Abstract
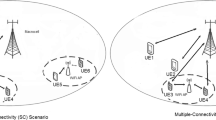
It is envisaged that next generation wireless networks (NGWN) will be heterogeneous, consisting of multiple radio access technologies (RATs) coexisting in the same geographical area. In these heterogeneous wireless networks, mobile terminals of different capabilities (heterogeneous terminals) will be used by subscribers to access network services. We investigate the effect of using heterogeneous mobile terminals (e.g. single-mode, dual-mode, triple-mode, etc.) on call blocking and call dropping probabilities in cooperative heterogeneous wireless networks. We develop analytical models for heterogeneous mobile terminals and joint radio resource management in heterogeneous wireless networks. Using a two-class three-RAT heterogeneous wireless network as an example, the effect of using heterogeneous terminals in the network is evaluated. Results show the overall call blocking/dropping probability experienced by subscribers in heterogeneous wireless networks depends on the capabilities of mobile terminals used by the subscribers. In the worst case scenario, when all subscribers use single-mode mobile terminals, each subscriber is confined to a single RAT and consequently, joint radio resource management in heterogeneous wireless network has no improvement on new call blocking and handoff call dropping probabilities. However, in the best case scenario, when all subscribers use three-mode terminals, new class-1 call blocking probability decreases from 0.37 (for 100% single-mode terminals) to 0.05, at the arrival rate of 6 calls per minute. New class-2 call blocking probability also decreases from 0.8 to 0.52. Similarly, handoff class-1 call dropping probability decreases from 0.14 to 0.003, and handoff class-2 call dropping probability decreases from 0.44 to 0.09.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Wu, G., Mizuno, M., & Havinga, P. J. M. (2002). MIRAI architecture for heterogeneous network. IEEE Communications Magazine 40(2), 126–134.
Pérez-Romero, J., Sallent, O., Agustí, R., & Díaz-Guerra, M. A. (2005). Radio resource management strategies in UMTS. New York: Wiley.
Falowo, O. E., & Chan, H. A. (2007). Joint call admission control algorithms: requirements, approaches, and design considerations. Computer Communications, 31(6), 1200–1217. doi:10.1016/j.comcom.2007.10.044.
Niyato, D., & Hossain, E. (2008). Noncooperative game-theoretic framework for radio resource management in 4G heterogeneous wireless access networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 7(3), 332–345.
Gelabert, X., Pérez-Romero, J., Sallent, O., & Agustí, R. (2008). A Markovian approach to radio access technology selection in heterogeneous multiaccess/multiservice wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 7(10), 1257–1270.
Hasib, A., & Fapojuwo, A. O. (2008). Analysis of common radio resource management scheme for end-to-end QoS support in multiservice heterogeneous wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 57(4).
Yiping, C., & Yuhang, Y. (2007). A new 4G architecture providing multimode terminals always best connected services. IEEE Wireless Communications, April 2007.
Frattasi, S., Fathi, H., Fitzek, F. H. P., Prasad, R., & Katz, M. D. (2006). Defining 4G technology from the user’s perspective. IEEE Network, January/February 2006.
Song, W., & Zhuang, W. (2009). Multi-service load sharing for resource management in the cellular/WLAN integrated network. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 8(2), 725–735.
Buljore, S., Harada, H., Filin, S., Houze, P., Tsagkaris, K., Holland, O., Nolte, K., Farnham, T., & Ivanov, V. (2009). Architecture and enablers for optimized radio resource usage in heterogeneous wireless access networks: The IEEE 1900.4 Working Group. Communications Magazine, IEEE, 47(1), 122–129.
Lee, S., Sriram, K., Kim, K., Kim, Y., & Golmie, N. (2009). Vertical handoff decision algorithms for providing optimized performance in heterogeneous wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(2), 865–881.
Vanem, E., Svaet, S., & Paint, F. (2003). Effects of multiple access alternatives in heterogeneous wireless networks. IEEE Wireless and Networking, 3, 1696–1700.
Furuskar, A., & Zander, J. (2005). Multiservice allocation for multi-access wireless systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 4(Jan.), 174–184.
