Abstract
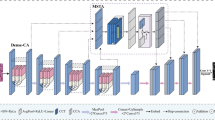
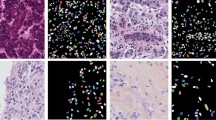
The intricacy of segmentation is intensified by the morphological variability of cell nuclei. While, the U-Net model can achieve commendable outcomes in such contexts, it encounters difficulties, including semantic inconsistencies between the encoder and decoder, as well as an excessive number of parameters. To tackle these challenges, this study presents a lightweight multi-scale attention fusion (MAF) module intended to supplant conventional skip connections, with the goal of alleviating semantic discrepancies arising from multi-level downsampling and upsampling processes. Specifically, we establish multi-scale skip connections utilizing various attention mechanisms to enhance the flow of information. Furthermore, we introduce a deformable attention Condense (DACond) module designed to replace convolution operations, thereby reducing the overall parameter count and enhancing ability to learn the shape of the nucleus. The proposed model is designated as Lightweight Multi-scale Attention Fusion UNet (LMAF-UNet). Our LMAF-UNet exhibits enhanced segmentation performance across four publicly available datasets, while concurrently minimizing parameter size and computational complexity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not required.
References
Schreiber B, Denholm J, Jaeckle F, Arends MJ, Branson K, Schönlieb C-B, Soilleux E (2024) Rapid artefact removal and h &e-stained tissue segmentation. Sci Rep 14(1):309
Dong N, Feng Q, Chang J, Mai X (2024) White blood cell classification based on a novel ensemble convolutional neural network framework. J Supercomput 80(1):249–270
Burçak KC, Baykan ÖK, Uguz H (2021) A new deep convolutional neural network model for classifying breast cancer histopathological images and the hyperparameter optimisation of the proposed model. J Supercomput 77(1):973–989
Mahbod A, Schaefer G, Bancher B, Löw C, Dorffner G, Ecker R, Ellinger I (2021) Cryonuseg: a dataset for nuclei instance segmentation of cryosectioned h &e-stained histological images. Comput Biol Med 132:104349
Otsu N (1979) A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans Syst, Man, Cybern 9(1):62–66
Zhang W, Wang Z (2024) An approach of separating the overlapped cells or nuclei based on the outer canny edges and morphological erosion. Cytom Part A 105(4):266–275
Phillip JM, Han K-S, Chen W-C, Wirtz D, Wu P-H (2021) A robust unsupervised machine-learning method to quantify the morphological heterogeneity of cells and nuclei. Nat protoc 16(2):754–774
Kumar N, Verma R, Sharma S, Bhargava S, Vahadane A, Sethi A (2017) A dataset and a technique for generalized nuclear segmentation for computational pathology. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 36(7):1550–1560
Song Y, Tan E, Jiang X, Cheng J, Ni D, Chen S, Lei B, Wang T (2016) Accurate cervical cell segmentation from overlapping clumps in pap smear images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 36(1):288–300
Vuola AO, Akram SU, Kannala J (2019) Mask-Rcnn and U-Net Ensembled for Nuclei Segmentation. In: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp. 208–212
Alemi Koohbanani N, Jahanifar M, Gooya A, Rajpoot N (2019) Nuclear Instance Segmentation Using a Proposal-Free Spatially Aware Deep Learning Framework. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), pp. 622–630
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), pp. 234–241
Lin J, Liao X, Yu L, Pan J (2020) Res-unet based optic disk segmentation in retinal image. J Comput 31(3):183–194
Cao Y, Liu S, Peng Y, Li J (2020) Denseunet: densely connected unet for electron microscopy image segmentation. IET Image Process 14(12):2682–2689
