Abstract
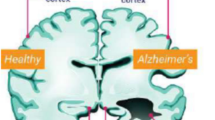
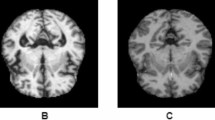
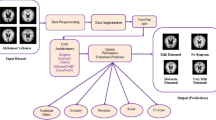
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), characterized by progressive neurological degeneration and cognitive decline, necessitates early detection for effective intervention before symptom onset. Deep learning (DL) methodologies have emerged as promising tools for predicting and classifying AD. In this context, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) exhibit proficiency in discerning specific AD features, enabling accurate diagnosis. To this end, this study proposes an effective deep learning optimized CNN model, namely, AlzONet, tailored to address the intricate challenges of Alzheimer’s patient brain classification. To explore the generalization of the AlzONet model through three gradient optimization algorithms: Adam, SGD, and RMSProp, this study focuses on how each algorithm impacts the model’s ability to minimize the loss function during training and how well it generalizes to new, unseen data. The Kaggle AD dataset, which includes normal, mild, very mild, and moderate stages, assesses the model’s performance. K fold cross-validation is applied to evaluate the model’s efficacy and generalization capability reliably. In contrast, a transfer learning-based comparison was conducted with five pre-trained models (VGG-16, DenseNet-121, ResNet-50, Inception-V3, and Xception). The results reveal that AlzONet trained with Adam achieves exceptional accuracy of 98.1% with a learning rate of 0.0001, while SGD and RMSProp yield 97.3% and 96.6% with a learning rate of 0.001 during training. In the testing phase, the optimized AlzONet model with Adam surpasses expectations with 96.5% accuracy, 96.7% F1-score, and 99.7% AUC.











Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availability Statements
The authors declare that they have accessed Data Availability. (n.d.). 2022. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/uraninjo/augmented-alzheimer-mri-dataset
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- Adam:
-
Adaptive moment estimation
- AdaGrad:
-
Adaptive gradient algorithm
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- AWS:
-
Amazon web services
- CAD:
-
Computer-aided diagnosis
- Caps Net:
-
Capsule networks
- CNN:
-
Convolutional neural network
- DenseNet121:
-
Densely connected convolutional network 121-layer network
- DL:
-
Deep learning
- ET:
-
Extremely randomized tree
- FDA:
-
Food and drug administration
- FN:
-
False negative
- FP:
-
False positive
- FPR:
-
False-positive rate
- Gaussian NB:
-
Gaussian Naive Bayes
- GRNN:
-
General regression neural network
- LR:
-
Logistic regression
- LR-SGD:
-
Logistic regression with stochastic gradient descent
- LSTM:
-
Long short-term memory
- MCI:
-
Mild cognitive impairment
- ML:
-
Machine learning
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MPNN:
-
Multilayer perceptron neural network
- NMDA:
-
N-Methyl-D-Aspartate
- RBNN:
-
Radial basis neural network
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- PRC:
-
Precision-recall curve
- ResNet-50:
-
Residual network 50-layer network
- RESTful API:
-
Representational state transfer application programming interface
- RMSProp:
-
Root mean square propagation
- SGD:
-
Stochastic gradient descent
- SMOTE:
-
Synthetic minority over-sampling technique
- SVM:
-
Support vector machine
- TN:
-
True negative
- TP:
-
True positive
- TPR:
-
True-positive rate
- XAL:
-
Explainable artificial intelligence
References
De Marco M, Brandi AL, Bieger A, Krug B, Camozzato A, Picon PD, Chaves MLF, Castilhos RM (2023) Disparity in the use of Alzheimer’s disease treatment in Southern Brazil. Sci Rep 13(1):9555
Lopez-Lee C, Torres ERS, Carling G (2024) Gan L (2024) Mechanisms of sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 112(8):1208–1221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2024.01.024
ZhouQ., Wang J, Yu X, Wang S, Zhang Y, (2023) A survey of deep learning for Alzheimer’s disease. Mach Learn Knowl Extract 5(2):611–668
