Abstract
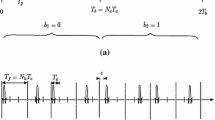
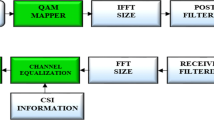
In this paper, the architecture of a low-complexity Direct Sequence Ultra-Wideband (DS-UWB) receiver subsystem which incorporates a Channel Estimator (CE) and a novel hybrid Partial/Selective (HPS) maximal ratio combining (MRC) RAKE receiver is presented. Three different design techniques followed by FPGA implementation are investigated and compared and system performance results are provided. The proposed architectures combine the benefits of both partial and selective RAKE receiver algorithms and the obtained results demonstrate the trade-off between energy capture, performance and receiver complexity. All design approaches focus on a highly parallel, modular and optimized for high performance system which is necessary for demanding and low-cost applications of UWB communications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nikoogar, H., & Prasad, R. (2009). Introduction to ultra wideband for wireless communications. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 978-1-4020-6632-0.
Fisher, R., Kohno, R., McLaughlin, M., & Welborn, M. (2005). DS-UWB physical layer submission to IEEE 802.15 Task Group 3a (P802.15-04/0137r4). IEEE P802.15, Jan.
Zhang, J., Kennedy, R. A., & Abhayapala, T. D. (2003). Conditions and performance of ideal RAKE reception for ultra-wideband signals in lognormal fading channels. International Journal of Wireless Information Networks, 10(4), 193–200.
Win, M. Z., & Scholtz, R. A. (1998). On the energy capture of ultra-wide bandwidth signals in dense multipath environments. IEEE Communications Letters, 2(9), 245–247.
Cassioli, D., Win, M. Z., Vatalaro, F., & Molisch, A. (2002). Performance of low-complexity rake reception in a realistic UWB channel. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on communications, ICC’02 (Vol. 2, pp. 763–767). Aug. 2002.
Thomos, C., & Kalivas, G. (2010). FPGA-based architecture of a DS-UWB Channel Estimator and RAKE Receiver employing a hybrid selection scheme. In Proceedings of 17th IEEE international conference on telecommunications, ICT’10 (pp. 903–909). 4–7 April 2010.
Thomos, C., Papadopoulos, C., & Kalivas, G. (2010). Design and implementation of a low-complexity RAKE receiver and channel estimator for DS-UWB. In Proceedings of 15th IEEE mediterranean electrotechnical conference, MELECON’10 (pp. 93–98). 26–28 April 2010.
Xilinx Inc. (2010). ISE Design Suite. http://www.xilinx.com/tools/dsp.htm.
Xilinx Inc. (2010). Virtex-4 Family Overview. http://www.xilinx.com/.
Mielczarek, B., Wessman, M. O., & Svensson, A. (2003). Performance of coherent UWB rake receivers with channel estimators. In Proceeding of IEEE vehicular technology conference, VTC’04 (Vol. 3, pp. 1880–1884). Oct. 2003.
Eslami, M., & Dong, X. (2005). Rake-MMSE-equalizer performance for UWB. IEEE Communications Letters, 9(6), 502–504.
Parihar, A., Lampe, L., Schober, R., & Leung, C. (2005). Analysis of equalization for DS-UWB systems. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on ultra-wideband, ICUWB’05 (pp. 170–175). Sept. 2005.
Rajeswaran, A., Somayazulu, V. S., & Foerster, J. R. (2003). Rake performance for a pulse based UWB system in a realistic UWB indoor channel. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on communications, ICC’03 (Vol. 4, pp. 2879–2883). May 2003.
Zhang, L., & Yang, Ch. (2004). The equalization performance of RAKE receiver in UWB system. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on signal processing, ICSP’04 (Vol. 2, pp. 1723–1726). Sept. 2004.
Li, Q., & Rusch, L. A. (2003). Hybrid RAKE/multiuser receivers for UWB. In Proceedings of the IEEE radio and wireless conference, RAWCON’03 (pp. 203–206). August 2003.
Li, Y., Molisch, A. F., & Zhang, J. (2003). Channel estimation and signal detection for UWB. In IEEE wireless personal multimedia communications, WPMC’03. Oct. 2003.
Kim, S. W., Ha, D. S., & Reed, J. H. (2003). Minimum selection GSC and adaptive low-power rake combining scheme. In Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems, ISCAS’03 (Vol. 4, pp. 357–360). May 2003.
Gupta, P., Bansal, N., & Mallik, R. K. (2004). Analysis of minimum selection GSC in Rayleigh fading. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on communications, ICC’04 (Vol. 6, pp. 3364–3368). June 2004.
Alouini, M.-S., & Yang, H. C. (2005). Minimum estimation and combining generalized selection combining (MEC-GSC). In Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on information theory, ISIT’05 (pp. 578–582). Sept. 2005.
Li, W., Zhong, J., & Gulliver, T. A. (2005). A low complexity rake receiver for ultra-wideband systems. In Proceedings of IEEE vehicular technology conference, VTC’05 (Vol. 3, pp. 1393–1396). Sept. 2005.
Aranda, F. E., Brown, N., & Arslan, H. (2003). RAKE receiver finger assignment for ultra-wideband radio. In Proceedings of IEEE workshop on signal processing advances in wireless communications, SPAWC’03 (pp. 239–243). June 2003.
Yong, Y., Nenghai, Y., & Weijie, D. (2006). A research of UWB rake receiver based on novel RLS adaptive algorithm. Journal of Electronics, 23(3), 341–345.
Blazquez, R., Newaskar, P. P., & Lee, F. S. (2004). A baseband processor for pulsed ultra-wideband signals. In Proceedings of IEEE custom integrated circuits conference, CICC’04 (pp. 587–590). Oct. 2004.
O’Donnell, I. D., & Brodersen, R. W. (2006). A 2.3 mW baseband impulse-UWB transceiver front-end in CMOS. In Proceedings of IEEE symposium on VLSI circuits (pp. 200–202). June 2006.
Foerster, J. R. (2003). Channel modeling sub-committee report (final) (Technical Report P802.15-02/490rl-SG3a). IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs). Feb.
Newaskar, P. P., Blazquez, R., & Chandrakasan, A. P. (2004). A/D precision requirements for digital ultra-wideband radio receivers. Journal of VLSI Signal Processing, 39(1–2), 175–188.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomos, C., Kalivas, G. FPGA-based architecture and implementation techniques of a low-complexity hybrid RAKE receiver for a DS-UWB communication system. Telecommun Syst 52, 2115–2132 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-011-9489-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-011-9489-1