Abstract
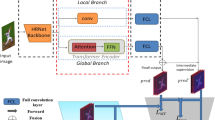
Human pose estimation has important applications in medical diagnosis (such as early diagnosis of autism in children and assisting with the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease), human-computer interaction, animation, and other fields. Currently, many human pose estimation algorithms are based on deep learning. However, most research focuses only on increasing the depth and width of the network model. This approach overlooks that merely enlarging the network’s depth and width results in excessive parameterization, without enhancing the model’s effective receptive field or its ability to extract multi-scale features. Hence, this paper constructs a network model, named MS-HRNet (Multi-Scale High-Resolution Network), for human pose estimation. Specifically, we propose a more concise and efficient version of HRNet framework as the backbone network of MS-HRNet. This addresses the challenges of HRNet complex structure and large number of parameters that cause training difficulties, and its inadequacy in handling multi-scale information. Additionally, we designed a multi-scale convolutional kernel parallel module named MSBlock (Multi-Scale Block) as the basic block of MS-HRNet. By introducing coordinate attention modules and ASFF (Adaptive Spatial Feature Fusion ) modules, the model’s ability to extract information is effectively increased, and the issue of feature conflict during the fusion of features with different resolutions is resolved, with only a small increase in the number of model parameters. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed model, we conducted comparison experiment and ablation experiments using popular human pose estimation datasets, including COCO2017 and MPII, against multiple existing human pose estimation models.On the COCO 2017 dataset, the number of MS-HRNet parameters are decreased by 41% than the baseline model HRNet, the computational complexity by 59%, and the detection accuracies(mAP) are increased by 2.4 point.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request
References
Papandreou G, Zhu T, Kanazawa N, Toshev A, Tompson J, Bregler C, Murphy K (2017) Towards Accurate Multi-person Pose Estimation in the Wild, 4903–4911
Kocabas M, Karagoz S, Akbas E (2018) Multiposenet: Fast Multi-person Pose Estimation Using Pose Residual Network, 417–433
Cao Z, Simon T, Wei S-E, Sheikh Y (2017) Realtime Multi-person 2D Pose Estimation Using Part Affinity Fields, 7291–7299
Toshev A, Szegedy C (2014) Deeppose: Human Pose Estimation via Deep Neural Networks, 1653–1660
Tompson J, Goroshin R, Jain A, LeCun Y, Bregler C (2015) Efficient Object Localization Using Convolutional Networks, 648–656
Newell A, Yang K, Deng J (2016) Stacked Hourglass Networks for Human Pose Estimation, 483–499. Springer
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, October 5-9, 2015, Proceedings, Part III 18, pp. 234–241. Springer
Noh H, Hong S, Han B (2015) Learning Deconvolution Network for Semantic Segmentation, 1520–1528
Ige AO, Tomar NK, Aranuwa FO, Oriola O, Akingbesote AO, Noor MHM, Mazzara M, Aribisala BS (2023) Convsegnet: automated polyp segmentation from colonoscopy using context feature refinement with multiple convolutional kernel sizes. IEEE Access 11:16142–16155
Xu J, Liu W, Xing W, Wei X (2023) Mspenet: multi-scale adaptive fusion and position enhancement network for human pose estimation. Vis Comput 39(5):2005–2019
Sun K, Xiao B, Liu D, Wang J (2019) Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Human Pose Estimation, 5693–5703
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition, 770–778
Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ (2017) Densely Connected Convolutional Networks, 4700–4708
Tan M, Le Q (2019) Efficientnet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks, 6105–6114. PMLR
Zhang X, Zhou X, Lin M, Sun J (2018) Shufflenet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Mobile Devices, 6848–6856
Hou Q, Zhou D, Feng J (2021) Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design, 13713–13722
Qiao Y, Guo Y, He D (2023) Cattle body detection based on YOLOv5-ASFF for precision livestock farming. Comput Electron Agric 204:107579
