Abstract
Snake optimizer (SO) is an optimization algorithm drawn from the reproductive habits of serpents. It exhibits outstanding effectiveness in solving continuous optimization problems. However, SO may face some performance challenges related to its population diversity and early convergence behavior. In this paper, we address the challenges of SO by introducing the Hybrid snake optimizer algorithm (HSOA). HSOA is a novel approach to optimization that incorporates two new optimization techniques into the SO algorithm. First, it incorporates a new opposition-based learning technique called Oppositional-mutual learning into the initialization stage of the SO algorithm. Second, it integrates dynamic polynomial mutation, which is an intelligent mutation method, into the initialization and optimization stages of the SO algorithm. These integrated approaches aim to increase the population’s diversity of SO, while improving its searchability during its optimization stage. In power systems, the economic load dispatch (ELD) is an intricate optimization problem that becomes more challenging when the restrictions of the valve point effect (VPE) are incorporated into it. ELD with VPE is non-convex, lacking smoothness, and exhibiting nonlinearity that considers operational limitations expressed as both equality and inequality constraints to generate electricity. The suggested HSOA algorithm underwent evaluation and was compared with 47 renowned optimization algorithms across five real-world ELD problems with different specifications: generators with different unit capacities, transmission losses, prohibited operation zones, and Ramp Rate restrictions. The experimental results demonstrate that HSOA produces competitive solutions for the five real-world ELD problems. In detail, HSOA achieves the top rank in three cases of ELD problems with a 3-unit generator, and it secures the second and third positions in high-dimensional ELD problems with 40-unit and 80-unit generators, respectively. The statistical tests confirm the reliability and efficiency of HSOA. In addition, the effectiveness of HSOA was evaluated using the single-objective IEEE-CEC 2014 functions and compared to the results of eight popular metaheuristic algorithms. The results demonstrate that HSOA is a competitive optimization algorithm capable of solving the functions of IEEE-CEC 2014.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okwu MO, Tartibu LK (2021) Particle swarm optimisation. Stud Comput Intell 927:5–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-61111-8_2
Yang XS, Deb S (2009) "Cuckoo Search via Lévy flights," 2009 World Congress on Nature & Biologically Inspired Computing (NaBIC), Coimbatore, India, pp 210-214.
Bramer MA, Ellis R (2010) Programme chairs introduction. Res Dev Intell Syst XXVI Inc Appl Innov Intell Syst XVII. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84882-983-1
Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-pour H, Saryazdi S (2009) GSA: a gravitational search algorithm. Inf Sci (Ny) 179(13):2232–2248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2009.03.004
Mirjalili S (2019) Ant colony optimisation. Stud Comput Intell 780:33–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93025-1_3
Grefenstette JJ (1993) “Genetic algorithms and machine learning.” In: Proceedings of the Sixth Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory, pp. 3–4, https://doi.org/10.1145/168304.168305.
Karaboga D, Basturk B (2007) A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. J Glob Optim 39(3):459–471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-007-9149-x
I. Fister, I. Fister, X. -S. Yang, S. Fong and Y. Zhuang, (2014) "Bat algorithm: Recent advances," 2014 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Informatics (CINTI), Budapest, Hungary, pp 163-167. https://doi.org/10.1109/CINTI.2014.7028669.
