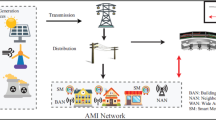
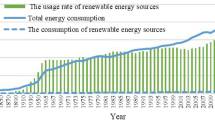
Abstract
Data aggregation is considered as the crucial aspect of the smart grid to assess the electricity consumption information which acts as a basis of management decision making for utility provider. However, smart meters are lightweight devices therefore, subject to technical crashes and deferment in forwarding their data that hinders the efficient and accurate communication of data. Consequently, the consumption data of the faulty smart meters remain uncommunicated which can affect the accuracy of the final aggregate significantly and can misguide the utility companies in the power management decisions. Therefore, considering the stated challenge, a novel AI-driven fault-tolerant aggregation model is proposed that is established on the prediction mechanism of artificial neural network. The novelty of the proposed work lies in the efficient fault-handling of unavailability of data by utilizing previous available information. Furthermore, the proposed model also provides mechanism to track the affected meters and acknowledge the utility provider. The experimental simulation and comparison results reveal the outperforming results of the proposed model from state-of-the-art works which is validated using root mean squared error and mean absolute error. Additionally, the aggregation accuracy is achieved up to 99.95% with a relative improvement of 23.92%.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The data are available upon reasonable request to the corresponding authors.
References
Singh AK, Kumar J (2023) A secure and privacy-preserving data aggregation and classification model for smart grid. Multimed Tools Appl 82:22997–23015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14599-4
Wang X, Yining L, Choo K-KR (2020) Fault-tolerant multisubset aggregation scheme for smart grid. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 17(6):4065–4072
Saxena D, Gupta I, Kumar J, Singh AK, Wen X (2021) A secure and multiobjective virtual machine placement framework for cloud data center. IEEE Syst J 16(2):3163–3174
Saxena D, Gupta I, Singh AK, Lee C-N (2022) A fault tolerant elastic resource management framework toward high availability of cloud services. IEEE Trans Netw Serv Manag 19(3):3048–3061
Saxena D, Singh AK (2022) A high availability management model based on vm significance ranking and resource estimation for cloud applications. IEEE Trans Serv Comput 16(3):1604–1615. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSC.2022.3206417
Saxena D, Singh AK (2020) Security embedded dynamic resource allocation model for cloud data centre. Electron Lett 56(20):1062–1065
Merad-Boudia OR, Senouci SM (2020) An efficient and secure multidimensional data aggregation for fog-computing-based smart grid. IEEE Internet Things J 8(8):6143–6153
Gope P, Sikdar B (2018) Lightweight and privacy-friendly spatial data aggregation for secure power supply and demand management in smart grids. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 14(6):1554–1566
Mohammadali A, Haghighi MS (2021) A privacy-preserving homomorphic scheme with multiple dimensions and fault tolerance for metering data aggregation in smart grid. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 12(6):5212–5220
Huang C et al (2021) A lightweight and fault-tolerable data aggregation scheme for privacy-friendly smart grids environment. Clust. Comput. 24(4):3495–3514
Guan Z, Si G (2017) Achieving privacy-preserving big data aggregation with fault tolerance in smart grid. Digit. Commun. Netw. 3(4):242–249
Chen Y, Yang S, Martínez J-F, López L, Yang Z (2023) A resilient group-based multi-subset data aggregation scheme for smart grid. IEEE Internet Things J
Li H, Li X, Cheng Q (2023) A fine-grained privacy protection data aggregation scheme for outsourcing smart grid. Front Comput Sci 17(3):173806
Zhang X, Tang W, Dawu G, Zhang Y, Xue J, Wang X (2022) Lightweight multidimensional encrypted data aggregation scheme with fault tolerance for fog-assisted smart grids. IEEE Syst J 16(4):6647–6657
Zuo X, Li L, Peng H, Luo S, Yang Y (2020) Privacy-preserving multidimensional data aggregation scheme without trusted authority in smart grid. IEEE Syst J 15(1):395–406
Qian J, Cao Z, Dong X, Shen J, Liu Z, Ye Y (2020) Two secure and efficient lightweight data aggregation schemes for smart grid. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 12(3):2625–2637
Gope P, Sikdar B (2019) An efficient privacy-friendly hop-by-hop data aggregation scheme for smart grids. IEEE Syst J 14(1):343–352
Chen Y, Martínez-Ortega J-F, Castillejo P, López L (2019) A homomorphic-based multiple data aggregation scheme for smart grid. IEEE Sens J 19(10):3921–3929. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2019.2895769
Bao H, Lu R (2015) A new differentially private data aggregation with fault tolerance for smart grid communications. IEEE Internet Things J 2(3):248–258
Shi Z et al (2015) Diverse grouping-based aggregation protocol with error detection for smart grid communications. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 6(6):2856–2867
Ni J et al (2017) Differentially private smart metering with fault tolerance and range-based filtering. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 8(5):2483–2493
Singh AK, Kumar J (2022) A privacy-preserving multidimensional data aggregation scheme with secure query processing for smart grid. J Supercomput 79(4):3750–3770
Shen H, Zhang M, Shen J (2017) Efficient privacy-preserving cube-data aggregation scheme for smart grids. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 12(6):1369–1381
Chen Y, Martínez-Ortega JF, López L, Yu H, Yang Z (2021) A dynamic membership group-based multiple-data aggregation scheme for smart grid. IEEE Internet Things J 8(15):12360–12374
Bao H, Rongxing L (2017) A lightweight data aggregation scheme achieving privacy preservation and data integrity with differential privacy and fault tolerance. Peer-to-Peer Netw Appl 10(1):106–121
(2011) Electricity smart metering customer behaviour trials findings report, Comm. Energy Regul., Dublin, Ireland, Technical Report CER/11/080a
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Institute of Technology, Kurukshetra, India, for financially supporting this research work.
Funding
National Institute of Technology, Kurukshetra, India, funded this research under the Institute fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors have discussed and constructed the ideas, designed the Virtual Machine Placement framework, and wrote the paper together.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest regarding the publication.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A.K., Rani, P. An AI-driven fault-tolerant aggregation model for smart grid. J Supercomput 79, 20665–20683 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-023-05461-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-023-05461-3