Abstract
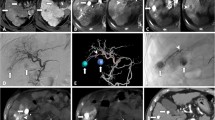
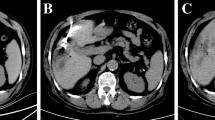
To explore the clinical efficacy of computed tomography (CT)-guided microwave ablation (MWA) sequential transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) based on edge calculation for primary liver cancer larger than 5 cm in diameter, CT images based on edge calculation were reconstructed and the model was constructed, and the treatment of the images was evaluated. A total of 30 patients with primary liver cancer over 5 cm in diameter who were admitted to Liaocheng People’s Hospital and Liaocheng Tumor Hospital from January 2020 to January 2021 were randomly divided into TACE group and MWA group. In the CT image processing based on edge computing, appropriate prior information was introduced into the CT reconstruction model to obtain high-quality CT images. The tumor volume, blood supply loss rate, complete necrosis rate, and other indexes of patients treated with TACE alone and TACE combined with MWA were compared. The results showed that CT-guided MWA images were relatively clearer, helping doctors to treat more accurately. There was no considerable difference in survival at 6 months, 12 months, and 36 months between the two groups. In addition, the probability of loss of blood supply, tumor size, and the probability of complete tumor necrosis were not substantially different between the two groups. Subjective evaluation was conducted on the CT image segmentation effect of all patients with liver cancer lesions over 5 cm participating in this study. PSNR and SSIM were higher than other reconstructed model images. After treatment, alpha fetal protein level was substantially lower than before treatment, and alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels were substantially higher than before treatment, with considerable differences between the two groups. In short, the CT image quality based on edge calculation was improved, which provided a reference for the CT image-guided MWA sequential TACE treatment of primary liver cancer.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broutier L, Mastrogiovanni G, Verstegen MM et al (2017) Human primary liver cancer-derived organoid cultures for disease modeling and drug screening. Nat Med 23(12):1424–1435
Orcutt ST, Anaya DA (2018) Liver resection and surgical strategies for management of primary liver cancer. Cancer Control 25(1):1073274817744621
Sia D, Villanueva A, Friedman SL et al (2017) Liver cancer cell of origin, molecular class, and effects on patient prognosis. Gastroenterology 152(4):745–761
Kim EK, Song MJ, Jung Y et al (2019) Proteomic analysis of primary colon cancer and synchronous solitary liver metastasis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 16(6):583–592
Shiani A, Narayanan S, Pena L et al (2017) The role of diagnosis and treatment of underlying liver disease for the prognosis of primary liver cancer. Cancer Control 24(3):1073274817729240
Xu F, Jin T, Zhu Y et al (2018) Immune checkpoint therapy in liver cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37(1):110
Sarmati L, Malagnino V (2019) HBV infection in HIV-driven immune suppression. Viruses 11(11):1077
Megahed FAK, Zhou X, Sun P (2020) The Interactions between HBV and the Innate Immunity of Hepatocytes. Viruses 12(3):285
Li F, Wang Z, Hu F et al (2020) Cell culture models and animal models for HBV study. Adv Exp Med Biol 1179:109–135
Chen KH, Siow TF, Chio UC et al (2018) Laparoscopic donor hepatectomy. Asian J Endosc Surg 11(2):112–117
Kwon CHD, Choi GS, Joh JW (2019) Laparoscopic right hepatectomy for living donor. Curr Opin Organ Transplant 24(2):167–174
Au KP, Chok KSH (2018) Minimally invasive donor hepatectomy, are we ready for prime time? World J Gastroenterol 24(25):2698–2709
Raoul JL, Forner A, Bolondi L et al (2019) Updated use of TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: How and when to use it based on clinical evidence. Cancer Treat Rev 72:28–36
Kamachi N, Sakai M, Suzuki H et al (2020) Increased arterio-portal shunt formation after drug-eluting beads TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 98(8):558–565
Wang H, Cao C, Wei X et al (2020) A comparison between drug-eluting bead-transarterial chemoembolization and conventional transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis of six randomized controlled trials. J Cancer Res Ther 16(2):243–249
Han T, Yang X, Zhang Y et al (2019) The clinical safety and efficacy of conventional transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and drug-eluting beads-transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Biosci Trends 13(5):374–381
Izzo F, Granata V, Grassi R et al (2019) Radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation in liver tumors: an update. Oncologist 24(10):e990–e1005
Kaltenbach B, Hohenforst-Schmidt W, Lin H, et al. Thermal ablation of lung tumors: focus on microwave ablation. Rofo. 2017;189(9):828–843. English.
Wang T, Lu Y, Cao Z et al (2019) When sensor-cloud meets mobile edge computing. Sensors (Basel) 19(23):5324
Passian A, Imam N (2019) Nanosystems, edge computing, and the next generation computing systems. Sensors (Basel) 19(18):4048
Hamdan S, Ayyash M, Almajali S (2020) Edge-computing architectures for internet of things applications: a survey. Sensors (Basel) 20(22):6441
Klonoff DC (2017) Fog computing and edge computing architectures for processing data from diabetes devices connected to the medical internet of things. J Diabetes Sci Technol 11(4):647–652
Kruepunga N, Hakvoort TBM, Hikspoors JPJM et al (2019) Anatomy of rodent and human livers: what are the differences? Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1865(5):869–878
Li H, Wu F, Duan M, Zhang G. Drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) vs conventional TACE in treating hepatocellular carcinoma patients with multiple conventional TACE treatments history: a comparison of efficacy and safety. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(21):e15314.
Sapisochin G, Barry A, Doherty M, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy vs. TACE or RFA as a bridge to transplant in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. an intention-to-treat analysis. J Hepatol. 2017;67(1):92–99.
Takahashi H, Berber E (2020) Role of thermal ablation in the management of colorectal liver metastasis. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr 9(1):49–58
Tan W, Deng Q, Lin S et al (2019) Comparison of microwave ablation and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Hyperthermia 36(1):264–272
van Tilborg AA, Scheffer HJ, de Jong MC et al (2016) MWA versus RFA for perivascular and peribiliary CRLM: a retrospective patient- and lesion-based analysis of two historical cohorts. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 39(10):1438–1446
Glassberg MB, Ghosh S, Clymer JW et al (2019) Microwave ablation compared with radiofrequency ablation for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther 12:6407–6438
Nour-Eldin NA, Exner S, Al-Subhi M et al (2017) Ablation therapy of non-colorectal cancer lung metastases: retrospective analysis of tumour response post-laser-induced interstitial thermotherapy (LITT), radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation (MWA). Int J Hyperthermia 33(7):820–829
Liu Y, Zhao P, Cheng M et al (2018) AST to ALT ratio and arterial stiffness in non-fatty liver Japanese population: a secondary analysis based on a cross-sectional study. Lipids Health Dis 17(1):275
Asai M, Kumakura S, Kikuchi M (2019) Review of the efficacy of AST-120 (KREMEZIN®) on renal function in chronic kidney disease patients. Ren Fail 41(1):47–56
Yang W, Wang D, Huang L et al (2018) Thalidomide Combined with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization (TACE) for Intermediate or Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and GRADE Approach. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 19(8):2043–2055
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, R., Tian, Y., Yu, Z. et al. Clinical efficacy of computed tomography-guided microwave ablation sequential transcatheter arterial chemoembolization under edge calculation for primary liver cancer over 5 cm in diameter. J Supercomput 78, 11298–11317 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-04118-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-04118-3