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Grey wolf optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007
Yang XS (2009) Harmony search as a metaheuristic algorithm. Stud Comput Intell 191:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00185-7_1
R. Storn (1996) "On the usage of differential evolution for function optimization," Proceedings of North American Fuzzy Information Processing, Berkeley, CA, USA, pp. 519-523. https://doi.org/10.1109/nafips.1996.534789
Braik MS, Awadallah MA, Al-Betar MA, Hammouri AI, Zitar RA (2023) A non-convex economic load dispatch problem using chameleon swarm algorithm with roulette wheel and levy flight methods. Appl Intell. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04363-w
Al-Betar MA, Khader AT, Doush IA (2014) Memetic techniques for examination timetabling. Ann Oper Res 218(1):23–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-013-1500-7
Alkoffash MS, Awadallah MA, Alweshah M, Zitar RA, Assaleh K, Al-Betar MA (2021) A non-convex economic load dispatch using hybrid salp swarm algorithm. Arab J Sci Eng 46(9):8721–8740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05646-z
Hashim FA, Hussien AG (2022) Snake Optimizer: A novel meta-heuristic optimization algorithm. Knowl-Based Syst 242:108320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2022.108320
Xu Y et al (2021) An enhanced differential evolution algorithm with a new oppositional-mutual learning strategy. Neurocomputing 435:162–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.01.003
Hamdan M (2011) A dynamic polynomial mutation for evolutionary multi-objective optimization algorithms. Int J Artif Intell Tools 20(1):209–219. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218213011000097
Amjady N, Sharifzadeh H (2010) Solution of non-convex economic dispatch problem considering valve loading effect by a new modified differential evolution algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 32(8):893–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2010.01.023
Sinha N, Chakrabarti R, Chattopadhyay PK (2003) Brief Papers. IEEE Trans Evol Computat 7(1):83–94
Walters DC, Sheble GB (1993) Genetic algorithm solution of economic dispatch with valve point loading. IEEE Trans Power Syst 8(3):1325–1332. https://doi.org/10.1109/59.260861
Rawa M (2022) Towards avoiding cascading failures in transmission expansion planning of modern active power systems using hybrid snake-sine cosine optimization algorithm. Mathematics 10(8):1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10081323
Selvakumar AI, Thanushkodi K (2009) Optimization using civilized swarm: Solution to economic dispatch with multiple minima. Electr Power Syst Res 79(1):8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2008.05.001
Hemamalini S, Simon SP (2010) Artificial bee colony algorithm for economic load dispatch problem with non-smooth cost functions. Electr Power Compon Syst 38(7):786–803. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325000903489710
Pothiya S, Ngamroo I, Kongprawechnon W (2010) Ant colony optimisation for economic dispatch problem with non-smooth cost functions. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 32(5):478–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2009.09.016
Basu M, Chowdhury A (2013) Cuckoo search algorithm for economic dispatch. Energy 60:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.07.011
Mandal B, Roy PK, Mandal S (2014) Economic load dispatch using krill herd algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 57:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2013.11.016
Kamboj VK, Bath SK, Dhillon JS (2016) Solution of non-convex economic load dispatch problem using grey wolf optimizer. Neural Comput Appl 27(5):1301–1316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1934-8
Yu JJQ, Li VOK (2016) A social spider algorithm for solving the non-convex economic load dispatch problem. Neurocomputing 171:955–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.07.037
Abbas G et al (2017) Solution of an economic dispatch problem through particle swarm optimization : a detailed survey-part I. IEEE Access 3536:15105. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2723862
Shilaja C, Ravi K (2017) Optimization of emission/economic dispatch using euclidean affine flower pollination algorithm (eFPA) and binary FPA (BFPA) in solar photo voltaic generation. Renew Energy 107:550–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.02.021
Tripati P, Tomar U, Singh VK, Bhoi AK (2018) Solution of economic load dispatch problems through moth flame optimization algorithm. In: Bera R, Sarkar SK, Chakraborty S (eds) Advances in Communication, Devices and Networking. Springer, Singapore, pp 287–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7901-6_31
Mohammadi F, Abdi H (2018) A modified crow search algorithm (MCSA) for solving economic load dispatch problem. Appl Soft Comput J 71:51–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.06.040
Kumar M, Dhillon JS (2018) Hybrid artificial algae algorithm for economic load dispatch. Appl Soft Comput J 71:89–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.06.035
Zhu B, Xie L, Han D, Meng X, Teo R (2017) A survey on recent progress in control of swarm systems. Sci China Inf Sci 60(7):1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-016-9088-2
Barisal AK (2013) Dynamic search space squeezing strategy based intelligent algorithm solutions to economic dispatch with multiple fuels. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 45(1):50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2012.08.049
