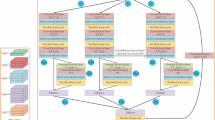
Abstract
Plaque segmentation in ultrasound images is essential for diagnosing carotid artery diseases but is hindered by challenges like noise, low contrast, and irregular plaque shapes. This paper proposes DPSMUNet, an enhanced UNet-based deep neural network incorporating a Dual Pooling Self-Attention Module (DPSM) and a Depthwise Separable Feedforward Network (DSFN). DPSM enables multi-scale global self-attention, while DSFN fuses semantic information across layers. Our experimental results, conducted on our carotid ultrasound image dataset as well as publicly available datasets (breast ultrasound image dataset and nerve ultrasound image dataset), demonstrate that DPSMUNet achieves strong performance across all metrics (DSC, IoU, recall, precision, parameter count, and inference time), with DSC, IoU, and recall being the most optimized. These findings suggest that DPSMUNet effectively segments plaque boundaries in carotid ultrasound images with relatively low computational complexity.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics (2024) National Vital Statistics System, Mortality 2018-2022 on CDC WONDER Online Database. http://wonder.cdc.gov/ucd-icd10-expanded.html. Accessed on Sep 2, 2024 9:23:52 AM
Gujjar AR (2018) Diabetes and stroke: More than just accelerated atherosclerosis? Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J 18(3):261
Zarins CK, Xu C, Glagov S (2001) Atherosclerotic enlargement of the human abdominal aorta. Atherosclerosis 155(1):157–164
Qian C, Yang X (2018) An integrated method for atherosclerotic carotid plaque segmentation in ultrasound image. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 153:19–32
Gao P, Chen Z-Q, Bao Y-H, Jiao L-Q, Ling F (2007) Correlation between carotid intraplaque hemorrhage and clinical symptoms: systematic review of observational studies. Stroke 38(8):2382–2390
Jiao Y, Qin Y, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Liu H, Li C (2020) Early identification of carotid vulnerable plaque in asymptomatic patients. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 20:1–10
Polak JF (2001) Carotid ultrasound. Radiol Clin North Am 39(3):569–589
Pignoli P, Longo T (1988) Evaluation of atherosclerosis with b-mode ultrasound imaging. J Nucl Med Allied Sci 32(3):166–173
Faita F, Gemignani V, Bianchini E, Giannarelli C, Ghiadoni L, Demi M (2008) Real-time measurement system for evaluation of the carotid intima-media thickness with a robust edge operator. J Ultrasound Med 27(9):1353–1361
Lee Y-B, Choi Y-J, Kim M-H (2010) Boundary detection in carotid ultrasound images using dynamic programming and a directional haar-like filter. Comput Biol Med 40(8):687–697
Cheng D-C, Jiang X (2008) Detections of arterial wall in sonographic artery images using dual dynamic programming. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 12(6):792–799
Ukwatta E, Awad J, Ward A, Buchanan D, Samarabandu J, Parraga G, Fenster A (2011) Three-dimensional ultrasound of carotid atherosclerosis: semiautomated segmentation using a level set-based method. Med Phys 38(5):2479–2493
Ukwatta E, Yuan J, Buchanan D, Chiu B, Awad J, Qiu W, Parraga G, Fenster A (2013) Three-dimensional segmentation of three-dimensional ultrasound carotid atherosclerosis using sparse field level sets. Med Phys 40(5):052903
Lekadir K, Galimzianova A, Betriu A, Mar Vila M, Igual L, Rubin DL, Fernández E, Radeva P, Napel S (2016) A convolutional neural network for automatic characterization of plaque composition in carotid ultrasound. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 21(1):48–55
Mishra D, Chaudhury S, Sarkar M, Soin AS (2018) Ultrasound image segmentation: a deeply supervised network with attention to boundaries. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 66(6):1637–1648
Azzopardi C, Hicks YA, Camilleri KP (2017) Automatic carotid ultrasound segmentation using deep convolutional neural networks and phase congruency maps. In: 2017 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2017), pp 624–628. IEEE
Kb J, Madian N (2018) Convolutional neural network for segmentation and measurement of intima media thickness. J Med Syst 42:1–8
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, October 5-9, 2015, Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer, pp 234–241
Zhou Z, Rahman Siddiquee MM, Tajbakhsh N, Liang J (2018) Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In: Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, September 20, 2018, Proceedings 4. Springer, pp 3–11
Zhang Z, Liu Q, Wang Y (2018) Road extraction by deep residual u-net. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 15(5):749–753
Jha D, Smedsrud PH, Riegler MA, Johansen D, De Lange T, Halvorsen P, Johansen HD (2019) Resunet++: an advanced architecture for medical image segmentation. In: 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM), pp 225–2255. IEEE
Chen J, Lu Y, Yu Q, Luo X, Adeli E, Wang Y. et al (2021) Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.04306
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser L, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst
Dosovitskiy A (2020) An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929
Xie E, Wang W, Yu Z, Anandkumar A, Alvarez JM, Luo P (2021) Segformer: simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 34:12077–12090
Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, Hu H, Wei Y, Zhang Z, Lin S, Guo B (2021) Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 10012–10022
Xiao H, Li L, Liu Q, Zhu X, Zhang Q (2023) Transformers in medical image segmentation: a review. Biomed Signal Process Control 84:104791
