Abstract
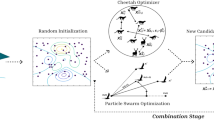
Traditional metaheuristic methods often rely on random exploration and exploitation mechanisms, which can lead to inefficient search processes because of a lack of guidance. This paper introduces a novel metaheuristic algorithm that overcomes these limitations using two specialized mechanisms for exploration and exploitation. The population is divided into explorer and exploiter agents, each using distinct strategies. Explorer agents that resemble a swarm follow a trajectory generated through Latin hypercube sampling to efficiently explore the search space. Exploiters use evolutionary game theory, where weaker agents adopt the strategies of stronger ones, ensuring efficient exploitation. This integration of global information enhances diversity, improves the solution quality, and reduces computational costs. Validated against benchmark functions, the proposed algorithm delivered superior results, achieving faster convergence and higher-quality solutions.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Chong E (2013) An Introduction to Optimization. Wiley, New York
Song J, Cui Y, Wei P, Valdebenito MA, Zhang W (2024) Constrained Bayesian optimization algorithms for estimating design points in structural reliability analysis. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 241:109613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2023.109613
Saleem S, Ahmad I, Ahmed SH, Rehman A (2024) Artificial intelligence based robust nonlinear controllers optimized by improved gray wolf optimization algorithm for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles in grid to vehicle applications. J Energy Storage 75:109332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2023.109332
Abualigah L et al (2022) Meta-heuristic optimization algorithms for solving real-world mechanical engineering design problems: a comprehensive survey, applications, comparative analysis, and results. Neural Comput Appl 34(6):4081–4110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06747-4
Adby P (2013) Introduction to Optimization Methods. Springer Science and Business Media, Berlin
Cuevas E, Rodríguez A (2020) Metaheuristic computation with MATLAB. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Yang X-S (2011) Metaheuristic optimization. Scholarpedia 6(8):11472. https://doi.org/10.4249/scholarpedia.11472
Newton J (2018) Evolutionary game theory: a renaissance. Games (Basel) 9(2):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/g9020031
Tuyls K, Parsons S (2007) What evolutionary game theory tells us about multiagent learning. Artif Intell 171(7):406–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artint.2007.01.004
Hussain K, Mohd Salleh MN, Cheng S, Shi Y (2019) Metaheuristic research: a comprehensive survey. Artif Intell Rev 52(4):2191–2233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9605-z
Abdel-Basset M, Abdel-Fatah L, Sangaiah AK (2018) Metaheuristic Algorithms: A Comprehensive Review. In: Computational Intelligence for Multimedia Big Data on the Cloud with Engineering Applications, Elsevier, pp 185–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813314-9.00010-4
Holland JH (1992) Genetic algorithms. Sci Am 267(1):66–73 [Online]. Available: http://www.jstor.org/stable/24939139
Back T (1996) Evolutionary Algorithms in Theory and Practice: Evolution Strategies, Evolutionary Programming, Genetic Algorithms. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Storn R, Price K (1997) Differential evolution—a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J Global Optim 11(4):341–359. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008202821328
Beyer H-G (2013) The Theory of Evolution Strategies, vol 1. Springer Science and Business Media, Berlin
Beyer H-G, Schwefel H-P (2002) Evolution strategies: a comprehensive introduction. Nat Comput 1(1):3–52. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015059928466
Yang X-S (2010) A New Metaheuristic Bat-Inspired Algorithm. pp 65–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12538-6_6
Yang XS, He X (2013) Bat algorithm: literature review and applications. Int J Bio-Inspired Comput 5(3):141. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBIC.2013.055093
Yang X-S, Deb S (2009) Cuckoo Search via Lévy flights. In: 2009 World Congress on Nature & Biologically Inspired Computing (NaBIC). IEEE, pp 210–214. https://doi.org/10.1109/NABIC.2009.5393690
