Abstract
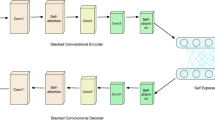
Deep subspace clustering methods use deep neural networks to project input data into the latent space, leveraging the inherent self-expressiveness (SE) properties of the data as a similarity metric to handle high-dimensional data effectively. However, existing methods focus solely on the SE relationships within the latent space, which constrains their capacity to capture subspace structures. To overcome this limitation, we introduce a novel deep subspace clustering method using dual self-expressiveness and convolutional fusion (DSCDC), which computes SE relationships in both the latent and input spaces. This dual-focus approach captures multi-source SE relationships, enhancing the quality of the SE matrix. Additionally, we designed a convolutional fusion module that effectively integrates the multiple SE matrices through a learnable fusion approach. Experimental results across various datasets validate the superiority of our DSCDC compared to competing methods. Ablation studies further confirm the effectiveness of the proposed modules.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Deng X, Huang D, Chen DH et al (2023) Strongly augmented contrastive clustering. Pattern Recogn 139:109470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109470
Ma X, Zhou Y, Wang H et al (2023) Image as set of points. In: The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2303.01494
Lin S, Yang A, Lai T et al (2023) Multi-motion segmentation via co-attention-induced heterogeneous model fitting. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2023.3298319
Hafeezallah A, Al-Dhamari A, Abu-Bakar SAR (2024) Motion segmentation using ward’s hierarchical agglomerative clustering for crowd disaster risk mitigation. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 102:104262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2024.104262
Yang B, Yang Y, Su X (2022) Deep structure integrative representation of multi-omics data for cancer subtyping. Bioinformatics 38(13):3337–3342. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac345
Yang B, Yang Y, Wang M et al (2023) Mrgcn: cancer subtyping with multi-reconstruction graph convolutional network using full and partial multi-omics dataset. Bioinformatics 39(6):btad353. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btad353
Yang B, Xin TT, Pang SM et al (2021) Deep subspace mutual learning for cancer subtypes prediction. Bioinformatics 37(21):3715–3722. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btab625
Ikotun AM, Ezugwu AE, Abualigah L et al (2023) K-means clustering algorithms: a comprehensive review, variants analysis, and advances in the era of big data. Inf Sci 622:178–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2022.11.139
Ran X, Xi Y, Lu Y et al (2023) Comprehensive survey on hierarchical clustering algorithms and the recent developments. Artif Intell Rev 56(8):8219–8264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-022-10366-3
Qu W, Xiu X, Chen H et al (2023) A survey on high-dimensional subspace clustering. Mathematics 11(2):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11020436
Elhamifar E, Vidal R (2013) Sparse subspace clustering: algorithm, theory, and applications. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(11):2765–2781. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2013.57
Liu G, Lin Z, Yan S et al (2012) Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(1):171–184. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.88
Von Luxburg U (2007) A tutorial on spectral clustering. Stat Comput 17:395–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-007-9033-z
Peng Z, Liu H, Jia Y et al (2022) Adaptive attribute and structure subspace clustering network. IEEE Trans Image Process 31:3430–3439. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2022.3171421
Patel VM, Vidal R (2014) Kernel sparse subspace clustering. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). IEEE, pp 2849–2853. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2014.7025576
Sun M, Wang S, Zhang P et al (2021) Projective multiple kernel subspace clustering. IEEE Trans Multimed 24:2567–2579. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3086727
Abdolali M, Gillis N (2021) Beyond linear subspace clustering: a comparative study of nonlinear manifold clustering algorithms. Comput Sci Rev 42:100435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosrev.2021.100435
Ren Y, Pu J, Yang Z et al (2024) Deep clustering: a comprehensive survey. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2024.3403155
Ji P, Zhang T, Li H et al (2017) Deep subspace clustering networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp 23–32. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1709.02508
Zhao L, Ma Y, Chen S et al (2023) Deep double self-expressive subspace clustering. In: ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP49357.2023.10095270
Lv J, Kang Z, Lu X et al (2021) Pseudo-supervised deep subspace clustering. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:5252–5263. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3079800
Vidal R, Favaro P (2014) Low rank subspace clustering (lrsc). Pattern Recogn Lett 43:47–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2013.08.006
You C, Robinson D, Vidal R (2016a) Scalable sparse subspace clustering by orthogonal matching pursuit. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 3918–3927. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.425
You C, Li CG, Robinson DP et al (2016b) Oracle based active set algorithm for scalable elastic net subspace clustering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 3928–3937. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.426
Jia H, Zhu D, Huang L et al (2023) Global and local structure preserving nonnegative subspace clustering. Pattern Recogn 138:109388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109388
Wang J, Wu B, Ren Z et al (2024) Decomposed deep multi-view subspace clustering with self-labeling supervision. Inf Sci 653:119798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2023.119798
Qi T, Feng X, Gao B et al (2024) An end-to-end graph convolutional network for semi-supervised subspace clustering via label self-expressiveness. Knowl-Based Syst 286:111393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2024.111393
Zhou P, Hou Y, Feng J (2018) Deep adversarial subspace clustering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1596–1604. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00172
Zhang J, Li CG, You C et al (2019) Self-supervised convolutional subspace clustering network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 5473–5482. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00562
Shopov VK, Markova VD (2021) Application of Hungarian algorithm for assignment problem. In: 2021 International Conference on Information Technologies (InfoTech). IEEE, pp 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/InfoTech52438.2021.9548600
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (2024JC-YBMS-473), Key Scientific Research Program of Education Department of Shaanxi Provincial Government (22JS019), and Xi’an Major Scientific and Technological Achievements Transformation Industrialization Project (23CGZHCYH0008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ML and BY wrote the main manuscript text. TX and SH are respectively responsible for reviewing and drawing. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Yang, B., Xue, T. et al. Deep subspace clustering using dual self-expressiveness and convolutional fusion. J Supercomput 81, 390 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06885-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-06885-1