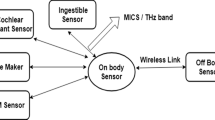
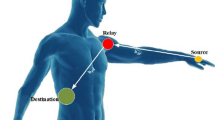
Abstract
Due to resource limited nature of nodes in body area networks (BAN), it is often very difficult to replace or recharge its power source. To prolong the network’s life, only way out is energy efficient communication system. In this article an energy efficient communication system based on collaborative communication is proposed for BAN. Signals from the implanted nodes are received out-of-phase at the base station with no line-of-sight through an AWGN channel. Mathematical model derived here is based on three figures of merit i.e, received power, bit error rate and energy consumption. Analysis of the proposed model and Monte Carlo simulation show that the gain in received power increases as the number of collaborative nodes increase whereas BER is directly related to SNR \((E_b/N_0)\). To evaluate energy consumption of the proposed system, it is compared with single-input-single-output (SISO) system. In this comparison it has been found that SISO performs well at short distances but collaborative communication outperforms SISO in case of long distances. It is also found that collaborative communication requires “N \(\times \) Transmitted power”, less transmission power in comparison to SISO systems. It is observed that collaborative communication achieve energy saving very close to 99 %. On the basis of these results it is safe to recommend collaborative communication for resource limited BAN.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Astaneh, S. A., & Gazor, S. (2009). Collaborative communications: Joint relay and protocol selection. In: 11th Canadian Workshop on IEEE Information Theory, 2009. CWIT 2009 (pp. 25–28).
AT86RF212, ATMEL products. (2012). http://www.atmel.com/devices/at86rf212.aspx.
Barriac, G., Mudumbai, R., & Madhow, U. (2004). Distributed beamforming for information transfer in sensor networks. In: Third IEEE International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, 2004. IPSN 2004 (pp. 81–88).
Bchlin, M., & Trster, G. (2012). Swimming performance and technique evaluation with wearable acceleration sensors. Pervasive and Mobile Computing 8(1), 68 – 81. doi:10.1016/j.pmcj.2011.05.003.
Blumenfeld, D. (2010). Operations research calculations handbook. New York: CRC Press.
Brown, D. R, I. I. I., & Poor, H. V. (2008). Time-slotted round-trip carrier synchronization for distributed beamforming. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 56(11), 5630–5643.
Callaway, E. H, Jr. (2004). Wireless sensor networks: Architectures and protocols. New York: CRC Press.
CC2420, Texas Instruments Chipcon products. (2013). http://www.ti.com/product/cc2420.
Chen, M., Gonzalez, S., Vasilakos, A., Cao, H., & Leung, V. C. (2011). Body area networks: A survey. Mobile Networks and Applications, 16(2), 171–193.
Cotton, S. L., & Scanlon, W. G. (2009). Characterization of the on-body channel in an outdoor environment at 2.45 GHz. In: 3rd IEEE European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, 2009. EuCAP 2009 (pp. 722–725).
Cui, S., Goldsmith, A. J., & Bahai, A. (2004). Energy-efficiency of mimo and cooperative mimo techniques in sensor networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 22(6), 1089–1098.
Ding, Z., Chin, W. H., & Leung, K. K. (2008). Distributed beamforming and power allocation for cooperative networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 7(5), 1817–1822.
Elias, J. (2014). Optimal design of energy-efficient and cost-effective wireless body area networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 13, 560–574. doi:10.1016/j.adhoc.2013.10.010.
Feng, J., Lu, Y. H., Jung, B., Peroulis, D., & Hu, Y. C. (2013). Energy-efficient data dissemination using beamforming in wireless sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 9(3), 31.
Goldsmith, A. (2005). Wireless communications. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Ikki, S. S., & Ahmed, M. H. (2010). Performance analysis of adaptive decode-and-forward cooperative diversity networks with best-relay selection. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 58(1), 68–72.
Jayaweera, S. K. (2006). Virtual mimo-based cooperative communication for energy-constrained wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 5(5), 984–989.
Junnila, S., Kailanto, H., Merilahti, J., Vainio, A. M., Vehkaoja, A., Zakrzewski, M., et al. (2010). Wireless, multipurpose in-home health monitoring platform: Two case trials. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 14(2), 447–455. doi:10.1109/TITB.2009.2037615.
Karp, B., & Kung, H. T. (2000). Gpsr: Greedy perimeter stateless routing for wireless networks. In: Proceedings of the 6th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, MobiCom ’00 ACM, New York, NY, USA (pp. 243–254). doi:10.1145/345910.345953.
Koyuncu, E., Jing, Y., & Jafarkhani, H. (2008). Distributed beamforming in wireless relay networks with quantized feedback. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 26(8), 1429–1439.
Kramer, G., Gastpar, M., & Gupta, P. (2005). Cooperative strategies and capacity theorems for relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 51(9), 3037–3063.
Madhow, U., Brown, D., Dasgupta, S., & Mudumbai, R. (2014). Distributed massive mimo: algorithms, architectures and concept systems. In: IEEE Information Theory and Applications Workshop (ITA), 2014 (pp. 1–7).
Malik, N., Esa, M., Yusof, S., Ismail, M., & Hamzah, S. (2013). Intelligent circular collaborative beamforming array in wireless sensor network for efficient radiation. In: IEEE Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference Proceedings (APMC) (pp. 1009–1011).
Mehrpouyan, H., & Blostein, S. D. (2011). Bounds and algorithms for multiple frequency offset estimation in cooperative networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(4), 1300–1311.