Hosseinnezhad V, Babaei E (2013) Economic load dispatch using θ-PSO. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 49(1):160–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2013.01.002
Zhisheng Z (2010) Quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization algorithm for economic load dispatch of power system. Expert Syst Appl 37(2):1800–1803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2009.07.042
Alsumait JS, Sykulski JK, Al-Othman AK (2010) A hybrid GA-PS-SQP method to solve power system valve-point economic dispatch problems. Appl Energy 87(5):1773–1781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2009.10.007
Bhattacharya A, Chattopadhyay PK (2010) Hybrid differential evolution with biogeography-based optimization for solution of economic load dispatch. IEEE Trans Power Syst 25(4):1955–1964. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2010.2043270
Aydin D, Özyön S, Yaşar C, Liao T (2014) Artificial bee colony algorithm with dynamic population size to combined economic and emission dispatch problem. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 54:144–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2013.06.020
Jiang S, Ji Z, Shen Y (2014) A novel hybrid particle swarm optimization and gravitational search algorithm for solving economic emission load dispatch problems with various practical constraints. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 55:628–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2013.10.006
Chopra N, Kumar G, Mehta S (2016) Hybrid GWO-PSO algorithm for solving convex economic load dispatch problem. Int J Res Adv Technol 4(6):37–41
Al-Betar MA, Awadallah MA, Khader AT, Bolaji AL, Almomani A (2018) Economic load dispatch problems with valve-point loading using natural updated harmony search. Neural Comput Appl 29(10):767–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2611-2
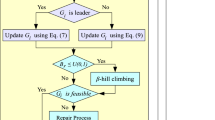
Al-Betar MA, Awadallah MA, Abu Doush I, Alsukhni E, ALkhraisat H (2018) A Non-convex economic dispatch problem with valve loading effect using a new modified β-hill climbing local search algorithm. Arab J Sci Eng 43(12):7439–7456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3098-1
Huang Z, Zhao J, Qi L, Gao Z, Duan H (2020) Comprehensive learning cuckoo search with chaos-lambda method for solving economic dispatch problems. Appl Intell 50(9):2779–2799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01654-y
Haghrah A, Nekoui MA, Nazari-Heris M, Mohammadi-ivatloo B (2021) An improved real-coded genetic algorithm with random walk based mutation for solving combined heat and power economic dispatch. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 12(8):8561–8584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02589-5
Ellahi M, Abbas G, Satrya GB, Rehan Usman M, Jason Gu (2021) A modified hybrid particle swarm optimization with bat algorithm parameter inspired acceleration coefficients for solving eco-friendly and economic dispatch problems. IEEE Access 9:82169–82187. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3085819
Al-Betar MA (2021) Island-based harmony search algorithm for non-convex economic load dispatch problems. J Electr Eng Technol 16(4):1985
Al-Betar MA, Awadallah MA, Zitar RA, Assaleh K (2022) Economic load dispatch using memetic sine cosine algorithm. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 14(9):11685–11713. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-022-03731-1
Al-Betar MA et al (2023) A hybrid Harris Hawks optimizer for economic load dispatch problems. Alexandria Eng J 64:365–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2022.09.010
H. R. Tizhoosh, (2005) "Opposition-Based Learning: A New Scheme for Machine Intelligence," In: International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Modelling, Control and Automation and International Conference on Intelligent Agents, Web Technologies and Internet Commerce (CIMCA-IAWTIC'06), Vienna, Austria, pp. 695-701 https://doi.org/10.1109/cimca.2005.1631345.
Rahnamayan S, Tizhoosh HR, Salama MMA (2008) Opposition versus randomness in soft computing techniques. Appl Soft Comput J 8(2):906–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2007.07.010
Verma S, Saha S, Mukherjee V (2018) Optimal rescheduling of real power generation for congestion management using teaching-learning-based optimization algorithm. J Electr Syst Inf Technol 5(3):889–907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesit.2016.12.008
Shaw B, Mukherjee V, Ghoshal SP (2012) A novel opposition-based gravitational search algorithm for combined economic and emission dispatch problems of power systems. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 35(1):21–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2011.08.012
Roy PK, Mandal D (2014) Oppositional biogeography-based optimisation for optimal power flow. Int J Power Energy Convers 5(1):47–69. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJPEC.2014.059983
Hamdan M (2010) On the disruption-level of polynomial mutation for evolutionary multi-objective optimisation algorithms. Comput Informatics 29(5):783–800
Abed-alguni BH (2019) Island-based cuckoo search with highly disruptive polynomial mutation. Int J Artif Intell 17(1):57–82
Alawad NA, Abed-alguni BH (2021) Discrete island-based cuckoo search with highly disruptive polynomial mutation and opposition-based learning strategy for scheduling of workflow applications in cloud environments. Arab J Sci Eng 46(4):3213–3233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05141-x
