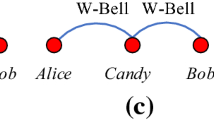
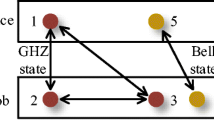
Abstract
Quantum wireless multi-hop networks are a fundamental component of the global quantum communication infrastructure. However, existing quantum communication protocols are constrained by limitations in capacity and efficiency, primarily due to their reliance on a single degree of freedom for encoding quantum information. In contrast, the protocol presented in this study leverages hyperentangled Bell states across both polarization and spatial-mode degrees of freedom, thereby overcoming these limitations. Compared to traditional approaches that employ bipartite entanglement within a single polarization degree of freedom, the proposed protocol significantly enhances the communication capacity. This innovative approach not only improves the overall efficiency of quantum communication but also contributes to the scalability of quantum multi-hop networks, offering a promising solution to the challenges encountered by current quantum communication protocols.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Cheng S-T, Wang C-Y, Tao M-H (2005) Quantum communication for wireless wide-area networks. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 23(7):1424–1432
Li Z-Z, Xu G, Chen X-B, Sun X, Yang Y-X (2016) Multi-user quantum wireless network communication based on multi-qubit ghz state. IEEE Commun Lett 20(12):2470–2473
Yu X-T, Xu J, Zhang Z-C (2012) Routing protocol for wireless ad hoc quantum communication network based on quantum teleportation
Yu X-T, Xu J, Zhang Z-C (2013) Distributed wireless quantum communication networks. Chin Phys B 22(9):090311
Wang K, Yu X-T, Lu S-L, Gong Y-X (2014) Quantum wireless multihop communication based on arbitrary bell pairs and teleportation. Phys Rev A 89(2):022329
Wang K, Gong Y-X, Yu X-T, Lu S-L (2014) Addendum to “quantum wireless multihop communication based on arbitrary bell pairs and teleportation’’. Phys Rev A 90(4):044302
Gao X-Q, Zhang Z-C, Sheng B (2018) Multi-hop teleportation in a quantum network based on mesh topology. Front Phys 13:1–7
Shi L-H, Yu X-T, Cai X-F, Gong Y-X, Zhang Z-C (2015) Quantum information transmission in the quantum wireless multihop network based on werner state. Chin Phys B 24(5):050308
Xiong P-Y, Yu X-T, Zhang Z-C, Zhan H-T, Hua J-Y (2017) Routing protocol for wireless quantum multi-hop mesh backbone network based on partially entangled ghz state. Front Phys 12:1–10
Xiong P-Y, Yu X-T, Zhan H-T, Zhang Z-C (2016) Multiple teleportation via partially entangled ghz state. Front Phys 11:1–8
Zhan H-T, Yu X-T, Xiong P-Y, Zhang Z-C (2016) Multi-hop teleportation based on w state and epr pairs. Chin Phys B 25(5):050305
Zhang Z, Wang J, Sun M (2018) Multihop teleportation via the composite of asymmetric w state and bell state. Int J Theor Phys 57:3605–3620
Zou Z-Z, Yu X-T, Gong Y-X, Zhang Z-C (2017) Multihop teleportation of two-qubit state via the composite ghz-bell channel. Phys Lett A 381(2):76–81
Zhou X-Z, Yu X-T, Zhang Z-C (2018) Multi-hop teleportation of an unknown qubit state based on w states. Int J Theor Phys 57:981–993
Cai X-F, Yu X-T, Shi L-H, Zhang Z-C (2014) Partially entangled states bridge in quantum teleportation. Front Phys 9:646–651
Barreiro JT, Langford NK, Peters NA, Kwiat PG (2005) Generation of hyperentangled photon pairs. Phys Rev Lett 95(26):260501
Ren B-C, Deng F-G (2014) Hyper-parallel photonic quantum computation with coupled quantum dots. Sci Rep 4(1):4623
