Abstract
Ad hoc networks present a challenging network paradigm because of energy-limited mobile devices and the lack of a reliable backbone infrastructure. If users have a choice, they might not be willing to share battery lifetime to support the ad hoc infrastructure. Irregular distributions of devices also limit connectivity of devices in dense areas and require long distant communication. Furthermore, jammers may disturb the communication and compromise connectivity. We present a modulation scheme addressing all three problems by establishing communication without increasing transmission power while reducing the data rate. Our key method is to repeat symbols using additional pseudo-random phase shift keying. So, we increase the signal-to-noise ratio of the wireless channel above the reception threshold and remove the constraint of correlated interferences of parallel communication. We show a constant factor overhead for negotiating the initial data rate and establishing the connections.













Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Notes
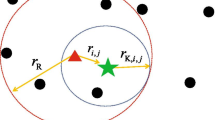
Standard techniques for local broadcast of hello-messages and multi-hop algorithms might be used to publish the attendance of a new node. The messages might be addressed to a dedicated ID receivable by all nodes.
References
Alsbih, A., Janson, T., & Schindelhauer, C. (2011). Analysis of peer-to-peer traffic and user behaviour. In Fourth International Conference on Internet Technologies & Applications (ITA 2011). Wales.
Awerbuch, B., Richa, A., & Scheideler, C. (2008). A jamming-resistant mac protocol for single-hop wireless networks. In Proceedings of the twenty-seventh ACM symposium on Principles of distributed computing (pp. 45–54). ACM.
Awerbuch, B., Richa, A., Scheideler, C., Schmid, S., & Zhang, J. (2014). Principles of robust medium access and an application to leader election. ACM Transactions on Algorithms, 10(4), 24:1–24:26. doi:10.1145/2635818.
Bentley, J. L., & Yao, A. C. C. (1976). An almost optimal algorithm for unbounded searching. Information Processing Letters, 5(3), 82–87. doi:10.1016/0020-0190(76)90071-5.
Chiang, J., & Hu, Y. C. (2011). Cross-layer jamming detection and mitigation in wireless broadcast networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 19(1), 286–298. doi:10.1109/TNET.2010.2068576.
Choi, J. I., Hong, S., Jain, M., Katti, S., Levis, P., & Mehlman, J. (2012). Beyond full duplex wireless. In 2012 Conference Record of the Forty Sixth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (ASILOMAR) (pp. 40–44). doi:10.1109/ACSSC.2012.6488954.
Ens, A., Janson, T., Reindl, L. M., & Schindelhauer, C. (2014). Robust multi-carrier frame synchronization for localization systems with ultrasound. In Proceedings of the 18th International OFDM Workshop 2014 (InOWo’14). Essen, Germany.
Gold, R. (1967). Optimal binary sequences for spread spectrum multiplexing. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 13(4), 619–621. doi:10.1109/TIT.1967.1054048.
Gudmundsdottir, H., Ásgeirsson, E. I., Bodlaender, M. H., Foley, J. T., Halldórsson, M. M., & Vigfusson, Y. (2014). Wireless scheduling algorithms in complex environments. In Proceedings of 17th ACM International Conference on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems (MSWiM).
Hetzel, P. (1988). Time dissemination via the LF transmitter DCF77 using a pseudo-random phase shift keying of the carrier. In 2nd Proceedings European Frequency and Time Forum.
Hong, S. S., Mehlman, J., & Katti, S. (2012). Picasso: Flexible rf and spectrum slicing. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM 2012 Conference on Applications, Technologies, Architectures, and Protocols for Computer Communication, SIGCOMM ’12 (pp. 37–48). ACM, New York, NY, USA. doi:10.1145/2342356.2342362.
Janson, T., & Schindelhauer, C. (2013). Broadcasting in logarithmic time for ad hoc network nodes on a line using MIMO. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM Symposium on Parallelism in Algorithms and Architectures, SPAA’13. ACM.
Locher, T., Moor, P., Schmid, S., & Wattenhofer, R. (2006). Free riding in bittorrent is cheap. In In HotNets.
Metcalfe, R. M., & Boggs, D. R. (1976). Ethernet: Distributed packet switching for local computer networks. Communications of the ACM, 19(7), 395–404.
Passiatore, C., & Camarda, P. (2014). A fair mac protocol for resource sharing in ad-hoc cognitive networks. Telecommunication Systems, 56(2), 269–283. doi:10.1007/s11235-013-9835-6.
Sandell, M., & Lee, B. S. (2007). Pseudo-Random Scrambling for Quasi-Static MIMO Channels. In IEEE 18th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC) (pp. 1–5). doi:10.1109/PIMRC.2007.4394385.
Shannon, C. E. (1998). Communication in the presence of noise. Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(2), 447–457. doi:10.1109/JPROC.1998.659497.
Wrona, K., & Mähönen, P. (2004). Analytical model of cooperation in ad hoc networks. Telecommunication Systems, 27, 2–4.
Zhenchao, W., & Shibing, Z. (2009). An improved scheme for noise reduction to DCSK based on its retransmission characteristic. In ICCSE ’09. 4th International Conference on Computer Science Education (pp. 366–370). doi:10.1109/ICCSE.2009.5228425.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janson, T., Traub-Ens, A. & Schindelhauer, C. Turning interferences into noise in ad hoc networks. Telecommun Syst 62, 435–448 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-015-0084-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-015-0084-8