Milenkovi, A., Otto, C., & Jovanov, E. (2006). Wireless sensor networks for personal health monitoring: Issues and an implementation. Computer Communications, 29(1314), 2521–2533. doi:10.1016/j.comcom.2006.02.011.
Mudumbai, R., Barriac, G., & Madhow, U. (2004). Spread-spectrum techniques for distributed space-time communication in sensor networks. In: IEEE Conference Record of the Thirty-Eighth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, vol. 1 (pp. 908–912).
Mudumbai, R., Barriac, G., & Madhow, U. (2007). On the feasibility of distributed beamforming in wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 6(5), 1754–1763.
Mudumbai, R., Brown, D. R., Madhow, U., & Poor, H. V. (2009). Distributed transmit beamforming: Challenges and recent progress. IEEE Communications Magazine, 47(2), 102–110.
Naqvi, H., Berber, S. M., & Salcic, Z. (2009). Performance analysis of collaborative communication in the presence of phase errors and awgn in wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing: Connecting the World Wirelessly, ACM (pp. 394–398).
Naqvi, H., Berber, S., & Salcic, Z. (2010). Collaborative communication with imperfect phase and frequency synchronization in AWGN channel in wireless sensor networks. In: IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS), (pp. 241–244).
Naqvi, H., Berber, S., & Salcic, Z. (2010). Energy efficient collaborative communication with imperfect phase synchronization and rayleigh fading in wireless sensor networks. Physical Communication, 3(2), 119–128.
Naqvi, H., Berber, S., & Salcic, Z. (2014). Energy efficient collaborative communications in AWGN and rayleigh fading channel in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 14(14), 1382–1396.
Ochiai, H., Mitran, P., Poor, H. V., & Tarokh, V. (2005). Collaborative beamforming for distributed wireless ad hoc sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 53(11), 4110–4124.
Parker, P. A., Mitran, P., Bliss, D. W., & Tarokh, V. (2008). On bounds and algorithms for frequency synchronization for collaborative communication systems. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 56(8), 3742–3752.
Qiao, D., Li, Y., & Li, H. (2014). Energy efficient techniques for implanted nodes in body sensor networks. In: The International Conference on Health Informatics, Springer (pp. 167–170).
Sayrafian-Pour, K., Yang, W. B., Hagedorn, J., Terrill, J., Yazdandoost, K. Y., & Hamaguchi, K. (2010). Channel models for medical implant communication. International Journal of Wireless Information Networks, 17(3–4), 105–112.
Sharma, S., Shi, Y., Hou, Y., Sherali, H., & Kompella, S. (2010). Cooperative communications in multi-hop wireless networks: Joint flow routing and relay node assignment. In: Proceedings of IEEE on INFOCOM (pp. 1–9). doi:10.1109/INFCOM.2010.5462024
Simic, L., Berber, S., & Sowerby, K. (2007). Energy-efficiency of cooperative diversity techniques in wireless sensor networks. In: IEEE 18th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, PIMRC 2007 (pp. 1–5). doi:10.1109/PIMRC.2007.4394562.
Simic, L., Berber, S.M., & Sowerby, K.W. (2007). Energy-efficiency of cooperative diversity techniques in wireless sensor networks. In: IEEE 18th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications. PIMRC 2007 (pp. 1–5).
Sklar, B., et al. (1997). Rayleigh fading channels in mobile digital communication systems part I: Characterization. In: IEEE communications Magazine. Citeseer.
Varshney, U. (2007). Pervasive healthcare and wireless health monitoring. Mobile Networks and Applications, 12(2–3), 113–127. doi:10.1007/s11036-007-0017-1.
Viittala, H., Hamalainen, M., Iinatti, J., & Taparugssanagorn, A. (2009). Different experimental wban channel models and ieee802. 15.6 models: comparison and effects. In: 2nd International Symposium on Applied Sciences in Biomedical and Communication Technologies. ISABEL 2009 (pp. 1–5).
Wei-ping, Z Hl Q. (2007). Collaborative beamforming for distributed wireless ad hoc sensor networks. Shanxi Electronic Technology, 5, 032.
Wu, K. K., Chang, M. K., Lee, S. Y., & Chan, Y. W. (2014). Novel protocols of modulation level selection in decode-and-forward multinode cooperative communication systems. In: Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering, Springer (pp. 133–138).
Xu, X., & Zhong, M. (2014). Wireless body sensor networks with cloud computing capability for pervasive healthcare: Research directions and possible solutions. In: Frontier and Future Development of Information Technology in Medicine and Education, Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol. 269, pp. 979–988. Springer, Netherlands.
Zarifi, K., Affes, S., & Ghrayeb, A. (2009). Distributed beamforming for wireless sensor networks with random node location. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 2009. ICASSP 2009 (pp. 2261–2264).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
1.1 Mean values of trigonometric functions
1.1.1 Mean value of \(\cos (\theta _f)\)
1.1.2 Mean value of \(\cos ^2(\theta _f)\)
1.1.3 Variance of \(\cos (\theta _f)\)
Using Eqs. (32) and (33) in the above equation we get
1.1.4 Variance of \(hS\cos (\theta _f)\)
Since all of these are independent random variables, therefore the multiplication can be calculated as
Since we know from Eqs. (32) and (34) that, \(Var(h) = \sigma _h^2 = (2-\frac{\pi }{2})b^2\) and \(E\left[ h\right] = \mu _h = \left( \sqrt{\frac{\pi }{2}}\right) b\)
by putting these values in Eq. (35), we get
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghani, A., Naqvi, H.A., Sher, M. et al. Energy efficient communication in body area networks using collaborative communication in Rayleigh fading channel. Telecommun Syst 63, 357–370 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-015-0125-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-015-0125-3