Abstract
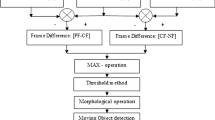
Most of the existing video object detection schemes are either computationally extensive or fail to detect moving objects in different challenging situations. In this paper, we propose a robust and computationally inexpensive scheme to detect moving objects in video. The threefold approach begins with computation of difference images using temporal information. Difference images are calculated by subtracting two input frames, at each pixel position. Instead of generating difference images using the traditional continuous frame difference approach, we propose using a fixed number of alternate frames centered around the current frame. This approach aids in reducing the computational complexity without compromising on quality of the difference images. After computation of difference images, a novel post-processing scheme is employed by utilizing gamma correction factor and Mahalanobis distance metric to reduce false positives and false negatives. Object segmentation is finally performed on the refined difference image by a local fuzzy thresholding scheme. This avoids problems that are usually encountered in hard thresholding, especially pixel misclassification, which is the most important one. For robust experimental analysis, videos from changedetction.net, CAVIAR, and http://perception.i2r datasets have been used. These selected videos contain a wide variety of common challenges faced during object detection. Some examples are the presence of dynamic backgrounds, shadows, bad weather, etc. The results establish the effectiveness of the proposed scheme over some of the existing schemes both qualitatively and quantitatively as delineated in the experimental result section.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
McFarlane N, Schofield C (1995) Segmentation and tracking of piglets in images. Br Mach Vision Assoc 8(3):187–193
Zheng J, Wang Y (2006) Extracting roadway background image: a mode based approach. J Transp Res Board 1944:82–88
Toyama K, Krumm J (1999) Wallflower: principles and practice of background maintenance. In: Proc. 7th. IEEE Int. Conf. on Computer Vision, pp 255–261
Messelodi S, Modena C (2005) A Kalman filter based background updating algorithm robust to sharp illumination changes. Lect Notes Comput Sci 3617:163–170
Wren C, Azarbayejani A (1997) Pfinder: Real-time tracking of the human body. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 19(7):780–785
Stauffer C, Grimson WEL (1999) Adaptive background mixture models for real-time tracking. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol 2, pp 2246–2252
Elgammal A, Duraiswami R, Harwood D, Davis LS (2002) Background and foreground modeling using nonparametric kernel density estimation for visual surveillance. Proc IEEE 90(7):1151–1163
Cavallaro A, Ebrahimi T (2000) Video object extraction based on adaptive background and statistical change detection. Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng 4310:465–475
Jodoin PM, Mignotte M, Konrad J (2007) Statistical background subtraction using spatial cues. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 17(12):1758–1763
Zhang H, Xu D (2006) Fusing color and texture features for background model. Lect Notes Comput Sci 4223:887–893
Baf FE, Bouwmans T, Vachon B (2008) Fuzzy integral for moving object detection. In: IEEE Int. Conf. on Fuzzy Systems, pp 1729–1736
Kameda Y, Minoh M (1996) A human motion estimation method using 3-successive video frames. In: Int. Conf. on Virtual Systems and Multimedia (VSMM). Gifu, Japan, pp 135–140
Collins R, Lipton A, Kanade T, Fijiyoshi H, Duggins D, Tsin Y, Tolliver D, Enomoto N, Hasegawa O, Burt P, Wixson L (2000) A system for video surveillance and monitoring, Tech. rep. Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburg
Zhang Y, Wang X, Qu B (2012) Three-frame difference algorithm research based on mathematical morphology. Proc Eng 29:2705–2709
Lipton AJ, Fujiyoshi H, Patil RS (1998) Moving target classification and tracking from real-time video. In: Proc., Fourth IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp 8–14
Desa SM, Salih QA (2004) Image subtraction for real time moving object extraction. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Computer Graphics, Imaging and Visualization, pp 41–45
Wang Z, Liao K, Xiang J, Zhang Q (2014) Moving object detection based on temporal information. IEEE Signal Process Lett 21(11):1403–1407
Otsu N (1979) A threshold selection method from gray-scale histogram. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 9(1):62–66
Kurita T, Otsu N, Abdelmalek N (1992) Maximum likelihood thresholding based on population mixture models. Pattern Recogn 25(10):1231–1240
Velasco FRD (1980) Thresholding using the iso data clustering algorithm. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 10:771–774
Lee H, Park RH (1980) Comments on an optimal threshold scheme for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 20:741–742
Pun T (1980) A new method for gray-level picture threshold using the entropy of the histogram. Signal Process 23:223–237
Hertz L, Schafer RW (1998) Multilevel thresholding using edge matching. Comput Vis Graph Image Process 44:279–295
Leung C, Lam F (1997) Maximum a posteriori spatial probability segmentation. Vis Image Signal Process IEEE Proc 144(3):161–167
Wu H, Barba J, Gil J (2000) Iterative thresholding for segmentation of cells from noisy images. J Microsc 197(3):296–304
Fernández A, Curiale SAH, Ferrero GVS (2015) A local fuzzy thresholding methodology for multiregion image segmentation. Knowl Based Syst 83:1–12
Zeng X, Singh M (1994) Approximation theory of fuzzy systems—SISO case. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 2(2):162–176
Zhang S, Yao H, Liu S, Chen X, Gao W (2008) A covariance-based method for dynamic background subtraction. In: Proc. 19th Int. Conf. on Pattern Recognition, pp 1–4
Kim K, Chalidabhongse TH, Harwood D, Davis LS (2005) Realtime foreground-background segmentation using codebook Model. Real Time Image 11:172–185
Matsuyame T, Ohya T, Habe H (2000) Background subtraction for non-stationary scene. In: Proc. Asian Conf. on Computer Vision, pp 622–667
Chiranjeevi P, Sengupta S (2011) Moving object detection in the presence of dynamic backgrounds using intensity and textural features. J Electron Imaging 20(4):043009
IEEE Workshop on Change Detection in Conjunction with CVPR2014. http://www.changedetection.net. Accessed 17 Jan 2016
EC Funded CAVIAR Project, IST 2001 37540. http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/CAVIAR/. Accessed 14 Oct 2015
ftp://ftp.pets.rdg.ac.uk/pub/PETS2000. Accessed 23 Dec 2015
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, N., Singh, A., Midya, A. et al. Moving object detection using modified temporal differencing and local fuzzy thresholding. J Supercomput 73, 1120–1139 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-016-1815-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-016-1815-7