Jha D, Riegler MA, Johansen D, Halvorsen P, Johansen HD (2020) Doubleu-Net: A Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Medical Image Segmentation. In: IEEE International Symposium on Computer-based Medical Systems (CBMS), pp. 558–564
Xu Q, Ma Z, Na H, Duan W (2023) Dcsau-net: a deeper and more compact split-attention u-net for medical image segmentation. Comput Biol Med 154:106626
Cao H, Wang Y, Chen J, Jiang D, Zhang X, Tian Q, Wang M (2022) Swin-Unet: Unet-Like Pure Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 205–218
Chen J, Lu Y, Yu Q, Luo X, Adeli E, Wang Y, Lu L, Yuille AL, Zhou Y (2021) TransUNet: Transformers Make Strong Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation
Xu G, Zhang X, He X, Wu X (2023) Levit-unet: Make Faster Encoders with Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation. In: Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision (PRCV), pp. 42–53
Zhou Z, Siddiquee MMR, Tajbakhsh N, Liang J (2019) Unet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(6):1856–1867
Wang H, Cao P, Wang J, Zaiane OR (2022) Uctransnet: Rethinking the Skip Connections in U-Net from a Channel-Wise Perspective with Transformer. In: AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 2441–2449
Ruan J, Xie M, Gao J, Liu T, Fu Y (2023) Ege-Unet: an Efficient Group Enhanced Unet for Skin Lesion Segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), pp. 481–490
Zhu W, Chen X, Qiu P, Farazi M, Sotiras A, Razi A, Wang Y (2024) Selfreg-Unet: Self-Regularized Unet for Medical Image Segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), pp. 601–611
Wang H, Cao P, Yang J, Zaïane OR (2024) Narrowing the semantic gaps in u-net with learnable skip connections: the case of medical image segmentation. Neural Net 178:106546
Garcia-Lamont F, Lopez-Chau A, Cervantes J, Ruiz S (2024) Nucleus Segmentation of white Blood Cells in Blood Smear Images By Modeling the Pixel’s Intensities as a Set of Three Gaussian Distributions. Med Biol Eng Comput, 1–18
Zhang L, Sonka M, Lu L, Summers RM, Yao J (2017) Combining Fully Convolutional Networks and Graph-Based Approach for Automated Segmentation of Cervical Cell Nuclei. In: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp. 406–409
Qian Z, Wang Z, Zhang X, Wei B, Lai M, Shou J, Fan Y, Xu Y (2024) Msnsegnet: attention-based multi-shape nuclei instance segmentation in histopathology images. Med Biol Eng Computing 62:1821–1836
Xu C, Zhang Y, Fan X, Lan X, Ye X, Wu T (2022) An efficient fluorescence in situ hybridization (fish)-based circulating genetically abnormal cells (cacs) identification method based on multi-scale mobilenet-yolo-v4. Quant Imaging Med Surge 12(5):2961
Li Z, Li Y, Li Q, Wang P, Guo D, Lu L, Jin D, Zhang Y, Hong Q (2024) Lvit: language meets vision transformer in medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 43(1):96–107
Alom MZ, Yakopcic C, Hasan M, Taha TM, Asari VK (2019) Recurrent residual u-net for medical image segmentation. J Med Imaging 6(1):014006
Li Y, Wang S, Wang J, Zeng G, Liu W, Zhang Q, Jin Q, Wang Y (2021) Gt U-Net: A U-Net Like Group Transformer Network for Tooth Root Segmentation. In: International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, pp. 386–395
Huang H, Lin L, Tong R, Hu H, Zhang Q, Iwamoto Y, Han X, Chen Y-W, Wu J (2020) Unet 3+: A full-Scale Connected Unet for Medical Image Segmentation. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 1055–1059
Oktay O, Schlemper J, Folgoc LL, Lee M, Heinrich M, Misawa K, Mori K, McDonagh S, Hammerla NY, Kainz B, et al. (2018) Attention U-Net: Learning Where to Look for the Pancreas. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999
Ibtehaz N, Rahman MS (2020) Multiresunet: rethinking the u-net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural net 121:74–87
