Abstract
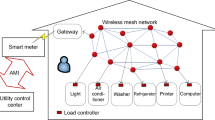
A smart grid uses automation and information communication technologies to guarantee its integrity. The first step of smart grid construction is the deployment of an advanced metering infrastructure system, which can read meter data automatically and maximize energy efficiency. Messages are collected at hubs distributed throughout the smart grid and sent through limited network resources. The advanced metering infrastructure system comprises a meter data management system, concentrators, relay stations between a set of smart meters and the control center, and smart meters that can collect the information of thousands of users. Concerns regarding this system are the loading on the control center, the volume of data traffic, and the quantity of the data. This study analyzes various situations of data traffic, uses Poisson process, and proposed two schemes to reduce the transmission frequency and the total data volume. A concentrator is determined to reduce the transmission frequency and compress the data from smart meters to the control center, thereby reducing the total data volume. Furthermore, the proposed scheme can reduce the loading on the control center.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Fang X, Misra S, Xue G, Yangand D (2012) Smart grid-the new and improved power grid: a survey. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 14(4):944–980
Yu N, Shah S, Johnson R, Sherick R, Hong M, Loparo K (2015) Big data analytics in power distribution systems. In: 2015 IEEE Power & Energy Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT)
Ma R, Chen H-H, Huang Y-R, Meng W (2013) Smart grid communication: its challenges and opportunities. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 4(1):36–46
Erol-Kantarci M, Mouftah HT (2015) Energy-efficient information and communication infrastructures in the smart grid: a survey on interactions and open issues. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 17(1):179–197
Gungor VC, Sahin D, Kocak T, Ergut S, Buccella C, Cecati C, Hancke GP (2013) A survey on smart grid potential applications and communication requirements. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 9(1):28–42
Castillo-Cagigal M, Matallanas E, Mass-Bote D, Caamano-Martin E, Gutierrez A, Monasterio F (2010) Self-consumption enhancement with storage system and demand-side management: GeDELOS-PV system. In: Proceedings of 5th International Renewable Energy Storage Conference (IRES). pp. 3–7
Chen L, Li N, Jiang L (2012) Control and optimization methods for electric smart grid
Roesener C, Ichimura J, Nishi H (2006) Implement of internet based demand controlling system. Proc Int Conf Ind Inf 381–386
Fan Z, Kulkarni P, Gormus S, Efthymiou C, Kalogridis G, Sooriyabandara M, Zhu Z, Lambotharan S, Chin WH (2013) Smart grid communications: overview of research challenges, solutions, and standardization activities. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 15(1):21–38
Ghofrani M, Hassanzadeh M, Etezadi-Amoli M, Fadali M (2011) Smart meter based short-term load forecasting for residential customers. In: Proceedings of North American Power Symposium (NAPS). 1–5
Wang S, Cui L, Que J, Choi D, Jiang X, Cheng S, Xie L (2012) A randomized response model for privacy preserving smart metering. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 3(3):1317–1324
Gungor VC, Sahin D, Kocak T, Ergut S, Buccella C, Cecati C, Hancke GP (2011) Smart grid technologies: communication technologies and standards. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 7(4):529–542
Yan Y, Qian Y, Sharif H, Tipper D (2013) A survey on smart grid communication infrastructures: motivations, requirements, and challenges. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 15(1):5–20
Yan Y, Hu RQ, Das SK, Sharif H, Qian Y (2013) An efficient security protocol for advanced metering infrastructure in smart grid. IEEE Netw 27(4):64–71
Yang Y, Roy S (2014) Grouping-based MAC protocols for EV charging data transmission in smart metering network. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 32(7):1328–1343
