Abstract
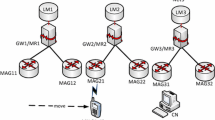
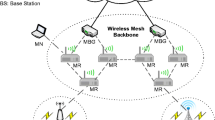
Routing optimization (RO) is an important support for Mobile IPv6 while performing handover. It can reduce the overhead of a home agent and make the traffic more fluent between MN and CN; however, Network Mobility (NEMO) in Mobile IPv6 lacks the capability of RO. In this paper, we propose an enhanced architecture by deploying Home Agents Location Registration Agents (HALRA) on cellular data switch (3G/B3G) network incorporating with Distributed Home Agents (NEMO-DHA) on NEMO for a Mobility Critical Area. Under this architecture, it can provide less handoff latency on the Mobility Critical Area and make a detour to avoid the perplexed NEMO routing optimization problem. Moreover, NEMO-DHA can also solve a sort of Nested-NEMO problems by setting authorized Mobile Routers to serve as a set of Distributed Home Agent, and we provides a Cross-Layer suggestion by utilizing R-bit to schedule fairly for NEMO connections. The wireless network can also benefit from Distributed Home Agents by cooperating cellular data switch network with sharing HALR resource. Most models in the paper are described through UML modeling language evaluated by a mathematical model and simulated by NS2-Mobiwan2 (http://www.ti-wmc.nl/, 2009).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson, D., Perkins, C., Arkko, J. (2004). Mobility support in IPv6. RFC 3775, June 2004.
Devarapalli, V., Wakikawa, R., Petrescu, A., & Thubert, P. (2005). NEMO basic support protocol. RFC 3963, Jan 2005.
Nuorvala, V., Petander, H., & Tuominen, A. (2005). MIPL mobile IPv6 for Linux, Feb 2005. http://www.mobile-ipv6.org/.
KAME, SHISA, Dec. 2004. http://www.mobileip.jp/.
Nautilus6. www.nautilus6.org.
Manner, J., & Kojo, M. (2004). Mobility related terminology. RFC 3753, June 2004.
Futuresoft protocol stacks. www.futsoft.com.
Ng, C., Thubert, P., & Ohnishi, H. (2005). Taxonomy of route optimization models in the NEMO Context. Draft 04, Feb 2005.
Zhao, F., Wu, S.F., Davis, U.C., Jung, S. (2005). NEMO route optimization problem statement and analysis. Draft 1, Feb 2005.
Watari, M., & Ernst, T. (2004). Route optimization with nested correspondent nodes. Draft 00, Oct 2004.
Clausen, T., Baccelli, E., & Wakikawa, R. (2004). NEMO route optimization problem statement. Draft 0, Oct 2004.
Thubert, P., Wakikawa, R., & Devarapalli, V. (2005). Global HA to HA protocol. Draft 01, Oct 2005.
Paik, E. K., Cho, H.-S., Ernst, T., & Choi, Y. (2004). Load sharing and session preservation with multiple mobile routers for large scale network mobility. Advanced information networking and applications.
Esaki, H. (2004). Multi-homing and multi-path architecture using mobile IP and NEMO framework. Symposium on Applications and the Internet.
Yen, Y.-S., Hsu, C.-C., & Chao, H.-C. (2004). Dynamic home agent discovery by global network anycast on mobile IPv6. TANET.
Hinden, R., & Deering, S. (2006). Internet protocol version 6 addressing architecture. RFC4291, Feb 2006.
Ng, C., Paik, E., & Ernst, T. (2007). Analysis of multihoming in network mobility support. Draft 07, Feb 2007.
Galli, S., Morera, R., & McAuley, A. (2004). An analytical approach to the performance evaluation of mobility protocols: the handoff delay case. In IEEE vehicular technology conference, VTC’04, May 2004.
Thubert, P., & Moteni, M. (2007). IPv6 reverse routing header and its application to mobile networks. Draft 07, Feb 2007.
Ng, C., & Hirano, J. (2004). Securing nested tunnels optimization with access router option. Draft 01, Jul 2004.
Website (2009). http://www.ti-wmc.nl/.
Shakkottai, S., Rappaport, T. S., & Karlsson, P. C. (2003). Cross-layer design for wireless networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, Oct. 2003.
Tseng, C.-C. et al. (2005). Topology-aided cross-layer fast handoff designs for IEEE 802.11/mobile IP environments. IEEE Communication Magazine, 43(12), 156–163.
Zhu, F., & McNair, J. (2005). Cross layer design for mobile IP handoff. In IEEE VTC ’05-Spring (vol. 4, pp. 2255–2259). May–June 2005.
Han, Y.-H., Jang, H., Choi, J.-H., Park, B., & McNair, J. (2007). A cross-layering design for IPv6 fast handover support in an IEEE 802.16e wireless MAN. IEEE Network, November/December 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, CS., Lin, F. & Chao, HC. Routing optimization over network mobility with distributed home agents as the cross layer consideration. Telecommun Syst 42, 63–76 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-009-9169-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-009-9169-6