Zhang L, Yao Q, Hu J, Qiu B, Xiao Y, Zhang Q, Zeng Y, Zheng S, Zhang Y, Wan Y (2024) Hotspots and trends of microglia in Alzheimer’s disease: a bibliometric analysis during 2000–2022. Eur J Med Res 29(1):75
Mishra A, Arora P, Jaiswal A, Mazumdar B (2024) Deep learning and extreme learning machine for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Authorea Preprints. https://doi.org/10.22541/au.170664821.18176002/v1
Hong J, Zhang YD, Chen W (2022) Source-free unsupervised domain adaptation for cross-modality abdominal multi-organ segmentation. Knowl-Based Syst 250:109155
Hong J, Yu SC, Chen W (2022) Unsupervised domain adaptation for cross-modality liver segmentation via joint adversarial learning and self-learning. Appl Soft Comput 121:108729
Zhang Y, Hong J, Chen S (2023) Medical big data and artificial intelligence for healthcare. Appl Sci 13(6):3745
Li S, Zhao S, Zhang Y, Hong J, Chen W (2024) Source-free unsupervised adaptive segmentation for knee joint MRI. Biomed Signal Process Control 92:106028
Alsubaie MG, Luo S, Shaukat K (2024) Alzheimer’s disease detection using deep learning on neuroimaging: a systematic review. Mach Learn Knowl Extract 6(1):464–505. https://doi.org/10.3390/make6010024
DiBenedetti DB, Menne H, Paulsen R et al (2023) Technical review of clinical outcomes assessments across the continuum of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Ther 12(2):571–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40120-023-00443-2
Saleem TJ, Zahra SR, Wu F, Alwakeel A, Alwakeel M, Jeribi F, Hijji M (2022) Deep learning-based diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Personal Med 12(5):815. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12050815
Diogo VS, Ferreira HA, Prata D et al (2022) Early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using machine learning: a multi-diagnostic, generalizable approach. Alz Res Therapy 14:107. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-022-01047-y
Uddin KMM, AlamM J, Jannat-E-Anawar, et al (2023) A novel approach utilizing machine learning for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Mater Dev 1:882–898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s44174-023-00078-9
Sharma A, Kaur S, Memon N, Fathima AJ, Ray S, Bhatt MW (2021) Alzheimer’s patients detection using support vector machine (SVM) with quantitative analysis. Neurosci Inform 1(3):100012
Dara OA, Lopez-Guede JM, Raheem HI, Rahebi J, Zulueta E, Fernandez-Gamiz U (2023) Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis using machine learning: a survey. Appl Sci 13(14):8298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148298
Sachidananda Murthy KB, Prasad SN (2023) Blockchain-enabled detection of neurological disorders using a deep learning approach. Eng Proc 59(1):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc202305918
Viswan V, Shaffi N, Mahmud M et al (2024) Explainable artificial intelligence in Alzheimer’s disease classification: a systematic review. Cogn Comput 16:1–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-023-10192-x
Xu F, Gao W, Zhang M, Zhang F, Sun X, Wu B, Liu Y, Li X, Li H (2024) Diagnostic implications of ubiquitination-related gene signatures in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep 14(1):10728
Ávila-Jiménez JL, Cantón-Habas V, del Pilar C-G, Rich-Ruiz M, VenturaS, (2024) A deep learning model for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis based on patient clinical records. Comput Biol Med 169:107814
Warren SL, Moustafa AA (2023) Functional magnetic resonance imaging, deep learning, and Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. J Neuroimaging 33(1):5–18
Alahmed H, Al-Suhail GA (2025). Alzheimer's disease diagnosis using deep learning for brain MRI images: a comparative analysis. Iraqi J Electr Electron Eng, in press.
Sharma G, Vijayvargiya A, Kumar R (2021) Comparative assessment among different convolutional neural network architectures for Alzheimer's disease detection. In: 2021 IEEE 8th Uttar Pradesh Section International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering (UPCON), Dehradun, India, 2021, pp 1–6, https://doi.org/10.1109/UPCON52273.2021.9667607.