Yu K, Arifuzzaman M, Wen Z, Zhang D, Sato T (2015) A key management scheme for secure communications of information centric advanced metering infrastructure in smart grid. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 64(8):2072–2085
Fadlullah ZM, Fouda MM, Kato N, Takeuchi A, Iwasaki N, Nozaki Y (2011) Toward intelligent machine-to-machine communications in smart grid. IEEE Commun Mag 49(4):60–65
Bernaudo D, Barto L, Spizzirri S, Penn T (2010) SmartGrid/AEIC AMI interoperability standard guidelines for ANSI C12.19/IEEE 1377/MC12.19 end device communications and supporting enterprise devices, networks and related accessories. In: The Association of Edison Illuminating Companies, Meter and Service Technical Committee report
Queen EE (2011) A discussion of smart meters and RF exposure issues. In: Edison Electric Institute, Washington, D.C, A Joint Project of the EEI and AEIC Meter Committee
Das U, Dev VC, Namboodiri V (2018) On the effectiveness of data aggregation to manage network congestion in smart grid AMI. In: IEEE Power and Energy Society Innovative Smard Grid Technologies Conference
Das U, Namboodiri V (2019) A quality-aware multi-level data aggregation approach to manage smart grid AMI traffic. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 30(2):245–256
Okafor KC, Ononiwu GC, Sam GVC, Chihindu CCU (2018) Towards complex dynamic fog network orchestration using embedded neural switch. Int J Comput Appl 43:91
Okafor KC, Achumba IE, Chukwudebe GA, Ononiwu GC (2017) Leveraging fog computing for scalable IoT datacenter using spine-leaf network topology. J Electr Comput Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2363240
Okafor KC (2019) Dynamic reliability modelling of cyber-physical edge computing network. Int J Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1080/1206212X.2019.1600830
Aroussi S, Mellouk A (2014) Survey on machine learning-based QoE-QoS correlation models. In: 2014 International Conference on Computing, Management and Telecommunications (ComManTel)
Kaur M, Gianey HK, Singh D, Sabharwal M (2019) Multi-objective differential evolution based random forest for e-health applications. Mod Phys Lett B 33(05):1950022
Lo YL, Huang SC, Lu CN (2014) Transformational benefits of AMI data in transformer load modeling and management. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 29(2):742–750
Karimi B, Namboodiri V, Jadliwala M (2013) On the scalable collection of metering data in smart grid through message concatenation. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications. pp. 318–323
Karimi B, Namboodiri V, Jadliwala M (2015) Scalable meter data collection in smart grids through message concatenation. IEEE Trans Smart Grid Commun 6(4):1697–1706
Allalouf M, Gershinsky G, Lewin-Eytan L, Naor J (2014) Smart grid network optimization: data-quality-aware volume reduction. IEEE Syst J 8(2):450–460
Zhou J, Qingyang HuR, Qian Y (2012) Scalable distributed communication architectures to support advanced metering infrastructure in smart grid. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 23(9):1632–1642
PRIME Alliance, PRIME: powerline intelligent metering evolution, Available at http://www.prime-alliance.org, last accessed, May 2016
Luan W, Sharp D, Landcashire S (2010) Smart grid communication network capacity planning for power utilities. In: Proceedings of IEEE/PES Transmission & Distribution Conference & Exposition (T&D). pp. 1–4
Johnson D, Menezes A, Vanstone S (2001) The elliptic curve digital signature algorithm (ECDSA). Int J Inf Secur 1:36–63
Li H, Han Z, Lai L, Qiu R, Yang D (2011) Efficient and reliable multiple access for advanced metering in future smart grid. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications. pp. 440–444
Choi K, Chae K (2014) Data aggregating using temporal and spatial correlations in advanced metering infrastructure. In: Proceedings of The International Conference on Information Networking. pp. 541–544
Gross D, Shortle JF, Thompson JM, Carl M (2008) Fundamentals of queueing theory
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsieh, SY., Hsu, CW., Yeh, CH. et al. Novel scheme for reducing communication data traffic in advanced metering infrastructure networks. J Supercomput 78, 8219–8246 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-04143-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-04143-2