Dantone M, Gall J, Leistner C, Van Gool L (2013) Human Pose Estimation Using Body Parts Dependent Joint Regressors, 3041–3048
Felzenszwalb PF, Huttenlocher DP (2005) Pictorial structures for object recognition. Int J Comput Vision 61:55–79
Newell A, Yang K, Den J (2016) Stacked Hourglass Networks for Human Pose Estimation, 483–499. Springer
Ke L, Chang M-C, Qi H, Lyu S (2018) Multi-scale Structure-aware Network for Human Pose Estimation, 713–728
Chu X, Yang W, Ouyang W, Ma C, Yuille AL, Wang X (2017) Multi-context Attention for Human Pose Estimation, 1831–1840
Yue G, Li S, Cong R, Zhou T, Lei B, Wang T (2023) Attention-guided pyramid context network for polyp segmentation in colonoscopy images. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 72:1–13
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks, 7132–7141
Woo S, Park J, Lee J-Y, Kweon IS (2018) CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module, 3–19
Liu Z, Mao H, Wu C-Y, Feichtenhofer C, Darrell T, Xie S (2022) A Convnet for the 2020s, 11976–11986
Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, Hu H, Wei Y, Zhang Z, Lin S, Guo B (2021) Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer Using Shifted Windows, 10012–10022
Luo W, Li Y, Urtasun R, Zemel R (2016) Understanding the effective receptive field in deep convolutional neural networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 29
Zhu X, Cheng D, Zhang Z, Lin S, Dai J (2019) An Empirical Study of Spatial Attention Mechanisms in Deep Networks, 6688–6697
Ramachandran P, Parmar N, Vaswani A, Bello I, Levskaya A, Shlens J (2019) Stand-alone self-attention in vision models. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 32
Vaswani A, Ramachandran P, Srinivas A, Parmar N, Hechtman B, Shlens J (2021) Scaling Local Self-attention for Parameter Efficient Visual Backbones, 12894–12904
Bertasius G, Wang H, Torresani L (2021) Is space-time attention all you need for video understanding?. ICML 2(3), 4
Howard A, Zhmoginov A, Chen L-C, Sandler M, Zhu M (2018) Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks: Mobile Networks for Classification, Detection and Segmentation, 4510–4520
Chen Y, Dai X, Chen D, Liu M, Dong X, Yuan L, Liu Z (2022) Mobile-Former: Bridging Mobilenet and Transformer, 5270–5279
Howard A, Sandler M, Chu G, Chen L-C, Chen B, Tan M, Wang W, Zhu Y, Pang R, Vasudevan V et al. (2019) Searching for Mobilenetv3, 1314–1324
Lin T-Y, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, Dollár P, Zitnick CL (2014) Microsoft Coco: Common Objects in Context, 740–755. Springer
Andriluka M, Pishchulin L, Gehler P, Schiele B (2014) 2D Human Pose Estimation: New Benchmark and State of the Art Analysis, 3686–3693
Loshchilov I, Hutter F (2018) Fixing Weight Decay Regularization in Adam
Xiao B, Wu H, Wei Y (2018) Simple Baselines for Human Pose Estimation and Tracking, 466–481
Li Y, Zhang S, Wang Z, Yang S, Yang W, Xia S-T, Zhou E (2021) Tokenpose: Learning Keypoint Tokens for Human Pose Estimation, 11313–11322
Chen Y, Wang Z, Peng Y, Zhang Z, Yu G, Sun J (2018) Cascaded Pyramid Network for Multi-person Pose Estimation, 7103–7112
Xiong Z, Wang C, Li Y, Luo Y, Cao Y (2022) Swin-pose: Swin Transformer Based Human Pose Estimation, 228–233. IEEE
Li Y, Liu R, Wang X, Wang R (2023) Human pose estimation based on lightweight basicblock. Mach Vis Appl 34(1):3
Liu H, Wu J, He R (2023) Idpnet: a light-weight network and its variants for human pose estimation. J Supercomput 1–23
Acknowledgements
We thank all participants who supported our study and the reviewers for constructive suggestions on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RW was responsible for the design and implementation of the experiments and the overall writing of the manuscript. YW was responsible for the review and revision of the manuscript. HS, DL, were responsible for some of the data visualization. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wang, R., Shi, H. et al. MS-HRNet: multi-scale high-resolution network for human pose estimation. J Supercomput 80, 17269–17291 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06125-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06125-6