Abstract
In the current internet community, secure data transfer is limited due to its attack made on data communication. So more robust methods are chosen so that they ensure secured data transfer. One of the solutions which came to the rescue is the audio Steganography.
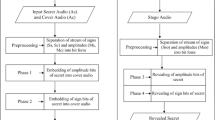
“A GA Based Audio Steganography with enhanced security” is one propose system which is based on audio Steganography and cryptography, ensures secure data transfer between the source and destination. Here we present a novel, principled approach to resolve the remained problems of substitution technique of audio Steganography. We use most powerful encryption algorithm (RSA) to encrypt message in the first level of security, which is very complex to break. In the second level, we use a more powerful GA based LSB (Least Significant Bit) Algorithm to encode the encrypted message into audio data. Here encrypted message bits are embedded into random and higher LSB layers, resulting in increased robustness against noise addition. The robustness specially would be increased against those intentional attacks which try to reveal the hidden message and also some unintentional attacks like noise addition as well. On the other hand, to reduce the distortion, GA operators are used.
The basic idea behind this paper is maintained randomness in message bit insertion into audio data for hiding the data from hackers and multi-objective GA is used to reduce distortion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Zamani, M., Manaf, A.A., Ahmad, R.B., Zeki, A.M., & Abdullah, S. (2009) A genetic-algorithm-based approach for audio steganography. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, 54.
Cvejic, N., & Seppänen, T. (2002). Increasing the capacity of LSB based audio steganography. In Proc. 5th IEEE international workshop on multimedia signal processing, St. Thomas, VI, December, 2002 (pp. 336–338).
Lee, Y. K., & Chen, L. H. (2000). High capacity image steganographic model. In IEEE proceedings vision, image and signal processing (pp. 288–294).
Pal, S. K., Saxena, P. K., & Mutto, S. K. (2002). The future of audio steganography. In Pacific Rim workshop on digital steganography, Japan.
Westfeld, A., & Pitzmann, A. (2000). Attacks on steganographic systems. : Vol. 1768. Lecture notes in computer science (pp. 61–75). Berlin: Springer.
Sridevi, R., Damodaram, A., & Narasimham, S. V. L. Efficient method of audio steganography by modified LSB algorithm and strong encryption key with enhanced security. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 2005–2009 JATIT.
Petitcolas, F. A. P., Anderson, R. J., & Kuhn, M. G. (1999). Information hiding—a survey. Proceedings of IEEE, 87(7), 1062–1078.
Cvejic, N., & Seppanen, T. (2004). Increasing robustness of LSB audio steganography using a novel embedding method. In International conference on information technology: coding and computing, The Orleans, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, April 5–7, 2004 (Vol. 2, pp. 533–537).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhowal, K., Bhattacharyya, D., Jyoti Pal, A. et al. A GA based audio steganography with enhanced security. Telecommun Syst 52, 2197–2204 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-011-9542-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-011-9542-0