Agushaka JO, Ezugwu AE, Abualigah L (2022) Dwarf mongoose optimization algorithm. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 391:114570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2022.114570
Kennedy J, Eberhart R. Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of ICNN’95 - International Conference on Neural Networks. IEEE, pp 1942–1948. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
Yang X-S (2009) Firefly Algorithms for Multimodal Optimization. pp 169–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04944-6_14
Han M, Du Z, Yuen KF, Zhu H, Li Y, Yuan Q (2024) Walrus optimizer: a novel nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 239:122413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122413
Al-Betar MA, Awadallah MA, Braik MS, Makhadmeh S, Doush IA (2024) Elk herd optimizer: a novel nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm. Artif Intell Rev 57(3):48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-023-10680-4
Dorigo M, Birattari M, Stutzle T (2006) Ant colony optimization. IEEE Comput Intell Mag 1(4):28–39. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCI.2006.329691
Geem ZW, Kim JH, Loganathan GV (2001) A new heuristic optimization algorithm: harmony search. Simulation 76(2):60–68. https://doi.org/10.1177/003754970107600201
Cuevas E et al (2021) Search patterns based on trajectories extracted from the response of second-order systems. Appl Sci 11(8):3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083430
Kirkpatrick S, Gelatt CD, Vecchi MP (1983) Optimization by simulated annealing. Science (1979) 220(4598):671–680. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.220.4598.671
Hajek B (1985) A tutorial survey of theory and applications of simulated annealing. In: 1985 24th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. IEEE, pp 755–760. https://doi.org/10.1109/CDC.1985.268599
Cuevas E, Echavarría A, Ramírez-Ortegón MA (2014) An optimization algorithm inspired by the states of matter that improves the balance between exploration and exploitation. Appl Intell 40(2):256–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-013-0458-0
Abdel-Basset M, Mohamed R, Azeem SAA, Jameel M, Abouhawwash M (2023) Kepler optimization algorithm: a new metaheuristic algorithm inspired by Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. Knowl Based Syst 268:110454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2023.110454
Glover F (1989) Tabu search—part I. ORSA J Comput 1(3):190–206. https://doi.org/10.1287/ijoc.1.3.190
Glover F (1990) Tabu search—part II. ORSA J Comput 2(1):4–32. https://doi.org/10.1287/ijoc.2.1.4
Du H, Wu X, Zhuang J (2006) Small-World Optimization Algorithm for Function Optimization. pp 264–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/11881223_33
Rao RV, Savsani VJ, Vakharia DP (2011) Teaching–learning-based optimization: a novel method for constrained mechanical design optimization problems. Comput-Aided Des 43(3):303–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2010.12.015
Nassef AM, Abdelkareem MA, Maghrabie HM, Baroutaji A (2024) The role of random walk-based techniques in enhancing metaheuristic optimization algorithms—a systematic and comprehensive review. IEEE Access 12:139573–139608. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3466170
Yang X-S, Ting TO, Karamanoglu M (2013) Random Walks, Lévy Flights, Markov Chains and Metaheuristic Optimization. pp 1055–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-6516-0_116
Chen S, Islam S, Bolufe-Rohler A, Montgomery J, Hendtlass T (2021) A Random Walk Analysis of Search in Metaheuristics. In: 2021 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). IEEE, pp 2323–2330. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC45853.2021.9504687
Wang G-G, Tan Y (2019) Improving metaheuristic algorithms with information feedback models. IEEE Trans Cybern 49(2):542–555. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2017.2780274
Talbi E-G (2022) Machine learning into metaheuristics. ACM Comput Surv 54(6):1–32. https://doi.org/10.1145/3459664
Crawford B et al (2021) Q-Learnheuristics: towards data-driven balanced metaheuristics. Mathematics 9(16):1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9161839
Dell RB, Holleran S, Ramakrishnan R (2002) Sample size determination. ILAR J 43(4):207–213. https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar.43.4.207