Falowo, O. E., & Chan, H. A. (2007). Adaptive bandwidth management and joint call admission control to enhance system utilization and QoS in heterogeneous wireless networks. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2007(3), 1–11. doi:10.1155/2007/34378.
Zhang, W. (2005). Performance of real-time and data traffic in heterogeneous overlay wireless networks. In: Proceedings of the 19th international teletraffic congress (ITC 19), Beijing, 2005.
Pillekeit, A., Derakhshan, F., Jugl, E., & Mitschele-Thiel, A. (2004). Force-based load balancing in co-located UMTS/GSM networks, VTC 2004-Fall. In: 2004 IEEE 60th (Vol. 6, pp. 4402–4406), September 26–29.
Vidales, P., Baliosian, J., Serrat, J., Mapp, G., Stajano, F., & Hopper, A. (2005). Autonomic system for mobility support in 4G networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 23(12), 2288–3204.
Lincke, S. J. (2005). Vertical handover policies for common radio resource management. International Journal of Communication 18, 527–543.
Holma, H., & Toskala, A. (2001). WCDMA for UMTS (2nd edn.). New York: Wiley.
Pla, V., Giménez-Guzmány, J. M., Martínez, J., & Casares-Giner, V. (2004). Optimal admission control using handover prediction in mobile cellular networks. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international working conference on performance modelling and evaluation of heterogeneous networks (HET-NETs ’04), Ilkley, West Yorkshire, UK, July 2004.
Kesidis, G., Walrand, J., & Chang, C.-S. (1993). Effective bandwidths for multi-class Markov fluids and other ATM sources. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 4(4), 424–428.
Ga̧bowski, M., Stasiak, M., Wísniewski, A., & Zwierzykowski, P. (2005). Uplink blocking probability calculation for cellular systems with WCDMA radio interface, finite source population and differently loaded neighbouring cells. In: Proceedings of the 11th Asia-Pacific conference on communications (APCC ’05), Perth, Western Australia, October 2005, pp. 138–142.
Nasser, N., & Hassanein, H. (2004). Dynamic threshold-based call admission framework for prioritized multimedia traffic in wireless cellular networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE global telecommunications conference (GLOBECOM ’04) (Vol. 2, pp. 644–649), Dallas, Texas, USA, November-December, 2004.
Guo, Y., & Chaskar, H. (2002). Class-based quality of service over air interfaces in 4G mobile networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 40(3), 132–137.
Chung, S.-P., & Lee, J.-C. (2005). Performance analysis and overflowed traffic characterization in multi-service hierarchical wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 4(3), 904–918.
Houeto, F., & Pierre, S. (2004). Characterization of jitter and admission control in multi-service networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 8(2), 125–127.
Fettweis, G. (2009). Current frontiers in wireless communications: fast & green & dirty. In: IEEE wireless communications & networking conference (WCNC), Budapest, Hungary, April 5–8, 2009.
Wang, J., Zeng, Q.-A., & Agrawal, D. P. (2003). Performance analysis of a pre-emptive and priority reservation handoff scheme. Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2(1), 65–75.
Bo, X., & Chen, Z. (2004). On call admission and performance evaluation for multi-service CDMA networks. ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review, 8(1), 98–108.
Orlik, P. V., & Rappaport, S. S. (2001). On the handoff arrival process in cellular communications. Wireless Networks, 7(2), 147–157.
Bertsekas, D. P., & Tsitsiklis, J. N. (2002). Introduction to probability. Belmont: Athena Scientific.
Falowo, O. E., & Chan, H. A. (2009). Effect of mobile terminal heterogeneity on connection-level QoS in next generation wireless networks. In: Proceedings of 22nd Canadian conference on electrical and computer engineering (CCECE 2009), St. John’s, Newfoundland, Canada, 3–6 May 2009, ISBN: 978-1-4244-3508-1, ISSN: 0840-7789.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work is supported in part by Telkom, Nokia Siemens Networks, TeleSciences, and National Research Foundation, South Africa, under the Broadband Center of Excellence program.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falowo, O.E., Chan, H.A. Effect of mobile terminal heterogeneity on call blocking/dropping probability in cooperative heterogeneous cellular networks. Telecommun Syst 47, 337–349 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-010-9322-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-010-9322-2