Abstract
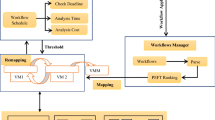
A distributed scientific workflow mapping algorithm for maximized reliability under certain end-to-end delay (EED) bound is proposed. It is studied in a heterogeneous distributed computing environment, where computing node and communication link failures are inevitable. The mapping decision and the stored table information is distributed among various nodes in order to achieve scalability and robustness, which are especially important for large-scale distributed systems. This Distributed Reliability Maximization workflow mapping algorithm under End-to-end Delay constraint (dis-DRMED) considers both the maximum reliability and the minimum EED objectives in a two-step procedure. In the first step, a mapping algorithm combining iterative Critical Path search and Layer-based priority assigning techniques (CPL) is adopted to minimize the EED by focusing on the optimal allocation of tasks on the critical path. In the second step, tasks on noncritical paths are remapped to improve the overall execution reliability. Simulation results under various system setups demonstrated that dis-DRMED achieved considerably higher reliability values under the same EED constraint compared with some representative workflow mapping algorithms.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
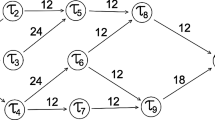
Partial EED of each individual task u i is the end-to-end delay of a path from the starting task u 1 to u i .
References
Agarwalla B, Ahmed N, Hilley D, Ramachandran U (2007) Streamline: a scheduling heuristic for streaming application on the grid. In: The 13th multimedia computing and networking conf, pp 69–85
Benoit A, Hakem M, Robert Y (2008) Fault tolerant scheduling of precedence task graphs on heterogeneous platforms. In: IEEE international symposium on parallel and distributed processing, pp 1–8
Buyya R, Murshed M (2002) GridSim: a toolkit for the modeling and simulation of distributed resource management and scheduling for grid computing. Concurr Comput 14(13–15):1175–1220
Calheiros RN, Ranjan R, Belglazov A, De Rose CAF, Buyya R (2011) CloudSim: a toolkit for modeling and simulation of cloud computing environments and evaluation of resource provisioning algorithms. Softw Pract Exp 41(1):23–50
Chen W, Zhang J (2009) An ant colony optimization approach to a grid workflow scheduling problem with various QoS requirements. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern, Part C, Appl Rev 39(1):29–43
Cirou B, Jeannot E (2001) Triplet: a clustering scheduling algorithm for heterogeneous systems. In: IEEE ICPP international workshop on Metacomputing Systems and Applications (MSA ’2001), pp 231–236
Condor. http://www.cs.wisc.edu/condor
Dabrowski C (2009) Reliability in grid computing systems. Concurr Comput 21(8):927–959
DOE UltraScienceNet. http://www.csm.ornl.gov/ultranet
Dogan A, Ozguner F (2000) Reliable matching and scheduling of precedence-constrained tasks in heterogeneous distributed computing. In: Proc. of the 29th international conference on parallel processing, pp 307–314
Dogan A, Ozguner F (2002) Matching and scheduling algorithms for minimizing execution time and failure probability of applications in heterogeneous computing. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 13(3):308–323
Dogan A, Ozguner F (2005) Bi-objective scheduling algorithms for execution time-reliability trade-off in heterogeneous computing systems. Comput J 48(3):300–314
Dongarra J, Jeannot E, Saule E, Shi Z (2007) Bi-objective scheduling algorithms for optimizing makespan and reliability on heterogeneous systems. In: Proc. of the nineteenth annual ACM symposium on parallel algorithms and architectures (SPAA ’07). ACM, New York, pp 280–288
ESnet. http://www.es.net/
Globus. http://www.globus.org
Hakem M, Butelle F (2006) A Bi-objective algorithm for scheduling parallel applications on heterogeneous systems subject to failures. In: Renpar 17, canet en roussillon, pp 280–288
Hakem M, Butelle F (2007) Reliability and scheduling on systems subject to failures. In: Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Parallel Processing (ICPP ’07). IEEE Comput Soc, Washington, p 38