Loh W-L (1996) On Latin hypercube sampling. Ann Stat. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1069362310
Deutsch JL, Deutsch CV (2012) Latin hypercube sampling with multidimensional uniformity. J Stat Plan Infer 142(3):763–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspi.2011.09.016
Escobar-Cuevas H, Cuevas E, Avila K, Avalos O (2024) An advanced initialization technique for metaheuristic optimization: a fusion of Latin hypercube sampling and evolutionary behaviors. Computat Appl Math 43(4):234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-024-02744-0
Escobar-Cuevas H, Cuevas E, Lopez J, Perez-Cisneros M (2025) Integration of metaheuristic operators through unstructured evolutive game theory approach: a novel hybrid methodology. Evol Intell 18(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-024-00988-7
Escobar-Cuevas H, Cuevas E, Gálvez J, Toski M (2024) A novel optimization approach based on unstructured evolutionary game theory. Math Comput Simul 219:454–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2023.12.027
Escobar-Cuevas H et al (2024) Differential Evolution Search Strategy Enhancement Through Evolutionary Game Theory. In: 2024 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). IEEE, pp 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC60901.2024.10612179
Shields MD, Zhang J (2016) The generalization of Latin hypercube sampling. Reliab Eng Syst Sa 148:96–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2015.12.002
Huntington DE, Lyrintzis CS (1998) Improvements to and limitations of Latin hypercube sampling. Probab Eng Mech 13(4):245–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-8920(97)00013-1
Maynard Smith J (1980) Evolutionary Game Theory. pp 73–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-93161-1_5
Shubik M (1991) Game Theory, Law, and the Concept of Competition, 285th ed., vol 60
Cuevas E, Luque A, Aguirre N, Navarro MA, Rodríguez A (2024) Metaheuristic optimization with dynamic strategy adaptation: an evolutionary game theory approach. Phys A: Stat Mech Appl 645:129831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2024.129831
Wilcoxon F (1947) Probability tables for individual comparisons by ranking methods. Biometrics 3(3):119. https://doi.org/10.2307/3001946
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.A. and E.C. wrote the original draft of the manuscript. A.L. performed software validation and formal analysis. H.E. conducted methodology and investigation. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix A
Name | Global minimum | Boundaries | Function | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{1}\) | Ackley | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(0,\ldots , 0\right)\) | \({[-30, 30]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)=-20\hbox{expexp} \left(-0.2\sqrt{\frac{1}{d}{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}{x}_{i}^{2}}\right) -\hbox{exp}\left(\frac{1}{d}{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\hbox{coscos} \left(2\pi {x}_{i}\right) \right)+20+\hbox{exp}(1)\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{2}\) | Griewank | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(0,\ldots , 0\right)\) | \({[-600, 600]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\frac{{x}_{i}^{2}}{4000}-{\prod }_{i=1}^{d}\hbox{coscos} \left(\frac{{x}_{i}}{\sqrt{i}}\right) +1\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{3}\) | Infinity | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(0,\ldots , 0\right)\) | \({[-1, 1]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}{x}_{i}^{6}\hbox{sen}({x}_{i}+2)\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{4}\) | Levy | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(1,\ldots , 1\right)\) | \({\left[-\text{10,10}\right]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)=\left(\pi {\omega }_{1}\right)+{\sum }_{i=1}^{d-1}{\left({\omega }_{1}-1\right)}^{2}\left[1+10\left(\pi {\omega }_{i}+1\right) \right]+{\left({\omega }_{d}-1\right)}^{2}\left[1+\left(2\pi {\omega }_{d}\right) \right]\) \({\omega }_{i}=1+\frac{{x}_{i}-1}{4}\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{5}\) | Multimodal | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(-1,\ldots , -1\right)\) | \({\left[-\text{10,10}\right]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\left|{x}_{i}\right|{\prod }_{i=1}^{d}\left|{x}_{i}\right|\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{6}\) | Penalty 1 | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(-1,\ldots , -1\right)\) | \({\left[-\text{50,50}\right]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)=\frac{\pi }{d}\times \left\{10\left(\pi {\varphi }_{1}\right)+{\sum }_{i=1}^{d-1}{\left({\varphi }_{i}-1\right)}^{2}\left[1+10\left(\pi {\varphi }_{i+1}\right) \right]+{\left({\varphi }_{d}-1\right)}^{2} \right\}+{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}u({x}_{i},a,k,m)\) \({\varphi }_{i}=1+\frac{1}{4}\left({x}_{i}+1\right), u\left({x}_{i},a,k,m\right)=\{k{\left({x}_{i}-a\right)}^{m} if {x}_{i}>a 0 if-a\le {x}_{i} k{\left(-{x}_{i}-a\right)}^{m} if {x}_{i}<a ;a=10, k=100, m=4\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{7}\) | Penalty 2 | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(1,\ldots , 1\right)\) | \({\left[-\text{50,50}\right]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)=0.1\times \left\{\left(3\pi {x}_{1}\right)+{\sum }_{i=1}^{d-1}{\left({x}_{i}-1\right)}^{2}\left[1+\left(3\pi {x}_{i+1}\right) \right]+{\left({x}_{d}-1\right)}^{2}[1+(2\pi {x}_{d})] \right\}+{\sum }_{i=1}^{n}u({x}_{i},a,k,m)\) \(u\left({x}_{i},a,k,m\right)=\{k{\left({x}_{i}-a\right)}^{m} if {x}_{i}>a 0 if-a\le {x}_{i} k{\left(-{x}_{i}-a\right)}^{m} if {x}_{i}<a ; a=5, k=100, m=4\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{8}\) | Perm 2 | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=(\text{1,1}/2,\ldots ,1/n)\) | \({\left[-d,d\right]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}{\left[{\sum }_{j=1}^{d}\left({j}^{i}+10\right)\left({x}_{j}^{i}-\frac{1}{{j}^{i}}\right)\right]}^{2}\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{9}\) | Plateau | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=30;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(0,\ldots , 0\right)\) | \({[-5.12, 5.12]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)=30+{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}|{x}_{i}|\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{10}\) | Powell | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(0,\ldots , 0\right)\) | \({[-4, 5]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^\frac{d}{4}[{\left({x}_{4i-3}+10{x}_{4i-2}\right)}^{2}+5{\left({x}_{i-1}+{x}_{4i}\right)}^{2}+{\left({x}_{4i-2}+{2x}_{4i-1}\right)}^{4}+10{\left({x}_{4i-3}+{x}_{4i}\right)}^{4}]\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{11}\) | Qing | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(0,\ldots , 0\right)\) | \({[-1.28, 1.28]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}{\left({x}_{i}^{2}-i\right)}^{2}\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{12}\) | Quartic | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(-1,\ldots , -1\right)\) | \({[-10, 10]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}i{x}_{i}^{4}+rand\left[\text{0,1}\right]\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{13}\) | Quintic | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(0,\ldots , 0\right)\) | \({[-5.12, 5.12]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\left|{x}_{i}^{5}-3{x}_{i}^{4}+4{x}_{i}^{3}+2{x}_{i}^{2}-10{x}_{i}-4\right|\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{14}\) | Rastrigin | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(1,\ldots , 1\right)\) | \({[-\text{5,10}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)=10d+{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\left[{x}_{i}^{2}-10\cos\left(2\pi {x}_{i}\right)\right]\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{15}\) | Rosenbrock | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(0.5,\ldots , 0.5\right)\) | \({[-\text{100,100}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}100{\left({x}_{i+1}-{x}_{i}^{2}\right)}^{2}+{\left({x}_{i}-1\right)}^{2}\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{16}\) | Schwefel 21 | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0;\) \({x}^{*}=\left(0,\ldots , 0\right)\) | \({[-\text{100,100}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)=\hbox{max}\left\{\left|{x}_{i}\right|,1\le i\le d\right\}\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{17}\) | Schwefel 22 | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0; {x}^{*}=\left(0,\ldots ,0\right)\) | \({[-\text{100,100}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=!