitan S (1998). The communication capabilities of partitioned optical passive star networks. In: Li K, Pan Y, Zheng S (eds) Parallel computing using optical interconnections. Kluwer, Boston, pp 77–98
Sahni S (2000) The partitioned optical passive stars network: simulations and fundamental operations. IEEE Trans Parallel Distributed Syst 11(7):739–748
Sahni S (2000) Matrix multiplication and data routing using a partitioned optical passive stars network. IEEE Trans Parallel Distributed Syst 11(7):720–728
Datta A, Soundaralakshmi S (2003) Summation and routing on a partitioned optical passive stars network with large group size. IEEE Trans Parallel Distributed Syst 14(12):1275–1285
Mei A, Rizzi R (2002) Routing permutations in partitioned optical passive stars networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international parallel and distributed processing symposium (IPDPS 2002)
Berthome P, Ferreira A (1996) Improved embeddings in POPS networks through stack-graph models. In: Proceedings of the third international workshop on massively parallel processing using optical interconnections, pp 130–136
Mei A, Rizzi R (2003) Mapping hypercube computations onto partitioned optical passive star networks. In: Proceedings of the high performance computing conference (HiPC 2003), pp 95–104
Mei A, Rizzi R (2003) Routing permutations in partitioned optical passive stars networks. J Parallel Distributed Comput 63(9):847–852
Mei A, Rizzi R (2006) Hypercube computations on partitioned optical passive stars networks. IEEE Trans Parallel Distributed Syst 17(6):497–507
Mei A, Rizzi R (2006) Online permutation routing in partitioned optical passive star networks. IEEE Trans Comput 55(12):1557–1571
Datta A, Soundaralakshmi S (2003). Fast merging and sorting on a partitioned optical passive stars network. In: Klein R, Six H, Wegner L (eds) Computer science in perspective. Springer, New York, pp 115–127
Rajasekaran S, Davila J (2005) Packet routing and selection on the POPS network. J Parallel Distributed Comput 65(8):927–933
Auriol BJ, Molakaseema R (2005) A parameterized linear array with reconfigurable pipelined bus system: LARPBS(p). Comput J 48(1):115–125
Gourlay I, Dew PM, Djemame K, Snowdon JF, Russell G (2004) Supporting bulk synchronous parallelism with a high-bandwidth optical interconnect. Concurr Comput Pract Experience 16(13):1247–1270
Chen Y, Shen H, Liu F (2006) Wavelength assignment for realizing parallel FFT on regular optical networks. J Supercomput 36(1):3–16
Al-Ayyoub A, Awwad A, Day K, Ould-Khaoua M (2006) Generalized methods for algorithm development on optical systems. J Supercomput 38(2):111–125
Jana P (2006) Polynomial interpolation and polynomial root finding on OTIS-mesh. Parallel Comput 32(4):301–312
Leighton FT (1992) Introduction to parallel algorithms and architectures: arrays-trees-hypercubes. Morgan Kauffman, San Mateo
Jaja J (1992) An introduction to parallel algorithms. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Kaklamanis C, Konstantopoulos C (2005). Optimal embedding of the hypercube on partitioned optical passive stars networks. In: Proceedings of the Euro-Par 2005—parallel processing conference, LNCS, vol 3648, Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 952–961
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konstantopoulos, C., Kaklamanis, C. Optimal hypercube simulation on the partitioned optical passive stars network. J Supercomput 42, 165–180 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-007-0130-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-007-0130-8