Xiao B, Pan Y, Zhang X (2023) Da-unet: Deformable Attention U-Net for Nucleus Segmentation. In: International Conference on Computer, Vision and Intelligent Technology (ICCVIT), pp. 1–5
Huang G, Liu S, Maaten L, Weinberger KQ (2018) Condensenet: An Efficient Densenet Using Learned Group Convolutions. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2752–2761
Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi SA (2016) V-net: Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation. In: International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), pp. 565–571
Kumar N, Verma R, Anand D, Zhou Y, Onder OF, Tsougenis E, Chen H, Heng P, Li J, Hu Z, Wang Y, Koohbanani NA, Jahanifar M, Tajeddin NZ, Gooya A, Rajpoot NM, Ren X, Zhou S, Wang Q, Shen D, Yang C, Weng C, Yu W, Yeh C, Yang S, Xu S, Yeung P, Sun P, Mahbod A, Schaefer G, Ellinger I, Ecker R, Smedby Ö, Wang C, Chidester B, Ton T, Tran M, Ma J, Do MN, Graham S, Vu QD, Kwak JT, Gunda A, Chunduri R, Hu C, Zhou X, Lotfi D, Safdari R, Kascenas A, O’Neil A, Eschweiler D, Stegmaier J, Cui Y, Yin B, Chen K, Tian X, Grüning P, Barth E, Arbel E, Remer I, Ben-Dor A, Sirazitdinova E, Kohl M, Braunewell S, Li Y, Xie X, Shen L, Ma J, Baksi KD, Khan MA, Choo J, Colomer A, Naranjo V, Pei L, Iftekharuddin KM, Roy K, Bhattacharjee D, Pedraza A, Bueno MG, Devanathan S, Radhakrishnan S, Koduganty P, Wu Z, Cai G, Liu X, Wang Y, Sethi A (2020) A multi-organ nucleus segmentation challenge. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(5):1380–1391
Gupta A, Gehlot S, Goswami S, Motwani S, Gupta R, Faura AG, Štepec D, Martinčič T, Azad R, Merhof D et al (2023) Segpc-2021: a challenge & dataset on segmentation of multiple myeloma plasma cells from microscopic images. Med Image Anal 83:102677
Isensee F, Jaeger PF, Kohl SA, Petersen J, Maier-Hein KH (2021) nnu-net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat Methods 18(2):203–211
Zhou Y, Zhou H, Yang Y, Li J, Irampaye R, Wang D, Zhang Z (2024) Lunet: an enhanced upsampling fusion network with efficient self-attention for semantic segmentation. Vis Comput Accept pap. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-024-03590-1
Pham T, Li X, Nguyen K (2024) Seunet-trans: a simple yet effective unet-transformer model for medical image segmentation. IEEE Access 12:122139–122154
Zhu C, Cheng K, Hua X (2024) A medical image segmentation network with multi-scale and dual-branch attention. Appl Sci 14(14):6299
Rahman MM, Munir M, Marculescu R (2024) Emcad: Efficient Multi-Scale Convolutional Attention Decoding for Medical Image Segmentation. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 11769–11779
Funding
This work is supported by the Natural Science Starting Project of SWPU (No. 2022QHZ023, 2022QHZ013), the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (No.2024YFHZ0022), the Sichuan Scientific Innovation Fund (No. 2022JDRC0009), the Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology Project (No. 2022NSFSC0283), the Key Research and Development Project of Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology (No.2023YFG0129). In addition, we also thank the High-Performance Computing Center, Southwest Petroleum University for its support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.Z., J.X., and D.H. conceived of the idea and developed the proposed approaches. K.W. helped edit the paper. L.W. improved the quality of the manuscript and the completed revision. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential Conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Ethics approval
Not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Xu, J., He, D. et al. Lightweight multi-scale attention group fusion structure for nuclei segmentation. J Supercomput 81, 199 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06710-9
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06710-9