Abstract
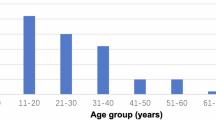
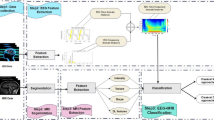
Interictal epileptiform discharges (IEDs) play a crucial role in the diagnosis and assessment of seizure risk in epilepsy. Their frequency, amplitude, and morphological characteristics serve as consistent markers of epileptogenesis. Currently, the clinical evaluation of IEDs heavily relies on visual detection by specialized experts, which is a subjective and time-consuming task. To address this, there is a need for an automated IEDs detection system that can provide faster and more reliable epilepsy diagnosis. In this paper, we propose a novel method for automatic identification of IEDs by inspecting the fulfillment of specific criteria. The decisions made by our method were compared with the combined decisions of three neurologists, serving as a benchmark for evaluation. The results and performance metrics obtained from this comparison demonstrate the effectiveness and potential of our automated IEDs identification method.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The EEG data are available online. The interictal epileptiform discharges annotations are kept confidential.
References
Benbadis SR, Tatum WO (2003) Overintepretation of EEGs and misdiagnosis of epilepsy. J Clin Neurophysiol 20:42–44
Benbadis SR (2007) Errors in EEGs and the misdiagnosis of epilepsy: importance, causes, consequences, and proposed remedies. Epilepsy Behav 11:257–262
Benbadis SR, Lin K (2008) Errors in EEG interpretation and misdiagnosis of epilepsy. Which EEG patterns are overread? Eur Neurol 59:267–71
Gaspard N, Alkawadri R, Farooque P, Goncharova II, Zaveri HP (2014) Automatic detection of prominent interictal spikes in intracranial EEG: Validation of an algorithm and relationsip to the seizure onset zone. Clin Neurophysiol 125(6):1095–1103
Noachtar S, Binnie C, Ebersole J, Maguière F, Sakamoto A, Westmoreland B (1999) A glossary of terms most commonly used by clinical electroencephalographers and proposal for the report for the EEG findings. Electroencephal Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 52:21–41
Dingle AA, Jones RD, Carroll GJ, Fright WR (1993) A multistage system to detect epileptiform activity in the EEG. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 40(12):1260–1268. https://doi.org/10.1109/10.250582
Zacharaki EI, Mporas I, Garganis K et al (2016) Spike pattern recognition by supervised classification in low dimensional embedding space. Brain Inf 3:73–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40708-016-0044-4
Chavakula V, Fernández IS, Peters JM, Popli G, Bosl W, Rakhade S, Rotenberg A, Loddenkemper T (2013) Automated quantification of spikes. Epilepsy Behav 26(2):P143-152
Wei B, Zhao X, Shi L, Xu L, Liu T, Zhang J (2021) A deep learning framework with multi-perspective fusion for interictal epileptiform discharges detection in scalp electroencephalogram. J Neural Eng 18(4):0460b3
Lourenço C, Tjepkema-Cloostermans MC, Teixeira LF, van Putten MJAM (2020) Deep learning for interictal epileptiform discharge detection from scalp EEG recordings. In: Henriques J., Neves N., de Carvalho P. (eds) XV Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing – MEDICON 2019. MEDICON 2019. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 76. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-31635-8_237.