Xu G, Zhang X, He X, Wu X (2023) Levit-unet: Make faster encoders with transformer for medical image segmentation. In: Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision (PRCV). Springer, pp 42–53
Cao H, Wang Y, Chen J, Jiang D, Zhang X, Tian Q, Wang M (2022) Swin-unet: Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, pp 205–218
Ibtehaz N, Rahman MS (2020) Multiresunet: Rethinking the u-net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural Netw 121:74–87
Wang Z, Zou Y, Liu PX (2021) Hybrid dilation and attention residual u-net for medical image segmentation. Comput Biol Med 134:104449
Lu H, She Y, Tie J, Xu S (2022) Half-unet: a simplified u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. Front Neuroinform 16:911679
Lin D, Li Y, Nwe TL, Dong S, Oo ZM (2020) Refineu-net: Improved u-net with progressive global feedbacks and residual attention guided local refinement for medical image segmentation. Pattern Recogn Lett 138:267–275
Zhang Z, Wu C, Coleman S, Kerr D (2020) Dense-inception u-net for medical image segmentation. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 192:105395
Zhou R, Azarpazhooh MR, Spence JD, Hashemi S, Ma W, Cheng X, Gan H, Ding M, Fenster A (2021) Deep learning-based carotid plaque segmentation from b-mode ultrasound images. Ultrasound Med Biol 47(9):2723–2733
Zhou R, Guo F, Azarpazhooh MR, Hashemi S, Cheng X, Spence JD, Ding M, Fenster A (2021) Deep learning-based measurement of total plaque area in b-mode ultrasound images. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 25(8):2967–2977
Jain PK, Sharma N, Giannopoulos AA, Saba L, Nicolaides A, Suri JS (2021) Hybrid deep learning segmentation models for atherosclerotic plaque in internal carotid artery b-mode ultrasound. Comput Biol Med 136:104721
Jain PK, Sharma N, Saba L, Paraskevas KI, Kalra MK, Johri A, Laird JR, Nicolaides AN, Suri JS (2021) Unseen artificial intelligence-deep learning paradigm for segmentation of low atherosclerotic plaque in carotid ultrasound: A multicenter cardiovascular study. Diagnostics 11(12):2257
Yin H, Shao Y (2023) Cfu-net: a coarse-fine u-net with multi-level attention for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas
Hu H, Jin Z, Zhou Q, Guan Q, Chen Q (2023) Cti-unet: hybrid local features and global representations efficiently. In: 2023 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp 735–739. IEEE
Li Y, Zhang Y, Liu J-Y, Wang K, Zhang K, Zhang G-S, Liao X-F, Yang G (2022) Global transformer and dual local attention network via deep-shallow hierarchical feature fusion for retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE Trans Cybern 53(9):5826–5839
Al Qurri A, Almekkawy M (2023) Improved unet with attention for medical image segmentation. Sensors 23(20):8589
Guo H, Zhang H, Li M, Quan X (2023) Ltunet: A lightweight transformer-based unet with multi-scale mechanism for skin lesion segmentation. In: CAAI International Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Springer, pp 147–158
Woo S, Park J, Lee J-Y, Kweon IS, et al (2018) Cbam: convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp 3–19
Howard AG (2017) Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04861
Wang Z, Cun X, Bao J, Zhou W, Liu J, Li H (2022) Uformer: a general u-shaped transformer for image restoration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 17683–17693
Xie E, Wang W, Yu Z, Anandkumar A, Alvarez JM, Luo P (2021) Segformer: simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 34:12077–12090
Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M, Zhmoginov A, Chen L-C (2018) Mobilenetv2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 4510–4520
Touboul P-J, Hennerici M, Meairs S, Adams H, Amarenco P, Bornstein N, Csiba L, Desvarieux M, Ebrahim S, Hernandez Hernandez R et al (2012) Mannheim carotid intima-media thickness and plaque consensus (2004–2006-2011) an update on behalf of the advisory board of the 3rd, 4th and 5th watching the risk symposia, at the 13th, 15th and 20th european stroke conferences, mannheim, germany, 2004, brussels, belgium, 2006, and hamburg, germany, 2011. Cerebrovasc Dis 34(4):290–296
Cheng J, Ye J, Deng Z, Chen J, Li T, Wang H, Su Y, Huang Z, Chen J, Jiang L, et al (2023) Sam-med2d. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.16184
Paszke A, Gross S, Massa F, Lerer A, Bradbury J, Chanan G, Killeen T, Lin Z, Gimelshein N, Antiga L, et al (2019) Pytorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 32
Oktay O (2018) Attention u-net: learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999
Hao H, Zhao H, Huang D, An H, Wang D, Wang X, Zhang J (2024) A new network for carotid artery plaque segmentation in ultrasound images. In: Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Intelligent Computing, pp 119–126
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Dr. Meizhen Fu from Shanghai East Hospital for her contribution to the creation of the ground-truth segmentation maps. This study was funded by Medical discipline Construction Project of Pudong Health Committee of Shang-hai (Grant No. PWYgy2021-05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wang Xiaolong and An Hedi wrote the main manuscript text and Zhang Jingsong reviewed and edited the writing. Huang Dongya supervised the draft preparation. Wen Junxian processed and checked the experimental data. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., An, H., Zhang, J. et al. DPSMUNet: a new network based on a dual-pooling self-attention module for carotid artery plaque segmentation in ultrasound images. J Supercomput 81, 267 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06770-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06770-x