Abed-alguni BH, Alawad NA (2021) Distributed grey wolf optimizer for scheduling of workflow applications in cloud environments. Appl Soft Comput 102:107113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107113
Abed-alguni BH, Barhoush M (2018) Distributed grey wolf optimizer for numerical optimization problems. Jordan J Comput Inf Technol. https://doi.org/10.5455/jjcit.71-1532897697
Abed-Alguni BH, Paul DJ (2020) Hybridizing the cuckoo search algorithm with different mutation operators for numerical optimization problems. J Intell Syst 29(1):1043–1062. https://doi.org/10.1515/jisys-2018-0331
Saka M, Eke I, Tezcan SS, Taplamacioglu MC (2017) Analysis of economic load dispatch with a lot of constraints using vortex search algorithm. Adv Sci Technol Eng Syst 2(6):151–156. https://doi.org/10.25046/aj020619
Al-Betar MA, Awadallah MA, Krishan MM (2020) A non-convex economic load dispatch problem with valve loading effect using a hybrid grey wolf optimizer. Neural Comput Applic 32:12127–12154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04284-9
Cai J, Li Q, Li L, Peng H, Yang Y (2012) A hybrid CPSO-SQP method for economic dispatch considering the valve-point effects. Energy Convers Manag 53(1):175–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2011.08.023
Tsai MT, Gow HJ, Lin WM (2011) A novel stochastic search method for the solution of economic dispatch problems with non-convex fuel cost functions. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 33(4):1070–1076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2011.01.026
H. R. Tizhoosh, "Opposition-Based Learning: A New Scheme for Machine Intelligence," International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Modelling, Control and Automation and International Conference on Intelligent Agents, Web Technologies and Internet Commerce (CIMCA-IAWTIC'06), Vienna, Austria, 2005, pp. 695-701, https://doi.org/10.1109/CIMCA.2005.1631345
Rao RV, Savsani VJ, Vakharia DP (2011) Teaching-learning-based optimization: a novel method for constrained mechanical design optimization problems. CAD Comput Aided Des 43(3):303–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2010.12.015
Deb K, Agrawal RB (1994) Simulated binary crossover for continuous search space. Complex Syst 9:1–34
Deb K, Tiwari S (2008) Omni-optimizer: a generic evolutionary algorithm for single and multi-objective optimization. Eur J Oper Res 185(3):1062–1087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2006.06.042
Kang F, Li J, Ma Z, Li H (2011) Artificial bee colony algorithm with local search for numerical optimization. J Softw 6(3):490–497. https://doi.org/10.4304/jsw.6.3.490-497
Singh D, Dhillon JS (2019) Ameliorated grey wolf optimization for economic load dispatch problem. Energy 169:398–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.11.034
Subbaraj P, Rengaraj R, Salivahanan S (2011) Enhancement of self-adaptive real-coded genetic algorithm using taguchi method for economic dispatch problem. Appl Soft Comput J 11(1):83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2009.10.019
Bhattacharya A, Chattopadhyay PK (2010) Biogeography-based optimization for different economic load dispatch problems. IEEE Trans Power Syst 25(2):1064–1077. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2009.2034525
Subathra MSP, Easter Selvan S, Albert Victoire TA, Hepzibah Christinal A, Amato U (2015) A hybrid with cross-entropy method and sequential quadratic programming to solve economic load dispatch problem. IEEE Syst J 9(3):1031–1044. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2013.2297471
Wang L, Li LP (2013) An effective differential harmony search algorithm for the solving non-convex economic load dispatch problems. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 44(1):832–843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2012.08.021
Cai J, Li Q, Li L, Peng H, Yang Y (2012) A fuzzy adaptive chaotic ant swarm optimization for economic dispatch. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 34(1):154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2011.09.020
Jayabarathi T, Raghunathan T, Adarsh BR, Suganthan PN (2016) Economic dispatch using hybrid grey wolf optimizer. Energy 111:630–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.05.105
Niu Q, Zhang H, Wang X, Li K, Irwin GW (2014) A hybrid harmony search with arithmetic crossover operation for economic dispatch. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 62:237–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2014.04.031
Kumar R, Sharma D, Sadu A (2011) A hybrid multi-agent based particle swarm optimization algorithm for economic power dispatch. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 33(1):115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2010.06.021
Waqas AB, Saifullah Y, Ashraf MM (2021) A Hybrid quantum inspired particle swarm optimization and least square framework for real-time harmonic estimation. J Mod Power Syst Clean Energy 9(6):1548–1556. https://doi.org/10.35833/MPCE.2019.000098
Dos L, Coelho S, Mariani VC (2009) An improved harmony search algorithm for power economic load dispatch. Energy Convers Manag 50(10):2522–2526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2009.05.034
Kumar A, Singhi R, Das S, Malakar T, Prakash O, Das P (2020) "Economic Load Dispatch Using Salp Swarm Algorithm," In: 2020 IEEE 9th Power India International Conference (PIICON), Sonepat, India, pp 1-6, https://doi.org/10.1109/PIICON49524.2020.9112882.