Mora-Rubio A, Bravo-Ortíz MA, Quiñones Arredondo S, Saborit Torres JM, Ruz GA, Tabares-Soto R (2023) Classification of Alzheimer’s disease stages from magnetic resonance images using deep learning. PeerJ Comput Sci 9:e1490. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.1490
Şener B, Acici K, Sümer E (2024) Categorization of Alzheimer’s disease stages using deep learning approaches with McNemar’s test. PeerJ Comput Sci 10:e1877. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.1877
Balaji P, Chaurasia MA, Bilfaqih SM, Muniasamy A, Alsid LEG (2023) Hybridized deep learning approach for detecting Alzheimer’s disease. Biomedicines 11(1):149
Oyewola DO, Alechenu B, Al-Mustapha KA, Oyewande OV (2020) Classification of dementia diseases using deep learning techniques. FUDMA J Sci 4(2), 371–379. https://doi.org/10.33003/fjs-2020-0402-197
Mathews E, Jabez J (2024) Classifying Alzheimer’s disease from sMRI data using a hybrid deep learning approaches. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología-Serie de Conferencias 3:651
Yuan Z, Li X, Hao Z, Tang Z, Yao X, Wu T (2024) Intelligent prediction of Alzheimer’s disease via improved multifeature squeeze-and-excitation-dilated residual network. Sci Rep 14(1):11994
Raza N, Naseer A, Tamoor M, Zafar K (2023) Alzheimer disease classification through transfer learning approach. Diagnostics 13(4):801. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13040801
Ghaffari H, Tavakoli H, Pirzad Jahromi G (2022) Deep transfer learning-based fully automated detection and classification of Alzheimer’s disease on brain MRI. Br J Radiol 95(1136):20211253. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20211253
Maqsood M, Nazir F, Khan U, Aadil F, Jamal H, Mehmood I, Song OY (2019) Transfer learning assisted classification and detection of Alzheimer’s disease stages using 3D MRI scans. Sensors 19(11):2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112645
Sarawgi U, Zulfikar W, Soliman N, Maes P (2020) Multimodal inductive transfer learning for detection of Alzheimer's dementia and its severity. arXiv 2009.00700.https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.00700
Hon M, Khan NM (2017) Towards Alzheimer's disease classification through transfer learning. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM) 1166–1169.https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBM.2017.8217822
Aderghal K, Khvostikov A, Krylov A, Benois-Pineau J, Afdel K, Catheline G (2018) Classification of Alzheimer disease on imaging modalities with deep CNNs using cross-modal transfer learning. 2018 IEEE international symposium computer-based medical systems (CBMS) 345–350.https://doi.org/10.1109/CBMS.2018.00067
Rallabandi VS, Tulpule K, Gattu M, Initiative ADN (2020) Automatic classification of cognitively normal, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease using structural MRI analysis. Inform Med Unlocked 18:100305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2020.100305
Rallabandi VS, Seetharaman K, Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2023) Classification of cognitively normal controls, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer's disease using transfer learning approach. Biomed Signal Process Control 79:104092.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2022.104092
Armonaite K, La Ventura M, Laura L (2023) Alzheimer’s disease detection from magnetic resonance imaging: a deep learning perspective. Explor Neuroprotect Therapy 3(3):139–150
Bamber SS, Vishvakarma T (2023) Medical image classification for Alzheimer’s using a deep learning approach. J Eng Appl Sci 70(1):54
Park SW, Yeo NY, Kim Y, Byeon G, Jang JW (2023) Deep learning application for the classification of Alzheimer’s disease using 18F-flortaucipir (AV-1451) tau positron emission tomography. Sci Rep 13(1):8096
Agarwal D, Berbís MÁ, Luna A, Lipari V, Ballester JB, de la Torre-Díez I (2023) Automated medical diagnosis of Alzheimer’ s disease using an efficient net convolutional neural network. J Med Syst 47(1):57
AparnaM., & Rao, B. S. (2023) A novel automated deep learning approach for alzheimer’s disease classification. IAES Int J Artif Intell 12(1):451
Al Shehri W (2022) Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis and classification using deep learning techniques. PeerJ Comput Sci 8:e1177
Helaly HA, Badawy M, Haikal AY (2022) Deep learning approach for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Cogn Comput 14(5):1711–1727
Alqahtani N, Alam S, Aqeel I, ShuaibM MK, I, Khan SB, & Malibari AA, (2023) Deep belief networks (DBN) with IoT-based alzheimer’s disease detection and classification. Appl Sci 13(13):7833
Tambe P, Saigaonkar R, Devadiga N, Chitte PH (2021) Deep Learning techniques for effective diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using MRI images. ITM Web of Conf 40:3021
Mohi ud din dar G, Bhagat A, Ansarullah SI, Othman MTB, Hamid Y, Alkahtani HK, Ullah I, Hamam H, (2023) A novel framework for classification of different Alzheimer’s disease stages using CNN model. Electronics 12(2):469
Talukder MA, Islam MM, Uddin MA et al (2023) An efficient deep learning model to categorize brain tumor using reconstruction and fine-tuning. Expert Syst Appl 230:120534
Shaffi N, Subramanian K, Vimbi V, Hajamohideen F, Abdesselam A, Mahmud M (2024) Performance evaluation of deep, shallow and ensemble machine learning methods for the automated classification of Alzheimer's disease. Int J Neural Syst, https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129065724500291.