}^{d}\left|{x}_{i}\right|+{\prod }_{i=1}^{d}\left|{x}_{i}\right|\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{18}\) | Step | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0; {x}^{*}=\left(0,\ldots,0\right)\) | \({[-\text{100,100}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\left|{x}_{i}^{2}\right|\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{19}\) | Styblinski-Tang | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=-39.1659n; {x}^{*}=\left(-2.9,\ldots,-2.9\right)\) | \({[-\text{5,5}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{2}{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\left({x}_{i}^{4}-{16x}_{i}^{2}+5{x}_{i}\right)\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{20}\) | Vincent | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=-n; {x}^{*}=(7.70,\ldots ,7.70);\) | \({[\text{0.25,10}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)=-\frac{1}{d}{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\hbox{sin}\left[10\log\left({x}_{i}\right)\right]\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{21}\) | Zakharov | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0; {x}^{*}=(0,\ldots ,0);\) | \({[-\text{5,10}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}{x}_{i}^{2}+{\left({\sum }_{i=1}^{d}0.5i{x}_{i}\right)}^{2}+{\left({\sum }_{i=1}^{d}0.5i{x}_{i}\right)}^{4}\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{22}\) | Rothyp | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0; {x}^{*}=(0,\ldots ,0);\) | \({[-65.536, 65.536] }^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}{\sum }_{j=1}^{i}{x}_{j}^{2}\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{23}\) | Schwefel 2 | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0; {x}^{*}=(0,\ldots ,0);\) | \({[-\text{100,100}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}{\left({\sum }_{j=1}^{i}{x}_{i}\right)}^{2}\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{24}\) | Sphere | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0; {x}^{*}=(0,\ldots ,0);\) | \({[-\text{100,100}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}{x}_{i}^{2}\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{25}\) | Sum squares | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0; {x}^{*}=(0,\ldots ,0);\) | \({[-\text{10,10}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}i{x}_{i}^{2}\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{26}\) | Sum powers | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0; {x}^{*}=(0,\ldots ,0);\) | \({[-\text{1,1}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)={\sum }_{i=1}^{d}{\left|{x}_{i}\right|}^{i+1}\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{27}\) | Rastrigin + Schwefel 22 + Sphere | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=0; {x}^{*}=(0,\ldots ,0);\) | \({[-\text{100,100}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)=\left[10d+{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\left[{x}_{i}^{2}-10\cos\left(2\pi {x}_{i}\right)\right]\right]+\left[{\sum }_{i=!}^{d}\left|{x}_{i}\right|+{\prod }_{i=1}^{d}\left|{x}_{i}\right|\right]+\left[{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}{x}_{i}^{2}\right]\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{28}\) | Griewank + Rastrigin + Rosenbrock | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=n-1; {x}^{*}=(0,\ldots ,0);\) | \({[-\text{100,100}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)=\left[{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\frac{{x}_{i}^{2}}{4000}-{\prod }_{i=1}^{d}\hbox{coscos} \left(\frac{{x}_{i}}{\sqrt{i}}\right) +1\right]+\left[10d+{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\left[{x}_{i}^{2}-10\cos\left(2\pi {x}_{i}\right)\right]\right]+\left[{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}100{\left({x}_{i+1}-{x}_{i}^{2}\right)}^{2}+{\left({x}_{i}-1\right)}^{2}\right]\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{29}\) | Ackley + Penalty 2 + Rosenbrock + Schwefel 22 | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=\left(1.1n\right)-1; {x}^{*}=(0,\ldots ,0);\) | \({[-\text{100,100}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)=\left[-20\hbox{expexp} \left(-0.2\sqrt{\frac{1}{d}{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}{x}_{i}^{2}}\right) -\hbox{exp}\left(\frac{1}{d}{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\hbox{coscos} \left(2\pi {x}_{i}\right) \right)+20+\hbox{exp}(1)\right]+\left[0.1\times \left\{\left(3\pi {x}_{1}\right)+{\sum }_{i=1}^{d-1}{\left({x}_{i}-1\right)}^{2}\left[1+\left(3\pi {x}_{i+1}\right) \right]+{\left({x}_{d}-1\right)}^{2}[1+(2\pi {x}_{d})] \right\}+{\sum }_{i=1}^{n}u({x}_{i},a,k,m)\right]+\left[{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}100{\left({x}_{i+1}-{x}_{i}^{2}\right)}^{2}+{\left({x}_{i}-1\right)}^{2}\right]+\left[{\sum }_{i=!