Abstract
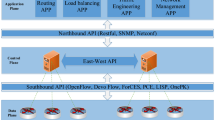
With the development of the Internet, data centers have become vital infrastructures which provide computing, storage and other services for the networks. According to statistics, data centers consume large amount of electricity all around the world. In most cases, the majority of network devices in data centers are relatively idle, resulting in a waste of energy. Software defined network (SDN) was proposed by UC Berkeley and Stanford University around 2008, which allows the administrators to manage the network and set configurations through abstraction of lower level functionality. It also separates the control plane and the data plane, so administrators can control the network traffic through centralized controller instead of access to physical devices. This paper discusses the energy-saving model in data center networks based on SDN. We propose two different energy-saving algorithms, which can be applied to different data centers. Through centralized management and preprocessing traffic by SDN, we get better energy efficiency and reduce the energy cost by 30–40 %. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work on energy saving in SDN architecture which provides two different algorithms that can be applied in different scenarios.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Global Energy Consumption. http://tech.qq.com/a/20120925/000095.htm. Accessed Sept 2012
Internet Energy Consumption. http://www.thebigdata.cn/YeJieDongTai/4274.html. Accessed Mar 2013
Heller B, Seetharaman S, Mahadevan P et al (2010) ElasticTree: saving energy in data center networks [C] NSDI. 3:19–21
Software-defined networking (SDN) definition. https://www.opennetworking.org/sdn-resources/sdn-definition. Accessed April 2012
McKeown N (2009) Software-defined networking [J]. INFOCOM keynote talk, April 2009
Jun L (2012) Explore of energy loss and energy saving measures in IDC. Silicon Valley 19:084
Shang Y, Li D, Xu M (2010) Energy-aware routing in data center network [C]. In: Proceedings of the first ACM SIGCOMM workshop on green networking. ACM, pp 1–8
Nedevschi S, Popa L, Iannaccone G et al (2008) Reducing network energy consumption via sleeping and rate-adaptation [C] NSDI. 8:323–336
Christensen K, Nordman B, Brown R (2004) Power management in networked devices [J]. Computer 37(8):91–93
Ryu B, Cheney D, Braun H-W (2001) Internet flow characterization: adaptive timeout strategy and statistical modeling. In: Proceedings of passive and active measurement workshop
Mahadevan P, Sharma P, Banerjee S et al (2009) A power benchmarking framework for network devices [M] networking. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 795–808
OpenFlow switch specification 1.4.0. https://www.opennetworking.org/images/stories/downloads/sdn-resources/onf-specifications/openflow/openflow-spec-v1.4.0.pdf. Accessed Oct 2013
Barroso LA, Holzle U (2007) The case for energy-proportional computing [J]. Computer 40(12):33–37
Gupta M, Singh S (2003) Greening of the internet [C]. In: Proceedings of the 2003 conference on applications, technologies, architectures, and protocols for computer communications. ACM, pp 19–26
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation of China under Grant 61171074, Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University under Grant NCET-11-0113, Shanghai Municipal R&D Foundation under Grant No. 13511500400 and the National S&T Major Project of China under Grant 2010ZX03003-003-03.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, R., Wang, X. & Yang, Y. Energy-saving model for SDN data centers. J Supercomput 70, 1477–1495 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-014-1237-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-014-1237-3