Ren B-C, Wang G-Y, Deng F-G (2015) Universal hyperparallel hybrid photonic quantum gates with dipole-induced transparency in the weak-coupling regime. Phys Rev A 91(3):032328
Li T, Long G-L (2016) Hyperparallel optical quantum computation assisted by atomic ensembles embedded in double-sided optical cavities. Phys Rev A 94(2):022343
Wei H-R, Deng F-G, Long GL (2016) Hyper-parallel toffoli gate on three-photon system with two degrees of freedom assisted by single-sided optical microcavities. Opt Express 24(16):18619–18630
Ren B-C, Deng F-G (2017) Robust hyperparallel photonic quantum entangling gate with cavity qed. Opt Express 25(10):10863–10873
Sheng Y-B, Deng F-G, Long GL (2010) Complete hyperentangled-bell-state analysis for quantum communication. Phys Rev A-Atomic, Mol , and Opt Phys 82(3):032318
Ren B-C, Wei H-R, Hua M, Li T, Deng F-G (2012) Complete hyperentangled-bell-state analysis for photon systems assisted by quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Opt Express 20(22):24664–24677
Wang T-J, Lu Y, Long GL (2012) Generation and complete analysis of the hyperentangled bell state for photons assisted by quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Phys Rev A-Atomic, Mol , and Opt Phys 86(4):042337
Liu Q, Zhang M (2015) Generation and complete nondestructive analysis of hyperentanglement assisted by nitrogen-vacancy centers in resonators. Phys Rev A 91(6):062321
Wang M, Yan F, Gao T (2018) Deterministic state analysis for polarization-spatial-time-bin hyperentanglement with nonlinear optics. Laser Phys Lett 15(12):125206
Wang G-Y, Ren B-C, Deng F-G, Long G-L (2019) Complete analysis of hyperentangled bell states assisted with auxiliary hyperentanglement. Opt Express 27(6):8994–9003
Li X-H, Ghose S (2017) Hyperentangled bell-state analysis and hyperdense coding assisted by auxiliary entanglement. Phys Rev A 96(2):020303
Li X-H, Ghose S (2016) Self-assisted complete maximally hyperentangled state analysis via the cross-kerr nonlinearity. Phys Rev A 93(2):022302
Zheng Y, Liang L, Zhang M (2019) Error-heralded generation and self-assisted complete analysis of two-photon hyperentangled bell states through single-sided quantum-dot-cavity systems. Sci China Phys , Mech & Astron 62:1–9
Huang C-X, Hu X-M, Liu B-H, Zhou L, Sheng Y-B, Li C-F, Guo G-C (2022) Experimental one-step deterministic polarization entanglement purification. Sci Bull 67(6):593–597
Yasir PA, Chandrashekar C (2022) Generation of hyperentangled states and two-dimensional quantum walks using j or q plates and polarization beam splitters. Phys Rev A 105(1):012417
Zhao P, Yang M-Y, Zhu S, Zhou L, Zhong W, Du M-M, Sheng Y-B (2023) Generation of hyperentangled state encoded in three degrees of freedom. Sci China Phys, Mech & Astron 66(10):100311
Zhao P, Yang M-Y, Zhu S, Zhou L, Zhong W, Du M-M, Sheng Y-B (2023) Generation of hyperentangled state encoded in three degrees of freedom. Sci China Phys, Mech & Astron 66(10):100311
Zhao P, Ying J-W, Yang M-Y, Zhong W, Du M-M, Shen S-T, Li Y-X, Zhang A-L, Zhou L, Sheng Y-B (2024) Direct generation of multi-photon hyperentanglement. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.08790
Wang M, Guo H, Yan F, Gao T (2023) Quantum remote implementation with polarization-temporal hyperentanglement. Phys Rev Appl 20(4):044016
Lu H-H, Alshowkan M, Myilswamy KV, Weiner AM, Lukens JM, Peters NA (2023) Generation and characterization of ultrabroadband polarization-frequency hyperentangled photons. Opt Lett 48(22):6031–6034