}^{d}\left|{x}_{i}\right|+{\prod }_{i=1}^{d}\left|{x}_{i}\right|\right]\) | |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{30}\) | Ackley + Griewank + Rastrigin + Rosenbrock + Schwefel 22 | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=n-1; {x}^{*}=(0,\ldots ,0);\) | \({[-\text{100,100}]}^{d}\) | \(f\left(x\right)=\left[-20\hbox{expexp} \left(-0.2\sqrt{\frac{1}{d}{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}{x}_{i}^{2}}\right) -\hbox{exp}\left(\frac{1}{d}{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\hbox{coscos} \left(2\pi {x}_{i}\right) \right)+20+\hbox{exp}(1)\right]+\left[{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\frac{{x}_{i}^{2}}{4000}-{\prod }_{i=1}^{d}\hbox{coscos} \left(\frac{{x}_{i}}{\sqrt{i}}\right) +1\right]+\left[10d+{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}\left[{x}_{i}^{2}-10\cos\left(2\pi {x}_{i}\right)\right]\right]+\left[{\sum }_{i=1}^{d}100{\left({x}_{i+1}-{x}_{i}^{2}\right)}^{2}+{\left({x}_{i}-1\right)}^{2}\right]+\left[{\sum }_{i=!}^{d}\left|{x}_{i}\right|+{\prod }_{i=1}^{d}\left|{x}_{i}\right|\right]\) | |
Appendix B
Name | Global minimum | Boundaries | |
|---|---|---|---|
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{1}\) | Shifted and Rotated Ackley’s function | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=500;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{2}\) | Shifted and Rotated Weierstrass function | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=600;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{3}\) | Shifted and Rotated Rastrigin’s function | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=900;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{4}\) | Shifted and Rotated Schwefel’s function | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=1100;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{5}\) | Shifted and Rotated Katsuura function | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=1200;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{6}\) | Shifted and Rotated HappyCat function | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=1300;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{7}\) | Shifted and Rotated HGBat function | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=1400;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{8}\) | Shifted and Rotated Expanded Griewank’s plus Rosenbrock’s function | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=1500;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{9}\) | Shifted and Rotated Expanded Scaffer’s F6 function | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=1600;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{10}\) | Hybrid function 2 (N = 3) | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=1800;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{11}\) | Hybrid function 3 (N = 4) | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=1900;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{12}\) | Composition function 1 (N = 5) | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=2300;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{13}\) | Composition function 2 (N = 3) | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=2400;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{14}\) | Composition function 3 (N = 3) | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=2500;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
\(f{\left(x\right)}_{15}\) | Composition function 4 (N = 5) | \(f\left({x}^{*}\right)=2600;\) | \({[-100, 100]}^{d}\) |
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aguirre, N., Cuevas, E., Luque-Chang, A. et al. An improved swarm optimization algorithm using exploration and evolutionary game theory for efficient exploitation. J Supercomput 81, 574 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-025-07007-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-025-07007-1
Keywords
Profiles
- Nahum Aguirre View author profile