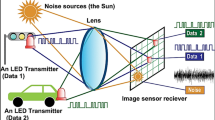
Abstract
This paper studies the performance of the reverse link adopting visible light communication at urban street environments. Firstly, the signal transmitting schemes are classified into two cases: only the head lamps are used or both the head lamps and the tail lamps are used; secondly, mathematical models corresponding the two different signal transmitting schemes for analyzing the performance of the reverse visible light communication link between a vehicle and the road side equipment are set up; thirdly, a method to improve the quality of the reverse visible light communication link is proposed; finally, three types of simulations are conducted to check the influence of receiver height and vehicle position on the link quality, respectively, and to check the validity of the proposed method.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Komine T, Nakagawa M (2004) Fundamental analysis for visible-light communication system using LED lights. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 50(1):100–107
Demir MS, Uysal M (2021) A cross-layer design for dynamic resource management of VLC Networks. IEEE Trans Commun 99:1858–1867
Guo JN, Zhang J, Zhang YY, Li L, Chen RH (2020) Multilevel transmission scheme based on parity check codes for VLC with dimming control. Opt Commun 467:125733
Wu S, Wang H, Youn CH (2014) Visible light communications for 5G wireless networking systems: from fixed to mobile communications. IEEE Network 12:41–45
Kim DH (2014) Energy-efficient brightness control and data transmission for visible light communication. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 26(8):781–784
Lee K, Park H (2011) Modulations for visible light communications with dimming control. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 23(16):1136–1138
Cailean AM, Dimian M (2016) Toward environmental-adaptive visible light communications receivers for automotive applications: a review. IEEE Sensor J 16(9):2803–2811
J.H. Lee, S.Y. Jung. SNR analyses of the multi-spectral light channels for optical wireless LED communications in intelligent transportation system, Proc. of VTC 2014, 2014, Seoul: 1–5
Nawaz T, Seminara M, Caputo S, Mucchi L, Cataliotti F, Catani J (2019) Ieee 802.15.7-compliant ultra-low latency relaying VLC system for safety-critical its. IEEE Trans Vehicular Technol 68(12):12040–12051
Boubakri W, Abdallah W, Boudriga N (2015) A light-based communication architecture for smart city applications. International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks. IEEE
Akanegawa M, Tanaka Y, Nakagawa M (2001) Basic study on traffic information system using LED traffic lights. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 2(4):197–203
Kitano S, Haruyama S, Nakagawa M. LED road illumination communications system[C]//2003 IEEE 58th Vehicular Technology Conference. VTC 2003-Fall (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37484). IEEE, 2003, 5: 3346–3350.
F. Knobloch, Channel gain and frame error rate for optical street lighting communication, Proc. of 13th International Conference on Telecommunications (ConTEL), 2015 , IEEE Press:1–5
R.P. Jimenez, J. Rabadan, J. Rufo and E. Solana, et al. Visible light communications technologies for smart tourism destinations, Proc. of IEEE First International Smart Cities Conference, 2015:1–5
S. J. Lee, J. K. Kwon, S. Y. Jung, and Y. H. Kwon. Simulation modeling of visible light communication channel for automotive applications, Proc. of the 15th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Alaska, USA, 2012:463–468
Kumar N, Lourenco NF (2012) Led-based visible light communication: a brief survey and investigation. J Eng Appl Sci 5(4):296–307
Cem BF et al (2017) Vehicles of the future: a survey of research on safety issues. IEEE Trans Intell Trans Syst 18:1046–1065
Uysal M, Ghassemlooy Z, Bekkali A et al (2015) Visible light communication for vehicular networking: performance study of a V2V system using a measured headlamp beam pattern model. IEEE Veh Technol Mag 10(4):45–53
Chen S. Dynamic spectrum access and cognitive radio for vehicular communication networks. Vehicular Commun Netw, 2015: 127–150.
Shen W H, Tsai H M.Testing vehicle-to-vehicle visible light communications in real-world driving scenarios[C]// 2017 IEEE Vehicular Networking Conference (VNC). IEEE, 2017.
