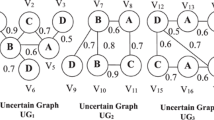
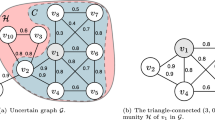
Abstract
Uncertain graphs are widespread in the real world. Enumerating maximal cliques over uncertain graphs is a fundamental problem in many applications. This paper studies the problem of enumerating the top \(k\) maximal cliques with the most number of vertices satisfying that their probabilities \(\ge \alpha\), where each maximal clique is called an \(\alpha\)-maximal-clique. Existing works are inefficient due to suffering from expensive computations on the cliques carrying little information. To address this problem, we propose an index-based top \(k\) \(\alpha\)-maximal-clique enumeration algorithm which computes \(\alpha\)-maximal-cliques based on an index to improve the efficiency. We propose two efficient indexes, called degree-based index and core-based index, which sort the vertices in descending order according to their degrees or core numbers to help prune unpromising vertices, such that to avoid enumerating redundant \(\alpha\)-maximal-cliques. We propose a support-based pruning strategy to further avoid enumerating the not chosen \(\alpha\)-maximal-cliques to speed up the enumeration. The experimental results on 20 real-world datasets show that our algorithms can return the top \(k\) \(\alpha\)-maximal-cliques efficiently.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gibson D, Kumar R, Tomkins A (2005) Discovering large dense subgraphs in massive graphs. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, Trondheim, Norway, August 30 - September 2, 2005, pp. 721–732 http://www.vldb.org/archives/website/2005/program/paper/thu/p721-gibson.pdf
Qin L, Li R, Chang L, Zhang C (2015) Locally densest subgraph discovery. In: Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Sydney, NSW, Australia, August 10-13, 2015, pp. 965–974 https://doi.org/10.1145/2783258.2783299
Modani N, Dey K (2009) Large maximal cliques enumeration in large sparse graphs. In: Chawla, S., Karlapalem, K., Pudi, V. (eds.) Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Management of Data, December 9-12, 2009, International School of Information Management, Mysore, India. Computer Society of India, India. http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/%7Ecomad/2009/proceedings/R3_1.pdf
Makino K, Uno T (2004) New algorithms for enumerating all maximal cliques. In: Hagerup, T., Katajainen, J. (eds.) Algorithm Theory - SWAT 2004, 9th Scandinavian Workshop on Algorithm Theory, Humlebaek, Denmark, July 8-10, 2004, Proceedings. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 3111, pp. 260–272. Springer, Germany. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-27810-8_23
Mukherjee AP, Xu P, Tirthapura S (2015) Mining maximal cliques from an uncertain graph. In: 31st IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering, ICDE 2015, Seoul, South Korea, April 13-17, 2015, pp. 243–254. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2015.7113288
Zou Z, Li J, Gao H, Zhang S (2010) Finding top-k maximal cliques in an uncertain graph. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Data Engineering, ICDE 2010, March 1-6, 2010, Long Beach, California, USA, pp. 649–652 https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2010.5447891
Li R, Dai Q, Wang G, Ming Z, Qin L, Yu JX (2019) Improved algorithms for maximal clique search in uncertain networks. In: 35th IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering, ICDE 2019, Macao, China, April 8-11, 2019, pp. 1178–1189. IEEE, New York https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2019.00108
Rashid A, Kamran M, Halim Z (2019) A top down approach to enumerate\(\alpha\)-maximal cliques in uncertain graphs. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 36(4):3129–3141. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-18263
Márquez R, Weber R (2019) Overlapping community detection in static and dynamic social networks. In: Proceedings of the Twelfth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, WSDM 2019, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, February 11-15, 2019, pp. 822–823 https://doi.org/10.1145/3289600.3291602
Xiao D, Du N, Wu B, Wang B (2007) Community ranking in social network. In: Proceeding of the Second International Multi-Symposium of Computer and Computational Sciences (IMSCCS 2007), August 13-15, 2007, The University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa, USA, pp. 322–329. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, CA, USA https://doi.org/10.1109/IMSCCS.2007.31
Meena J, Devi VS (2015) Overlapping community detection in social network using disjoint community detection. In: IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence, SSCI 2015, Cape Town, South Africa, December 7-10, 2015, pp. 764–771 https://doi.org/10.1109/SSCI.2015.114
Bai L, Cheng X, Liang J, Guo Y (2017) Fast graph clustering with a new description model for community detection. Inf Sci 388:37–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.01.026
Arab M, Afsharchi M (2014) Community detection in social networks using hybrid merging of sub-communities. J Netw Comput Appl 40:73–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2013.08.008
Newman M, EJ (2001)The structure of scientific collaboration networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Alduaiji N, Datta A, Li J (2018) Influence propagation model for clique-based community detection in social networks. IEEE Trans Comput Soc Syst 5(2):563–575. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSS.2018.2831694
Cheng J, Ke Y, Fu AW, Yu JX, Zhu L (201) Finding maximal cliques in massive networks by h*-graph. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, SIGMOD 2010, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA, June 6-10, 2010, pp. 447–458 https://doi.org/10.1145/1807167.1807217
Chen W, Wang Y, Yang S (2009) Efficient influence maximization in social networks. In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Paris, France, June 28 - July 1, 2009, pp. 199–208 https://doi.org/10.1145/1557019.1557047