Rani P, Lamba R, Sachdeva RK, Kumar K, Iwendi C (2024) A machine learning model for Alzheimer's disease prediction. IET Cyber‐Physical Systems: Theory & Applications.
George CM, Menon S (2024) Machine learning for Alzheimer Derection: a comprehensive approach. J Theoret Appl Inf Technol 102(4).
Zhang X, Gao L, Wang Z, YuY Zhang Y, Hong J (2024) Improved neural network with multi-task learning for Alzheimer’s disease classification. Heliyon. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26405
Rahat IS, Hossain T, Ghosh H, Reddy KLK, Palvadi SK, Ravindra JVR (2024) Exploring deep learning models for accurate Alzheimer’s disease classification based on MRI imaging. EAI Endorsed Trans Pervasive Health Technol. https://doi.org/10.4108/eetpht.10.5550
Fathi S, Ahmadi A, Dehnad A, Almasi-Dooghaee M, Sadegh M (2024) Initiative ADN (2024) A deep learning-based ensemble method for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using MRI images. Neuroinform 22:89–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-023-09646-2
Katabathula S, Wang Q, Xu R (2021) Predict Alzheimer’s disease using hippocampus MRI data: a lightweight 3D deep convolutional network model with visual and global shape representations. Alz Res Therapy 13:104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-021-00837-0
Data Availability (2022) Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/uraninjo/augmented-alzheimer-mri-dataset
Özkaraca O, Bağrıaçık Oİ, Gürüler H, Khan F, Hussain J, Khan J, Ue L (2023) Multiple brain tumor classification with dense CNN architecture using brain MRI images. Life 13(2):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020349
Gorriz, JM, Segovia F, Ramirez J, Ortiz A, Suckling J (2024) Is K-fold cross validation the best model selection method for Machine Learning? ArXiv Preprint https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2401.16407.
Kosolwattana T, Liu C, Hu R, Han S, Chen H, Lin Y (2023) A self- inspected adaptive SMOTE algorithm (SASMOTE) for highly imbalanced data classification in healthcare. BioData Mining 16(1):15
Zhao Y, Wong ZSY, Tsui KL (2018) A framework of rebalancing imbalanced healthcare data for rare events' classification: a case of look-alike sound-alike mix-up incident detection. J Healthcare Eng, 2018.
Murugan S, Venkatesan C, Sumithra MG, Gao XZ, Elakkiya B, Akila M, Manoharan S (2021) DEMNET: a deep learning model for early diagnosis of Alzheimer diseases and dementia from MR images. IEEE Access 9:90319–90329. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3090474
Desai C (2024) Impact of weight initialization techniques on neural network efficiency and performance: a case study with MNIST dataset. Int J Eng Comput Sci 13(04).