Large Hadron Collider. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Large_Hadron_Collider
Lewis EE (1987) Introduction to reliability engineering. Wiley, New York
Ma T, Buyya R (2005) Critical-path and priority based algorithms for scheduling workflows with parameter sweep tasks on global grids. In: Proc of the 17th int symp on computer architecture on high performance computing, pp 251–258
Plank JS, Elwasif WR (1998) Experimental assessment of workstation failures and their impact on checkpointing systems. In: Intl symp fault-tolerant computing, pp 48–57
Rahman M, Ranjan R, Buyya R (2009) A distributed heuristic for decentralized workflow scheduling. In: Global grids, 10th IEEE/ACM international conference on grid computing, pp 163–164
Sih G, Lee E (1993) A compile-time scheduling heuristic for interconnection-constrained heterogeneous processor architectures. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 4(2):175–187
Singh G, Kesselman C, Deelman E (2006) Optimizing grid-based workflow execution. J Grid Comput 3:201–219
Sonmez O, Yigitbasi N, Abrishami S, Iosup A, Epema D (2010) Performance analysis of dynamic workflow scheduling in multicluster grids. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM international symposium on High Performance Distributed Computing (HPDC ’10), pp 49–60
Topcuoglu S, Wu M (1999) Task scheduling algorithms for heterogeneous processors. In: 8th IEEE Heterogeneous Computing Workshop (HCW ’99), pp 3–14
Wang L, Kunze M, Tao J (2008) Performance evaluation of virtual machine-based grid workflow system. Concurr Comput 20(15):1759–1771
Wang L, Chen D, Huang F (2011) Virtual workflow system for distributed collaborative scientific applications on grid. Comput Electr Eng 37(3):300–310
Wang X, Yeo CS, Buyya R, Sua J (2011) Optimizing makespan and reliability for workflow applications with reputation and a look-ahead genetic algorithm. Future Gener Comput Syst 27(8):1124–1134
Wu Q, Gu Y (2008) Supporting distributed application workflows in heterogeneous computing environments. In: Proc of 14th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS ’08), vol 47, pp 8–22
Wu Q, Gu Y (2010) Distributed workflow mapping algorithm for minimum end-to-end delay under fault-tolerance constraint. In: IEEE 16th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS), pp 508–515
Wu Q, Gu Y, Zhu M (2008) Optimizing network performance of computing pipelines in distributed environments. In: IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing (IPDPS ’2008), pp 1–8
Wu Q, Zhu M, Lu X, Brown P, Lin Y, Gu Y, Cao F, Reuter M (2010) Automation and management of scientific workflows in distributed network environments. In: Proc of the 6th int workshop on sys man tech, proc, and serv, pp 1–8
Wu Q, Gu Y, Lin Y, Rao NSV (2011) Latency modeling and minimization for large-scale scientific workflows in distributed network environments. In: Proc. of the 44th Annual Simulation Symposium (ANSS ’2011), pp 205–212
Xing L, Shrest A (2006) Algorithms for minimal-length schedules. In: Computer and job-shop scheduling theory, vol 2, pp 473–479
Yang X, Bruin RP, Dove MT (2010) Developing an end-to-end scientific workflow. Comput Sci Eng 12(3):52–61
Yin PY, Yu SS, Wang PP, Wang YT (2007) Multi-objective task allocation in distributed computing systems by hybrid particle swarm optimization. Appl Math Comput 184:407–420
Zhu M, Wu Q, Rao NSV, Iyengar SS (2004) Adaptive visualization pipeline decomposition and mapping onto computer networks. In: Proc. of the IEEE internatioal conference on image and graphics, pp 402–405
Zhu M, Cao F, Mi J (2011) A hybrid mapping and scheduling algorithm for distributed workflow applications. In: A heterogeneous computing environment, intelligent distributed computing V, 5th international symposium on Intelligent Distributed Computing (IDC 2011). Springer, Berlin, pp 117–127
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, F., Zhu, M.M. Distributed workflow mapping algorithm for maximized reliability under end-to-end delay constraint. J Supercomput 66, 1462–1488 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-013-0938-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-013-0938-3