Li X, Zhang H, Lu Z (2019) A differential evolution algorithm based on multi-population for economic dispatch problems with valve-point effects. IEEE Access 7:95585–95609. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2927574
Mohammadi-Ivatloo B, Rabiee A, Soroudi A, Ehsan M (2012) Iteration PSO with time varying acceleration coefficients for solving non-convex economic dispatch problems. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 42(1):508–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2012.04.060
Lin WM, Gow HJ, Tsai MT (2011) Combining of direct search and signal-to-noise ratio for economic dispatch optimization. Energy Convers Manag 52(1):487–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2010.07.022
Awadallah MA, Al-Betar MA, Bolaji AL, Alsukhni EM, Al-Zoubi H (2019) Natural selection methods for artificial bee colony with new versions of onlooker bee. Soft Comput 23(15):6455–6494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3299-2
Kumar S, Naresh R (2009) Nonconvex economic load dispatch using an efficient real-coded genetic algorithm. Appl Soft Comput J 9(1):321–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2008.04.009
Srinivasa Reddy A, Vaisakh K (2013) Shuffled differential evolution for economic dispatch with valve point loading effects. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 46(1):342–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2012.10.012
Coelho LDS, Mariani VC (2010) An efficient cultural self-organizing migrating strategy for economic dispatch optimization with valve-point effect. Energy Convers Manag 51(12):2580–2587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2010.05.022
Al-Betar MA, Awadallah MA, Khader AT, Bolaji ALA (2016) Tournament-based harmony search algorithm for non-convex economic load dispatch problem. Appl Soft Comput J 47:449–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.05.034
Pothiya S, Ngamroo I, Kongprawechnon W (2008) Application of multiple tabu search algorithm to solve dynamic economic dispatch considering generator constraints. Energy Convers Manag 49(4):506–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2007.08.012
Abed-alguni BH, Alawad NA, Barhoush M, Hammad R (2021) Exploratory cuckoo search for solving single-objective optimization problems. Soft Comput 25(15):10167–10180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-05939-3
Verma S, Mukherjee V (2018) Investigation of static transmission expansion planning using the symbiotic organisms search algorithm. Eng Optim 50(9):1544–1560. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2017.1408085
Abed-alguni BH, Paul D, Hammad R (2022) Improved Salp swarm algorithm for solving single-objective continuous optimization problems. Appl Intell 52(15):17217–17236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03269-x
Tanabe R, Fukunaga AS (2014) "Improving the search performance of SHADE using linear population size reduction," In: 2014 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Beijing, China, pp 1658-1665. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2014.6900380
Dhabal S, Chakrabarti R, Mishra NS, Venkateswaran P (2021) An improved image denoising technique using differential evolution-based salp swarm algorithm. Soft Comput 25(3):1941–1961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05267-y
Sun G, Xu G, Jiang N (2020) A simple differential evolution with time-varying strategy for continuous optimization. Soft Comput 24(4):2727–2747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04159-0
Iacca G, dos Santos Junior VC, Veloso de Melo V (2021) An improved jaya optimization algorithm with lévy flight. Expert Syst Appl 165:113902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113902
Erlich I, Rueda JL, Wildenhues S, Shewarega F (2014) "Evaluating the mean-variance mapping optimization on the IEEE-CEC 2014 test suite," In: 2014 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Beijing, China, pp 1625-1632, https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2014.6900516.
Pierezan J, Dos Santos Coelho L (2018) "Coyote Optimization Algorithm: A New Metaheuristic for Global Optimization Problems," In: 2018 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, pp 1–8, https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2018.8477769.
Abed-alguni BH, Alawad NA, Al-Betar MA, Paul D (2023) Opposition-based sine cosine optimizer utilizing refraction learning and variable neighborhood search for feature selection. Appl Intell 53(11):13224–13260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04201-z
Abed-alguni BH, Al-Jarah SH (2024) IBJA: An improved binary DJaya algorithm for feature selection. J Comput Sci 75:102201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2023.102201
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The first author, Noor Aldeen Alawad, primarily contributed to the manuscript by writing the original draft, handling methodology, conducting validation and verification, and performing statistical analysis. The second author, Bilal H. Abed-alguni, was involved in writing the original draft, actively reviewed and edited the manuscript, and participated in validation and verification processes. The third author, Misaa El-ibini, played a crucial role in experimentation and contributed significantly to the validation and verification of the research findings.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alawad, N.A., Abed-alguni, B.H. & El-ibini, M. Hybrid Snake Optimizer Algorithm for Solving Economic Load Dispatch Problem with Valve Point Effect. J Supercomput 80, 19274–19323 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06207-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06207-5