Wang X-L, Cai X-D, Su Z-E, Chen M-C, Wu D, Li L, Liu N-L, Lu C-Y, Pan J-W (2015) Quantum teleportation of multiple degrees of freedom of a single photon. Nature 518(7540):516–519
Wang G-Y, Ai Q, Ren B-C, Li T, Deng F-G (2016) Error-detected generation and complete analysis of hyperentangled bell states for photons assisted by quantum-dot spins in double-sided optical microcavities. Opt Express 24(25):28444–28458
Wang T-J, Song S-Y, Long GL (2012) Quantum repeater based on spatial entanglement of photons and quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Phys Rev A-Atomic, Mol , Opt Phys 85(6):062311
Kwiat PG, Weinfurter H (1998) Embedded bell-state analysis. Phys Rev A 58(4):2623
Walborn S, Pádua S, Monken C (2003) Hyperentanglement-assisted bell-state analysis. Phys Rev A 68(4):042313
Schuck C, Huber G, Kurtsiefer C, Weinfurter H (2006) Complete deterministic linear optics bell state analysis. Phys Rev Lett 96(19):190501
Barbieri M, Vallone G, Mataloni P, De Martini F (2007) Complete and deterministic discrimination of polarization bell states assisted by momentum entanglement. Phys Rev A-Atomic, Mol, Opt Phys 75(4):042317
Zeng Z, Zhu K-D (2020) Complete hyperentangled bell state analysis assisted by hyperentanglement. Laser Phys Lett 17(7):075203
Zeng Z, Zhu K-D (2020) Complete hyperentangled state analysis using weak cross-kerr nonlinearity and auxiliary entanglement. New J Phys 22(8):083051
Sheng Y-B, Deng F-G (2010) Deterministic entanglement purification and complete nonlocal bell-state analysis with hyperentanglement. Phys Rev A-Atomic, Mol, Opt Phys 81(3):032307
Sheng Y-B, Deng F-G (2010) One-step deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys Rev A-Atomic, Mol, and Opt Phys 82(4):044305
Li X-H (2010) Deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys Rev A-Atomic, Mol, and Opt Phys 82(4):044304
Deng F-G (2011) One-step error correction for multipartite polarization entanglement. Phys Rev A-Atomic, Mol, Opt Phys 83(6):062316
Sheng Y-B, Zhou L (2014) Deterministic polarization entanglement purification using time-bin entanglement. Laser Phys Lett 11(8):085203
Ren B-C, Du F-F, Deng F-G (2014) Two-step hyperentanglement purification with the quantum-state-joining method. Phys Rev A 90(5):052309
Wang G-Y, Liu Q, Deng F-G (2016) Hyperentanglement purification for two-photon six-qubit quantum systems. Phys Rev A 94(3):032319
Wang M, Yan F, Gao T (2020) Entanglement purification of two-photon systems in multiple degrees of freedom. Quantum Inf Process 19:1–18
Du F-F, Li T, Long G-L (2016) Refined hyperentanglement purification of two-photon systems for high-capacity quantum communication with cavity-assisted interaction. Ann Phys 375:105–118
Hu X-M, Huang C-X, Sheng Y-B, Zhou L, Liu B-H, Guo Y, Zhang C, Xing W-B, Huang Y-F, Li C-F et al (2021) Long-distance entanglement purification for quantum communication. Phys Rev Lett 126(1):010503
Ecker S, Sohr P, Bulla L, Huber M, Bohmann M, Ursin R (2021) Experimental single-copy entanglement distillation. Phys Rev Lett 127(4):040506
Huang C-X, Hu X-M, Liu B-H, Zhou L, Sheng Y-B, Li C-F, Guo G-C (2022) Experimental one-step deterministic polarization entanglement purification. Sci Bull 67(6):593–597
Cozzolino D, Da Lio B, Bacco D, Oxenløwe LK (2019) High-dimensional quantum communication: benefits, progress, and future challenges. Adv Quantum Technol 2(12):1900038
Wu X-D, Zhou L, Zhong W, Sheng Y-B (2020) High-capacity measurement-device-independent quantum secure direct communication. Quantum Inf Process 19:1–14