Thomas J, Jin J, Thangavel P, Bagheri E, Yuvaraj R, Dauwels J, Rathakrishnan R, Halford JJ, Cash SS, Westover B (2020) Automated detection of interictal epileptiform discharges from scalp electroencephalograms by convolutional neural networks. Int J Neural Syst 30(11):2050030
da Silva Lourenço C, Tjepkema-Cloostermans MC, van Putten MJ (2021) Machine learning for detection of interictal epileptiform discharges. Clin Neurophysiol 132(7):1433–1443
Laboy-Juárez KJ, Ahn S, Feldman DE (2019) A normalized template matching method for improving spike detection in extracellular voltage recordings. Sci Rep 9:12087. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-48456-y
Kural MA, Duez L, Hansen VS, Larsson PG, Rampp S, Schulz R, Tankisi H, Wennberg R, Bibby BM, Scherg M, Beniczky S (2020) Criteria for defining interictal epileptiform discharges in EEG A clinical validation study. Neurology 94:e2139–e2147. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000009439
Kane N, Acharya J, Beniczky S, Caboclo L, Finnigan S, Kaplan PW, Shibasaki H, Pressler R, van Putten MJAM (2017) A revised glossary of terms most commonly used by clinical electroencephalographers and updated proposal for the report format of the EEG findings. Revision 2017. Clin Neurophysiol Pract 2:170–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnp.2017.07.002
Kural MA, Tankisi H, Duez L, Hansen VS, Udupi A, Wennberg R, Rampp S, Larsson PG, Schulz R, Beniczky S (2020) Optimized set of criteria for defining interictal epileptiform EEG discharges. Clin Neurophysiol 131(9):2250–2254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2020.06.026
Jabran Y, Mahmoudzadeh M, Martinez N, Heberlé C, Wallois F, Bourel-Ponchel E (2020) Temporal and spatial dynamics of different interictal epileptic discharges: a time-frequency EEG approach in pediatric focal refractory epilepsy. Front Neurol 11:941
Kane N, Acharya J, Beniczky S, Caboclo L, Finnigan S, Kaplan PW, Shibasaki H, Pressler R, Putten van MJAM (2017) A revised glossary of terms most commonly used by clinical electroencephalographers and updated proposal for the report format of the EEG findings. Revision 2017. Clinical Neurophysiology Practice 2 170–185.
Selvitelli MF, Walker LM, Schomer DL, Chang BS (2010) The relationship of interictal epileptiform discharges to clinical epilepsy severity: a study of routine EEGs and review of the literature. J Clin Neurophysiol 27(2):87–92
Janszky J, Hoppe M, Clemens Z, Janszky I, Gyimesi C, Schulz R, Ebner A (2005) Spike frequency is dependent on epilepsy duration and seizure frequency in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epileptic Disord 7(4):355–9
Asadollahi M, Noorbakhsh M, Salehifar V, Simani L (2021) The significance of interictal spike frequency in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 116:107730
Bisht A, Singh P (2021) Detection of muscle artifact epochs using entropy based M-DDTW technique in EEG signals. Biomed Signal Process Control 68:102653
Aung ST, Wongsawat Y (2021) Analysis of EEG signals contaminated with motion artifacts using multiscale modified-distribution entropy. IEEE Access 9:33911–33921
Zhang Ling, Wang Xiaolu, Jiang Jun, Xiao Naian, Guo Jiayang, Zhuang Kailong, Li Ling, Houqiang Yu, Tong Wu, Zheng Ming, Chen Duo (2023) Automatic interictal epileptiform discharge (IED) detection based on convolutional neural network (CNN). Front Mol Biosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2023.1146606
Hao Y, Khoo HM, von Ellenrieder N, Zazubovits N, Gotmana J (2018) DeepIED: an epileptic discharge detector for EEG-fMRI based on deep learning Neuroimage. Clinical 17:962–975
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through Research Groups Program under grant number (RGP2/166/44). Authors would like to thank the clinical partners for their cooperation.
Funding
King Khalid University, RGP2/166/44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
—O. Trigui and S. Dewid contributed by the design of the processing method, examination of results, and manuscript writing. —S. Dewid, M. Dammak, and C. Mhiri contributed by the annotation of the database. —M. Ghorbel, M. Dammak, C. Mhiri, and A. Ben Hamida contributed equally by the supervision of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Ahmed Ben Hamida reports that financial support was provided by King Khaled Universiy.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Trigui, O., Daoud, S., Ghorbel, M. et al. Automated identification and localization of interictal epileptiform discharges: leveraging morphological analysis, five-criterion fulfillment, and machine learning approach. J Supercomput 81, 1 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06558-z
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06558-z