Abstract
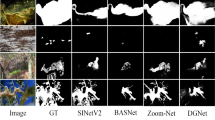
Camouflaged object detection (COD) aims to accurately segment camouflaged objects blending into the environment and is a challenging task. Most existing deep learning-based COD methods do not explicitly enhance the region information of camouflaged objects, nor do they use the region information for mask calibration. To solve this issue, we propose a novel mask stepwise calibration network (MSCNet) for camouflaged object detection, which achieves high-precision detection of camouflaged objects. Specifically, MSCNet consists of a region information enhancement encoder and a mask stepwise calibration decoder. In the encoder, we first utilize a PVT backbone network to extract different levels of features from camouflaged images. Then, we design a region information enhancement module to enhance the region information of camouflaged objects while suppressing the interference of background information by mining, embedding, and aggregating the region information in different levels of features. In the decoder, we first design a coarse mask generation module to generate coarse prediction masks of camouflaged objects by directly cross-fusing different levels of features extracted by the backbone. In addition, we also design a mask calibration module to calibrate coarse prediction masks of camouflaged objects using the region information of different levels of camouflaged objects as a guide. Extensive experimental results on four benchmark datasets show that our method effectively identifies camouflaged objects and surpasses most state-of-the-art COD methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Chen G, Liu SJ, Sun YJ et al (2022) Camouflaged object detection via context-aware cross-level fusion. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32(10):6981–6993
Chu HK, Hsu WH, Mitra NJ et al (2010) Camouflage images. ACM Trans Graph 29(4):51–1
Cong R, Sun M, Zhang S, et al (2023) Frequency perception network for camouflaged object detection. In: Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp 1179–1189
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, et al (2020) An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929
Fan DP, Cheng MM, Liu Y, et al (2017) Structure-measure: A new way to evaluate foreground maps. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 4548–4557
Fan DP, Ji GP, Sun G, et al (2020a) Camouflaged object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 2777–2787
Fan DP, Ji GP, Zhou T, et al (2020b) Pranet: Parallel reverse attention network for polyp segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Springer, pp 263–273
Fan DP, Ji GP, Cheng MM et al (2021) Concealed object detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 44(10):6024–6042
Fan DP, Ji GP, Qin X et al (2021) Cognitive vision inspired object segmentation metric and loss function. Sci Sin Inf 51:1475–1489
Han K, Xiao A, Wu E et al (2021) Transformer in transformer. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 34:15908–15919
He C, Li K, Zhang Y, et al (2023) Camouflaged object detection with feature decomposition and edge reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 22046–22055
Huang Z, Ben Y, Luo G, et al (2021) Shuffle transformer: rethinking spatial shuffle for vision transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.03650
Huang Z, Dai H, Xiang TZ, et al (2023) Feature shrinkage pyramid for camouflaged object detection with transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 5557–5566
Ji GP, Xiao G, Chou YC et al (2022) Video polyp segmentation: a deep learning perspective. Mach Intell Res 19(6):531–549
Ji GP, Zhu L, Zhuge M et al (2022) Fast camouflaged object detection via edge-based reversible re-calibration network. Pattern Recogn 123:108414
Jia Q, Yao S, Liu Y, et al (2022) Segment, magnify and reiterate: Detecting camouflaged objects the hard way. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 4713–4722
Kavitha C, Rao BP, Govardhan A (2011) An efficient content based image retrieval using color and texture of image sub blocks. Int J Eng Sci Technol (IJEST) 3(2):1060–1068
Lin CJ, Prasetyo YT (2019) A metaheuristic-based approach to optimizing color design for military camouflage using particle swarm optimization. Color Res Appl 44(5):740–748
Liu L, Wang R, Xie C et al (2019) Pestnet: an end-to-end deep learning approach for large-scale multi-class pest detection and classification. IEEE Access 7:45301–45312
Liu Y, Zhang K, Zhao Y et al (2023) Bi-rrnet: Bi-level recurrent refinement network for camouflaged object detection. Pattern Recogn 139:109514
Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, et al (2021) Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 10012–10022
