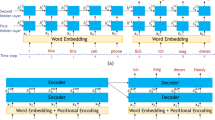
Abstract
The surge in automation driven by IoT devices has generated extensive time-series data with highly variable features, posing challenges in anomaly detection. DL, particularly Transformer networks, has shown promise in addressing these issues. However, Transformer networks struggle with accurately determining the position of data points and maintaining the order of data in sequences, leading to the development of Positional Encoding (PE). Initially, Absolute PE was introduced, but newer methods like Relative PE and Rotary PE have been adopted in natural language processing tasks to improve performance. This study evaluates the potential of PEs including Absolute PE, Rotary PE, and two modifications of Relative PE methods (Representative attention and Global attention), for multivariate time-series anomaly detection problems. The experimental results indicate that Absolute PE, with a 98% accuracy score, performs well across different window sizes. Representative attention, with a 98% F1-score, performs best for short sequences (8, 16, and 32); whereas, Global attention, with a 97% F1-score, is more effective for longer sequences (64 and 128). Additionally, Absolute PE has the shortest training times, starting at 25 for sequence length 8 and increasing to 192 for length 128. Rotary PE also has slightly longer training times compared to Absolute PE. On the other hand, Representative attention consistently has the longest times, starting at 48 for length 8 and reaching 366 for length 128. Overall, Absolute PE and Global attention are the most time-efficient; while, Representative attention has significantly higher training times, particularly for long sequences.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Fantin Irudaya Raj E, Appadurai M, Chithamabara Thanu M, Francy Irudaya Rani E (2023) IoT-based smart parking system for Indian smart cities, Chapter 15. Wiley
Laghari AA, Wu K, Laghari RA, Ali M, Khan AA (2022) Retracted article: a review and state of art of internet of things (IoT). Arch Comput Methods Eng 29:1395–1413
Gopinath A, Sivakumar S, Ranjani D, Kumari S, Perumal V, Prakash RB (2023) A communication system built on the internet of things for fully autonomous electric cars. In: 2023 7th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS). pp 1515–1520
Mayer-Schönberger V, Cukier K (2013) Big data: a revolution that will transform how we live, work, and think. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. An Eamon Dolan book, Business book summary
Shickel B, Rashidi P (2020) Sequential interpretability: methods, applications, and future direction for understanding deep learning models in the context of sequential data. Preprint at arXiv:2004.12524
Cochrane JH (2005) Time series for macroeconomics and finance. Technical report, Graduate School of Business, University of Chicago, 5807 S. Woodlawn, Chicago, p 60637, 1997. Spring 1997; Pictures added Jan
Luo M (2023) Machine learning for time series analysis and forecasting. Master’s thesis, Northeastern University, Boston. Accepted: April 2023, Awarded: May
Chandola V, Banerjee A, Kumar V (2009) Anomaly detection: a survey. ACM Comput Surv 41(3)
Teng M (2010) Anomaly detection on time series. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Progress in Informatics and Computing, vol 1, pp 603–608
Baidya R, Jeong H (2023) Anomaly detection in time series data using reversible instance normalized anomaly transformer. Sensors 23(22):9272
Edgeworth FY (1997) Xli. on discordant observations. London Edinburgh Dublin Philos Mag J Sci 23(143):364–375
Cook AA, Misirli Göksel G, Fan Z (2020) Anomaly detection for IoT time-series data: a survey. IEEE Internet Things J 7(7):6481–6494
Ringberg H, Soule A, Rexford J, Diot C (2007) Sensitivity of PCA for traffic anomaly detection. SIGMETRICS Perform Eval Rev 35(1):109–120
Tianqi Yu, Wang Xianbin, Shami Abdallah (2017) Recursive principal component analysis-based data outlier detection and sensor data aggregation in IoT systems. IEEE Internet Things J 4(6):2207–2216
Liu FT, Ting KM, Zhou ZH (2008) Isolation forest. In: 2008 eighth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, pp 413–422
Bay SD, Schwabacher M (2003) Mining distance-based outliers in near linear time with randomization and a simple pruning rule. In: Proceedings of the Ninth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD ’03, Association for Computing Machinery, New York, pp 29–38
Shi T, Horvath S (2006) Unsupervised learning with random forest predictors. J Comput Graph Stat 15(1):118–138
Singh A (2017) Anomaly detection for temporal data using long short-term memory (LSTM). Master’s thesis, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH). Award Date: 31 August 2017
Tang C, Xu L, Yang B, Tang Y, Zhao D (2023) Gru-based interpretable multivariate time series anomaly detection in industrial control system. Comput Secur 127:103094
Li D, Chen D, Jin B, Shi L, Goh J, Ng SK (2019) Mad-gan: Multivariate anomaly detection for time series data with generative adversarial networks. In: Tetko I, Kurková V, Karpov P, Theis F (eds) Artificial neural networks and machine learning—ICANN 2019: text and time series, volume 11730 of lecture notes in computer science. Springer, Cham
Park D, Hoshi Y, Kemp CC (2018) A multimodal anomaly detector for robot-assisted feeding using an LSTM-based variational autoencoder. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 3(3):1544–1551
