Abstract
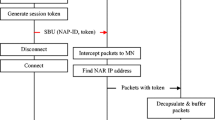
In the all-IP wireless networks, mobility management is a crucial issue, and it can be operated at different layers in the traditional Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) stack. Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is an application layer protocol used for the signaling and the mobility management without any modifications of the lower layer protocols, especially in the voice over IP environment. However, since it always gets the lowest priority in the networking model, it will produce the large handoff latency, the packet loss, and the handoff blocking probability. To provide an efficient mobility management, SIP can be combined with other protocols. In this paper, we propose a cross-layer mobility management scheme based on SIP and the Host Identity Protocol (HIP) which is a new protocol designed to provide secure and continuous communications between two nodes by separating the identifier and the locator roles of the traditional IP address. In the proposed scheme, the mobile node and the correspondent node use their host identity tags to establish the session connections, and the mobile nodes uses the HIP location update scheme instead of the SIP location update scheme to update its IP address when it moves to a new subnet. We discuss the proposed scheme’s architecture and the major mobility procedures, including the session setup, the handoff and the location update in this paper. We also develop an analytical model to study the handoff performance of the proposed scheme, the typical SIP, and the hybrid SIP/Mobile IP, respectively. The analytical results demonstrate that the proposed scheme outperforms the typical SIP and the hybrid SIP/Mobile IP in terms of the handoff latency, the packet loss, and the handoff blocking probability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Handley, M., Schulzrinne, H., Schooler, E., & Rosenberg, J. (1999). SIP: session initiation protocol. IETF RFC 2543.
Perkins, C. E., Patil, B., & Roberts, P. (2002). IP mobility support for IPv4. IETF RFC 3220.
Johnson, D. B., Perkins, C. E., & Arkko, J. (2004). Mobility support in IPv6. IETF RFC 3775.
Le, D., Fu, X., & Hogrefe, D. (2006). A review of mobility support paradigms for the Internet. IEEE Communications Survey & Tutorials, 8(1), 38–51.
Stewart, R., Xie, Q., Morneault, K., Sharp, C., Schwarzbauer, H., Taylor, T., Rytina, I., Kalla, M., Zhang, L., & Paxson, V. (2000). Stream control transmission protocol. IETF RFC 2960.
Kempf, J. (2007). Goals for network-based localized mobility management. IETF RFC 4831.
Balakrishnan, H., Lakshminarayanan, K., Ratnasamy, S., Shenker, S., Stoica, I., & Walfish, M. (2004). A layered naming architecture for the Internet. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 34(4), 343–352.
Moskowitz, R., & Nikander, P. (2006). Host identity protocol (HIP) architecture. IETF RFC 4423.
Moskowitz, R., Nikander, P., Jokela, P., & Henderson, T. R. (2007). Host identity protocol. IETF Internet Draft, draft-ietf-hip-base-09.
Jokela, P., Moskowitz, R., & Nikander, P. (2007). Using ESP transport format with HIP. IETF Internet Draft, draft-ietf-hip-esp-06.
Henderson, T. (2007). End-host mobility and multihoming with the host identity protocol. IETF Internet Draft, draft-ietf-hip-mm-05.
Nikander, P., & Laganier, J. (2007). Host identity protocol (HIP) domain name system (DNS) extensions. IETF Internet Draft, draft-ietf-hip-mm-dns-09.
Laganier, J., & Eggert, L. (2006). Host identity protocol (HIP) rendezvous extension. IETF Internet Draft, draft-ietf-hip-rvs-05.
Tschofenig, H., Ott, J., Schulzrinne, H., Henderson, T. R., & Camarillo, G. (2007). Interaction between SIP and HIP. IETF Internet Draft, draft-tschofenig-hiprg-host-identities-05.
Politis, C., Chew, K. A., & Tafazolli, R. (2003). Multilayer mobility management for all-IP networks: pure SIP vs. hybrid SIP/mobile IP. The 57th IEEE Semiannual Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC’2003-Spring) (vol. 4, pp. 2500–2504), Jeju, Korea.
Jung, J., Mudumbai, R., Montgomery, D., & Kahng, H. (2003). Performance evaluation of two layered mobility management using mobile IP and session initiation protocol. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference (GLOBECOM’2003) (vol. 3, pp. 1190–1194), San Francisco, USA.
Wang, Q., Abu-Rgheff, M. A., & Akram, A. (2004). Design and evaluation of an integrated mobile IP and SIP framework for advanced handoff management. In The 2004 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC’2004) (pp. 3921–3925), Paris, France.
Wong, K. D., Dutta, A., Burns, J., Jain, R., & Young, K. (2003). A multilayered mobility management scheme for auto-configured wireless IP networks. IEEE Wireless Communications, 10(5), 62–69.
Politis, C., Chew, K. A., Akhtar, N., Georgiades, M., & Tafazolli, R. (2004). Hybrid multilayer mobility management with AAA context transfer capabilities for all-IP networks. IEEE Wireless Communications, 11(4), 76–88.
Faccin, S. M., Lalwaney, P., & Patil, B. (2004). IP multimedia services: analysis of mobile IP and SIP interactions in 3G networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 42(1), 113–120.
Wang, Q., & Abu-Rgheff, M. A. (2006). Mobility management architectures based on joint mobile IP and SIP protocols. IEEE Wireless Communications, 13(6), 68–76.
Laganier, J., Koponen, T., & Eggert, L. (2006). Host identity protocol (HIP) registration extension. IETF Internet Draft, draft-ietf-hip-registration-02.
Bao, G. (1996). Performance evaluation of TCP/RLP protocol stack over CDMA wireless link. Journal of Wireless Networks (WINET), 2(3), 229–237.
Makaya, C., & Pierre, S. (2008). An analytical framework for performance evaluation of IPv6-based mobility management protocols. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 7(3), 972–983.
Mohanty, S., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2007). Performance analysis of handoff techniques based on mobile IP, TCP-migrate, and SIP. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 6(7), 731–747.
Akan, O. B., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2004). ATL: an adaptive transport layer suite for next-generation wireless Internet. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 22(5), 802–817.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Zhou, H., Qin, Y. et al. SHIP: Cross-layer mobility management scheme based on Session Initiation Protocol and Host Identity Protocol. Telecommun Syst 42, 5–15 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-009-9164-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-009-9164-y