Liu Z, Zhang Z, Tan Y, et al (2022) Boosting camouflaged object detection with dual-task interactive transformer. In: 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp 140–146
Luo XJ, Wang S, Wu Z, et al (2023) Camdiff: camouflage image augmentation via diffusion. CAAI Artif Intell Res 2
Lv Y, Zhang J, Dai Y, et al (2021) Simultaneously localize, segment and rank the camouflaged objects. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 11591–11601
Lv Y, Zhang J, Dai Y et al (2023) Towards deeper understanding of camouflaged object detection. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 33:3462–3476
Margolin R, Zelnik-Manor L, Tal A (2014) How to evaluate foreground maps? In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 248–255
Mei H, Ji GP, Wei Z, et al (2021) Camouflaged object segmentation with distraction mining. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 8772–8781
Pang Y, Zhao X, Xiang TZ, et al (2022) Zoom in and out: a mixed-scale triplet network for camouflaged object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 2160–2170
Pei J, Cheng T, Fan DP, et al (2022) Osformer: One-stage camouflaged instance segmentation with transformers. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp 19–37
Perazzi F, Krähenbühl P, Pritch Y, et al (2012) Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 733–740
Ren J, Hu X, Zhu L, et al (2021) Deep texture-aware features for camouflaged object detection. IEEE
Shamim S, Awan MJ, Mohd Zain A et al (2022) Automatic covid-19 lung infection segmentation through modified unet model. J Healthc Eng 1:6566982
Skurowski P, Abdulameer H, Błaszczyk J et al (2018) Animal camouflage analysis: chameleon database. Unpubl Manuscr 2(6):7
Song Z, Kang X, Wei X et al (2023) Fsnet: focus scanning network for camouflaged object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 32:2267–2278
Sun D, Jiang S, Qi L (2023) Edge-aware mirror network for camouflaged object detection. In: 2023 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), IEEE, pp 2465–2470
Sun Y, Chen G, Zhou T, et al (2021) Context-aware cross-level fusion network for camouflaged object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.12555
Tankus A, Yeshurun Y (2001) Convexity-based visual camouflage breaking. Comput Vis Image Underst 82(3):208–237
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al (2017) Attention is all you need. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 30
Wang W, Xie E, Li X et al (2022) Pvt v2: improved baselines with pyramid vision transformer. Comput Vis Media 8(3):415–424
Wei J, Wang S, Huang Q (2020) F\(^3\)net: fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 12321–12328
Wu J, Liang W, Hao F et al (2023) Mask-and-edge co-guided separable network for camouflaged object detection. IEEE Signal Process Lett 30:748–752
Xing H, Wang Y, Wei X et al (2023) Go closer to see better: camouflaged object detection via object area amplification and figure-ground conversion. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 33:5444–5457
Xu X, Zhu M, Yu J et al (2021) Boundary guidance network for camouflage object detection. Image Vis Comput 114:104283
Zhai Q, Li X, Yang F, et al (2021) Mutual graph learning for camouflaged object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 12997–13007
Zhang Q, Ge Y, Zhang C et al (2023) Tprnet: camouflaged object detection via transformer-induced progressive refinement network. Vis Comput 39(10):4593–4607
Zhang Q, Sun X, Chen Y et al (2023) Attention-induced semantic and boundary interaction network for camouflaged object detection. Comput Vis Image Underst 233:103719
Zhao W, Xie S, Zhao F et al (2023) Nowhere to disguise: spot camouflaged objects via saliency attribute transfer. IEEE Trans Image Process 32:3108–3120
Zhong Y, Li B, Tang L, et al (2022) Detecting camouflaged object in frequency domain. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 4504–4513
Zhou T, Zhou Y, Gong C et al (2022) Feature aggregation and propagation network for camouflaged object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 31:7036–7047
Zhuge M, Lu X, Guo Y, et al (2022) Cubenet: X-shape connection for camouflaged object detection. Pattern Recognit 127:108644
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by the Science and Technology Development Plan Project of Henan Province, China (No. 222102110135).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HD wrote the main manuscript text. MZ provided some suggestions for revision of the manuscript. WZ suggested the structure of the manuscript. KQ gave some help to the typesetting of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, H., Zhang, M., Zhang, W. et al. Mscnet: Mask stepwise calibration network for camouflaged object detection. J Supercomput 80, 24718–24737 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06376-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06376-3