Ghassemlooy Z, Haigh PA, Arca F et al (2013) Visible light communications: 3.75 Mbits/s data rate with a 160 kHz bandwidth organic photodetector and artificial neural network equalization. Photon Res 1(2):65–68
Haigh PA, Ghassemlooy Z, Rajbhandari S et al (2014) Visible light communications: 170 Mb/s using an artificial neural network equalizer in a low bandwidth white light configuration. J Lightwave Technol 32(9):1807–1813
Yesilkaya A, Karatalay O, Ogrenci A S, et al. Channel estimation for visible light communications using neural networks. 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). IEEE, 2016: 320–325.
Lee H, Lee I, Quek TQS et al (2018) Binary signaling design for visible light communication: a deep learning framework. Opt Express 26(14):18131–18142
Lee H, Lee I, Lee SH (2018) Deep learning based transceiver design for multi-colored VLC systems. Opt Express 26(5):6222
Dang QH, Yoo M (2017) Handover procedure and algorithm in vehicle to infrastructure visible light communication. IEEE Access 5:26466–26475
Zhao S, Ma X (2017) A spectral-efficient transmission scheme for dimmable visible light communication systems. J Lightwave Technol 35(17):3801–3809
Li H, Zhang Y, Chen X et al (2015) 682 Mbit/s phosphorescent white LED visible light communications utilizing analog equalized 16QAM-OFDM modulation without blue filter. Optics Commun 354:107–111
Wang Y, Huang X, Tao L et al (2015) 4.5-Gb/s RGB-LED based WDM visible light communication system employing CAP modulation and RLS based adaptive equalization. Optics Express 23(10):13626–13633
Fahs B, Chellis J, Senneca MJ et al (2016) A 6-m OOK VLC link using CMOS-compatible pn photodiode and red LED. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 28(24):2846–2849
Zhang H, Yang A, Feng L et al (2018) Gb/s Real-time visible light communication system based on white LEDs using T-bridge cascaded pre-equalization circuit. IEEE Photon J 10(2):1–7
Qian H, Yao SJ, Cai SZ et al (2014) Adaptive postdistortion for nonlinear LEDs in visible light communications. IEEE Photon J 6(4):7901508
Sharma R, Kumari AC (2017) Performance analysis of rectangular and circular shape building deployment for an indoor visible light communication system. Int J Comput Netw Inform Security 9(7):11
Liu H, Wang X, Chen Y et al (2017) Optimization lighting layout based on gene density improved genetic algorithm for indoor visible light communications. Opt Commun 390:76–81
Tan M, Chen J (2019) Dynamical optimized lamps distribution based on genetic algorithm for visible light communications. In: Eleventh International Conference on Information Optics and Photonics (CIOP 2019), 1120948
Wang S, Lu Z, Wei L et al (2016) Fitness-scaling adaptive genetic algorithm with local search for solving the multiple depot vehicle routing problem. SIMULATION 92(7):601–616
Van Gerven M, Bohte S (2017) Artificial neural networks as models of neural information processing. Front Comput Neurosci 11:114
Zhang Y-Y, Hong-Yi Yu, Zhang J-K (2016) On the optimality of spatial repetition coding for MIMO optical wireless communications. IEEE Commun Lett 20(5):846–849
Xinyue G, Shuangshuang LI (2018) MIMO channel correlation study of indoor visible light communication. Semicond Optoelectron 1(39):124–128
Ahmed M, Ahmmed KT, Hossan A et al (2016) Performance of free space optical communication systems over exponentiated Weibull atmospheric turbulence channel for PPM and its derivatives. Optik 127(20):9647–9657
Islam A, Hossan MT, Jang YM (2018) Convolutional neural networkscheme-based optical camera communication system for intelligent Internet of vehicles. Int J Distrib Sensor Netw 14(4):1–10
Kang SY, Kim TH, Chung WZ (2020) Hybrid RSS/AOA localization using approximated weighted least square in wireless sensor networks. Sensor 20(4):21–23
Zhao L, Mao Y, Xu P (2018) Single-station location algorithm based on secondary scatterer model. J Comput Methods Sci Eng 18(3):737–747
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Scientific and Technical Fund of South China Electrical Power Grid Corporation with item number 039920KK52150002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Huang, S. Improving the performance of uplink visible light communication in urban streets. J Supercomput 78, 3775–3790 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-04010-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-04010-0