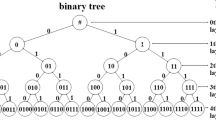
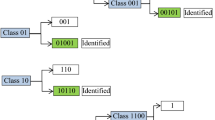
Abstract
RFID technology acts as a bridge to connect the physical world with the digital space, and RFID system is pervading our daily life in the last few years. The energy consumed by the reader and a tag in resolving the collisions caused by multiple tags is a key issue that affects life time of mobile reader and active tags, as well as the identification accuracy of passive tags. In this paper, the energy consumed by the reader and a tag in resolving the tag collision is examined for the commonly used RFID tag collision resolution protocols, including the frame slotted ALOHA based and the binary query tree based protocols. Numeric evaluation is also performed and the result verifies that regarding to energy consumption, the dynamic frame slotted ALOHA protocol for the Class-1 RFID system performs best among the frame slotted ALOHA protocols, and the modified binary query tree protocol also performs better than the standard binary query tree protocols.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Finkenzeller, K. (2003). RFID-handbook: fundamentals and applications in contactless smart cards and identification (2nd ed.). Swadlincote: Wiley.
Welbourne, E., Battle, L., et al. (2009). Building the Internet of things using RFID: the RFID ecosystem experience. IEEE Internet Computing, 13(3), 48–55.
Wolfram, G., Gampl, B., & Gabriel, P. (2008). The RFID roadmap: the next stpes for Europe. Berlin: Springer.
Wua, N. C., Nystrom, M.A., et al. (2006). Challenges to global RFID adoption. Technovation, 26(12), 1317–1323.
Jeffery, S. R., Franklin, M. J., & Gaorfalakis, M. (2008). An adaptive RFID middleware for supporting metaphysical data independence. The VLDB Journal, 17(3), 265–289.
Shih, D. H., Sun, P.L., et al. (2006). Taxonomy and survey of RFID anti-collision protocols. Computer Communications, 29(1), 2150–2156.
Zhou, F., Chen, C., et al. (2004). Evaluating and optimizing power consumption of anti-collision protocols for applications in RFID systems. In Proceedings of the 2004 international symposium on Low power electronics and design (pp. 357–362).
Namboodiri, V., & Gao, L. (2010). Energy-aware tag anticollision protocols for RFID systems. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 9(1), 44–59.
Abramsonm, N. (1970). The ALOHA system—another alternative for computer communications. In Proceeding of the 37th American Federation of Information Processing Societies computer conference, Houston, Texas, USA (pp. 281–285).
Roberts, L. G. (1975). ALOHA packet system with and without slots and capture. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 5(2), 28–42.
Schoute, F. C. (1983). Dynamic frame length ALOHA. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 31(4), 565–569.
Vogt, H. (2002). Multiple object identification with passive RFID tags. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on systems, man and cybernetics, Washington DC, USA (pp. 1854–1858).
Vogt, H. (2002). Efficient object identification with passive RFID tags. In Proceeding of the international conference on pervasive computing, LNCS. Berlin: Springer (pp. 98–113).
Cha, J. R., & Kim, J. H. (2006). Dynamic framed slotted ALOHA algorithms using fast tag estimation method for RFID system. In Proceeding of the 3rd IEEE conference on consumer communications and networking (pp. 768–772).
Law, C., Lee, K., & Sui, K. Y. (2000). Efficient memoryless protocol for tag identification. In Proceedings of the 4th international workshop on discrete algorithms and methods for mobile computing and communications (pp. 75–84).
Capentanakis, J. I. (1977). The multiple access broadcast channel: Protocol and capacity considration. Ph.D. Dissertation, Mass. Inst. Tech. Cambridge, MA.
Hayes, J. (1978). An adaptive technique for local distributation. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 26(8), 1178–1186.
Tsybakov, B. S., & Mikailov, V. A. (1978). Free synchronous packet access in a broadcast channel with feedback. Problemy Peredachi Infomatsii, 14(4), 32–59.
Hush, D. R., Wood, C. (1998). Analysis of tree algorithms for RFID arbitration. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE international symposium on information theory (p. 107).
Yan, X. Q., Yin, Z. P., & Xiong, Y. L. (2008). A comparative study on the performance of the RFID tag collision resolution protocols. In Proceeding of the 2nd international conference on future generation communication and networking (pp. 469–472).
McCanne, S., Floyd, S., et al., The network simulator NS-2, http://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The research of this paper is partly sponsored by the Science and Technology Research Project of He’nan Province (Grant No. 102102210223), the Program for Science & Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province (Grant No. 2011HASTIT020) and the Science Foundation for High Level Talents in North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Grant No. 200923).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, X., Liu, X. Evaluating the energy consumption of the RFID tag collision resolution protocols. Telecommun Syst 52, 2561–2568 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-011-9563-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-011-9563-8