Li L-Y, Wang T-J, Wang C (2020) The analysis of high-capacity quantum secure direct communication using polarization and orbital angular momentum of photons. Mod Phys Lett B 34(02):2050017
Zhao R-T, Cheng L-L (2020) High capacity information transmission with single-photon in polarization and spatial mode degrees of freedom over a collective noisy channel. Laser Phys 30(6):065204
Pan H-M (2020) Improvement of high-capacity three-party quantum secret sharing with single photons in both the polarization and the spatial-mode degrees of freedom. Int J Theor Phys 59(7):2208–2213
Lai H, Pieprzyk J, Luo M-X, Zhan C, Pan L, Orgun MA (2020) High-capacity (2, 3) threshold quantum secret sharing based on asymmetric quantum lossy channels. Quantum Inf Process 19(5):157
Amitonova LV, Tentrup TB, Vellekoop IM, Pinkse PW (2020) Quantum key establishment via a multimode fiber. Opt Express 28(5):5965–5981
Khorasani FM, Houshmand M, Anzabi-Nezhad NS (2020) Authenticated controlled quantum secure direct communication protocol based on five-particle brown states. Int J Theor Phys 59(5):1612–1622
Nape I, Otte E, Vallés A, Rosales-Guzmán C, Cardano F, Denz C, Forbes A (2018) Self-healing high-dimensional quantum key distribution using hybrid spin-orbit bessel states. Opt Express 26(21):26946–26960
Nawaz M, Ikram M et al (2018) Remote state preparation through hyperentangled atomic states. J Phys B: Atomic, Mol Opt Phys 51(7):075501
Cañas G, Vera N, Cariñe J, González P, Cardenas J, Connolly P, Przysiezna A, Gómez E, Figueroa M, Vallone G et al (2017) High-dimensional decoy-state quantum key distribution over multicore telecommunication fibers. Phys Rev A 96(2):022317
Steinlechner F, Ecker S, Fink M, Liu B, Bavaresco J, Huber M, Scheidl T, Ursin R (2017) Distribution of high-dimensional entanglement via an intra-city free-space link. Nat Commun 8(1):1–7
Williams BP, Sadlier RJ, Humble TS (2017) Superdense coding over optical fiber links with complete bell-state measurements. Phys Rev Lett 118(5):050501
Zeng H, Du M-M, Zhong W, Zhou L, Sheng Y-B (2024) High-capacity device-independent quantum secure direct communication based on hyper-encoding. Fundam Res 4(4):851–857
Sheng Y-B, Zhou L, Long G-L (2022) One-step quantum secure direct communication. Sci Bull 67(4):367–374
Zhou L, Sheng Y-B (2022) One-step device-independent quantum secure direct communication. Sci China Phys, Mech & Astron 65(5):250311
Ying J-W, Zhou L, Zhong W, Sheng Y-B (2022) Measurement-device-independent one-step quantum secure direct communication. Chin Phys B 31(12):120303
Lo H-K, Chau HF (1999) Unconditional security of quantum key distribution over arbitrarily long distances. Science 283(5410):2050–2056
Bennett CH, Brassard G, Popescu S, Schumacher B, Smolin JA, Wootters WK (1996) Purification of noisy entanglement and faithful teleportation via noisy channels. Phys Rev Lett 76(5):722
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Youth Fund Project of Beijing Wuzi University (No. 2022XJQN21), and R&D Program of Beijing Municipal Education Commission(KM202310037003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Confict of interest
The authors declare that they have no confict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Yang, Y. & Su, Y. High-capacity quantum wireless multi-hop network communication based on hyperentangled Bell states. J Supercomput 81, 641 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-025-07082-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-025-07082-4