AbdulAzeem Y, Bahgat WM, Badawy M (2021) A CNN based framework for classification of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Comput Appl 33:10415–10428
Thakur S, Kumar A (2021) X-ray and CT-scan-based automated detection and classification of covid-19 using convolutional neural networks (CNN). Biomed Signal Process Control 69:102920
Irfan D, Gunawan TS, Wanayumini W (2023) Comparison of SGD, RMSProp, and ADAM optimization in animal classification using CNNs. Proc Int Conf Inf Sci Technol Innov (ICoSTEC) 2(1):45–51
Zhou P, Feng J, Ma C, Xiong C, Hoi SCH (2020) Towards theoretically understanding why sgd generalizes better than adam in deep learning. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 33:21285–21296
Oktavian MW, Yudistira N, Ridok A (2022) Classification of Alzheimer’s disease using the convolutional neural network (CNN) with transfer learning and weighted loss. ArXiv Preprint https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2207.01584.
Haji SH, Abdulazeez AM (2021) Comparison of optimization techniques based on gradient descent algorithm: a review. PalArch’s J Archaeol Egypt/Egyptol 18(4):2715–2743
Arafa DA, Moustafa HED, Ali HA, Ali-Eldin AMT, Saraya SF (2024) A deep learning framework for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease on MRI images. Multimedia Tools Appl 83(2):3767–3799
Uppal M, Gupta D, Juneja S, Gadekallu TR, El Bayoumy I, Hussain J, Lee SW (2023) Enhancing accuracy in brain stroke detection: multilayer perceptron with Adadelta, RMSProp and AdaMax optimizers. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 11:1257591. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2023.1257591
Hicks SA, Strümke I, Thambawita V, Hammou M, Riegler MA, Halvorsen P, Parasa S (2022) On evaluation metrics for medical applications of artificial intelligence. Sci Rep 12(1):5979
Maxwell AE, Warner TA, Guillén LA (2021) Accuracy assessment in convolutional neural network-based deep learning remote sensing studies—Part 1: Literature review. Remote Sens 13(13):2450
Vujović Ž (2021) Classification model evaluation metrics. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 12(6):599–606
Mahjoubi MA, Hamida S, Gannour OE, Cherradi B, Abbassi AE, Raihani A (2023) Improved multiclass brain tumor detection using convolutional neural networks and magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 14(3):406–414
Kaur S, Gupta S, Singh S, Gupta I (2022) Detection of Alzheimer’s disease using deep convolutional neural network. Int J Image Graph 22(03):2140012
Liu, S., Masurkar, A. V., Rusinek, H., Chen, J., Zhang, B., Zhu, W., ... & Razavian, N. (2022). Generalizable deep learning model for early Alzheimer’s disease detection from structural MRIs. Scientific reports, 12(1), 17106.
Van der Maaten L, Hinton G (2012) Visualizing non-metric similarities in multiple maps. Mach Learn 87:33–55
Alahmad HA, Al-Suhail GA (2024) Medical image classification using deep learning for brain tumors detection: an overview. In: Vasant P et al. Intelligent computing and optimization. ICO 2023. Lecture notes in networks and systems, vol 1169. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73324-6_20
El-Latif AAA, Chelloug SA, Alabdulhafith M, Hammad M (2023) Accurate detection of Alzheimer’s disease using lightweight deep learning model on MRI data. Diagnostics 13(7):1216
Bangyal WH, Rehman NU, Nawaz A, Nisar K, Ibrahim AAA, Shakir R, Rawat DB (2022) Constructing domain ontology for Alzheimer disease using deep learning-based approach. Electronics, 11(12), 1890.
Irfan M, Shahrestani S, ElKhodr M (2023) The application of deep learning for classification of Alzheimer's disease stages by magnetic resonance imaging data.
El-Assy AM, Amer HM, Ibrahim HM, Mohamed MA (2024) A novel CNN architecture for accurate early detection and classification of Alzheimer’s disease using MRI data. Sci Rep 14(1):3463
Funding
The authors declare that there was no funding for this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, G.A.; Methodology, all authors; Data curation, H.A.; Formal analysis, all authors; Investigation, all authors.; Project administration, G.A.; Python Software Programming, H.A..; Supervision, G.A.; Validation, G.A.; Visualization and Figures, H.A. and G.A.; Writing—original draft, all authors; Writing—review and editing, all authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alahmed, H.A., Al-Suhail, G.A. AlzONet: a deep learning optimized framework for multiclass Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis using MRI brain imaging. J Supercomput 81, 423 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-025-06924-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-025-06924-5