Çavdar T, Ebrahimpour N, Kakız Muhammet T, Günay FB (2023) Decision-making for the anomalies in IIoTs based on 1D convolutional neural networks and Dempster–Shafer theory (DS-1DCNN). J Supercomput 79(2):1683–1704
Abbas S, Alsubai S, Ojo S, Sampedro GA, Almadhor A, Hejaili AA, Bouazzi I (2024) An efficient deep recurrent neural network for detection of cyberattacks in realistic IoT environment. J Supercomput 1–19
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser Ł, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS’17, Curran Associates Inc, Red Hook, pp 6000–6010
Devlin J, Chang M-W, Lee K, Toutanova K (2019) Bert: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: North American chapter of the association for computational linguistics
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X, Unterthiner T, Dehghani M, Minderer M, Heigold G, Gelly S, Uszkoreit J, Houlsby N (2020) An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. CoRR arXiv:2010.11929
Dong L, Xu S, Xu B (2018) Speech-transformer: a no-recurrence sequence-to-sequence model for speech recognition. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp 5884–5888
Shaw P, Uszkoreit J, Vaswani A (2018) Self-attention with relative position representations. CoRR arXiv:1803.02155
Huang CZ, Vaswani A, Uszkoreit J, Shazeer N, Hawthorne C, Dai AM, Hoffman MD, Eck D (2018) An improved relative self-attention mechanism for transformer with application to music generation. CoRR arXiv:1809.04281
Su J, Lu Y, Pan S, Wen B, Liu Y (2021) Roformer: enhanced transformer with rotary position embedding. CoRR arXiv:2104.09864
Meng H, Zhang Y, Li Y, Zhao H (2020) Spacecraft anomaly detection via transformer reconstruction error. In: Jing Z (ed) Proceedings of the International Conference on Aerospace System Science and Engineering 2019. ICASSE 2019, volume 622 of Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, Springer, Singapore
Zhang H, Xia Y, Yan T, Liu G (2021) Unsupervised anomaly detection in multivariate time series through transformer-based variational autoencoder. In: 2021 33rd Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC). pp 281–286
Xu J, Wu H, Wang J, Long M (2021) Anomaly transformer: time series anomaly detection with association discrepancy. CoRR arXiv:2110.02642
Chen Z, Chen D, Zhang X, Yuan Z, Cheng X (2022) Learning graph structures with transformer for multivariate time-series anomaly detection in IoT. IEEE Internet Things J 9(12):9179–9189
Tuli S, Casale G, Jennings NR (2022) Tranad: deep transformer networks for anomaly detection in multivariate time series data. Proc VLDB Endow 15(6):1201–1214
Zhang S, Liu Y, Zhang X, Cheng W, Chen H, Xiong H (2022) Cat: beyond efficient transformer for content-aware anomaly detection in event sequences. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD ’22. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, pp 4541–4550
Ding C, Zhao J, Sun S (2023) Concept drift adaptation for time series anomaly detection via transformer. Neural Process Lett 55(6):2081–2101
Li Y, Peng X, Zhang J, Li Z, Wen M (2023) DCT-GAN: dilated convolutional transformer-based GAN for time series anomaly detection. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 35(4):3632–3644
Song J, Kim K, Oh J, Cho S (2023) MEMTO: memory-guided transformer for multivariate time series anomaly detection. In: Thirty-Seventh Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems
Kim J, Kang H, Kang P (2023) Time-series anomaly detection with stacked transformer representations and 1d convolutional network. Eng Appl Artif Intell 120:105964
Shin A-H, Kim ST, Park G-M (2023) Time series anomaly detection using transformer-based GAN with two-step masking. IEEE Access 11:74035–74047
Wang X, Pi D, Zhang X, Liu H, Guo C (2022) Variational transformer-based anomaly detection approach for multivariate time series. Measurement 191:110791
Foumani NM, Tan CW, Webb GI, Salehi M (2024) Improving position encoding of transformers for multivariate time series classification. Data Min Knowl Discov 38:22–48
Ba JL, Kiros JR, Hinton GE (2016) Layer normalization
Chen P-C, Tsai H, Bhojanapalli S, Chung HW, Chang Y-W, Ferng C-S (2021) Demystifying the better performance of position encoding variants for transformer. CoRR arXiv:2104.08698
Shin H-K, Lee W, Yun J-H, Min B-G (2021) Two ics security datasets and anomaly detection contest on the hil-based augmented ics testbed. In: Proceedings of the 14th Cyber Security Experimentation and Test Workshop. pp 36–40
Akiba T, Sano S, Yanase T, Ohta T, Koyama M (2019) Optuna: A next-generation hyperparameter optimization framework. CoRR arXiv:1907.10902
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Methodology and writing—reviewing contributed by Abdul Amir Alioghli and Feyza Yıldırım Okay; editing and supervision contributed by Feyza Yıldırım Okay; conceptualization, software and visualization contributed by Abdul Amir Alioghli. All authors have read and legally accepted the final version of the article published in the journal.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no Conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alioghli, A.A., Yıldırım Okay, F. Enhancing multivariate time-series anomaly detection with positional encoding mechanisms in transformers. J Supercomput 81, 282 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06694-6
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06694-6