Pathak N, Mane S, Srivastava J (2006) Who thinks who knows who? Socio-cognitive analysis of email networks. In: Proceedings of the 6th IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM 2006), 18-22 December 2006, Hong Kong, China, pp. 466–477 https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2006.168
Hooi B, Song HA, Beutel A, Shah N, Shin K, Faloutsos C (2016) FRAUDAR: Bounding graph fraud in the face of camouflage. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, August 13-17, 2016, pp. 895–904 https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939747
Bron C, Kerbosch J (1973) Finding all cliques of an undirected graph (algorithm 457). Commun ACM 16(9):575–576
Tomita E, Tanaka A, Takahashi H (2006) The worst-case time complexity for generating all maximal cliques and computational experiments. Theor Comput Sci 363(1):28–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2006.06.015
Eppstein D, Löffler M, Strash D (2013) Listing all maximal cliques in large sparse real-world graphs. ACM J Exp Algorithmics. https://doi.org/10.1145/2543629
Aggarwal CC (2009) Managing and Mining Uncertain Data. Advances in Database Systems, vol. 35. Kluwer, Netherlands https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-09690-2
Adar E, Ré C (2007) Managing uncertainty in social networks. IEEE Data Eng Bull 30(2):15–22
Liben-Nowell D, Kleinberg JM (2007) The link-prediction problem for social networks. J Assoc Inf Sci Technol 58(7):1019–1031. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.20591
Liben-Nowell D, Kleinberg JM (2003) The link prediction problem for social networks. In: Proceedings of the 2003 ACM CIKM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, November 2-8, 2003, pp. 556–559 https://doi.org/10.1145/956863.956972
Boldi P, Bonchi F, Gionis A, Tassa T (2012) Injecting uncertainty in graphs for identity obfuscation. Proc VLDB Endow 5(11):1376–1387
Kuter U, Golbeck J (2010) Using probabilistic confidence models for trust inference in web-based social networks. ACM Trans Internet Techn 10(2):8–1823. https://doi.org/10.1145/1754393.1754397
Mehmood Y, Bonchi F, García-Soriano D (2016) Spheres of influence for more effective viral marketing. In: Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Management of Data, SIGMOD Conference 2016, San Francisco, CA, USA, June 26 - July 01, 2016, pp. 711–726 https://doi.org/10.1145/2882903.2915250
Kawahigashi H, Terashima Y, Miyauchi N, Nakakawaji T (2005) Modeling ad hoc sensor networks using random graph theory. In: 2nd IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference, CCNC 2005, Las Vegas, NV, USA, January 3-6, pp. 104–109 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/CCNC.2005.1405152
Yang B, Wen D, Qin L, Zhang Y, Chang L, Li R (2019) Index-based optimal algorithm for computing k-cores in large uncertain graphs. In: 35th IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering, ICDE 2019, Macao, China, April 8-11, 2019, pp. 64–75. IEEE, New York https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2019.00015
Abu-khzam FN, Baldwin NE, Langston MA, Samatova NF (2005) On the relative efficiency of maximal clique enumeration algorithms, with application to high-throughput. In: Computational Biology, Proceedings, International Conference on Research Trends in Science and Technology
Koch I, Lengauer T, Wanke E (1996) An algorithm for finding maximal common subtopologies in a set of protein structures. J Comput Biol 3(2):289–306. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.1996.3.289
Saha B, Hoch A, Khuller S, Raschid L, Zhang X (2010) Dense subgraphs with restrictions and applications to gene annotation graphs. In: Research in Computational Molecular Biology, 14th Annual International Conference, RECOMB 2010, Lisbon, Portugal, April 25-28, 2010. Proceedings, pp. 456–472 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12683-3_30
Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Tong H, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N (2005) Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network. Nature 437(7062):1173–8
Wang Weidong (2007) Emergence of a dna-damage response network consisting of fanconi anaemia and brca proteins. Nat Rev Genet 8(10):735
Lu Y, Huang R, Huang D (2019) Mining highly reliable dense subgraphs from uncertain graphs. KSII Trans Internet Inf Syst 13(6):2986–2999. https://doi.org/10.3837/tiis.2019.06.012
Yuan L, Qin L, Lin X, Chang L, Zhang W (2015) Diversified top-k clique search. In: 31st IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering, ICDE 2015, Seoul, South Korea, April 13-17, 2015, pp. 387–398 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2015.7113300
Sanei-Mehri S, Das A, Tirthapura S (2018) Enumerating top-k quasi-cliques. In: IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Big Data 2018, Seattle, WA, USA, December 10-13, 2018, pp. 1107–1112 https://doi.org/10.1109/BigData.2018.8622352
Wu J, Li C, Jiang L, Zhou J, Yin M (2020) Local search for diversified top-k clique search problem. Comput Op Res 116:104867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2019.104867
Zhao-Nian Z, Rong Z (2013) Mining top-k maximal cliques from large uncertain graphs. In: 2013 Chinese Jounrnal of Computers, pp. 2146–2155. CCF
Bai J, Zhou J, Du M, Zhong P (2021) Efficient (k, \(\alpha\))-maximal-cliques enumeration over uncertain graphs. IEEE Access 9:149338–149348. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3125198
Batagelj V, Zaversnik M (2003) An o(m) algorithm for cores decomposition of networks. Comput Sci 1(6):34–37
Che Y, Lai Z, Sun S, Wang Y, Luo Q (2020) Accelerating truss decomposition on heterogeneous processors. Proc VLDB Endow 13(10):1751–1764
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (No. 20ZR1402700) and from the Natural Science Foundation of China (No.: 61472339, 61873337).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, J., Zhou, J., Du, M. et al. Index-based top k α-maximal-clique enumeration over uncertain graphs. J Supercomput 78, 19372–19400 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-022-04613-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-022-04613-1