Abstract
The synthesis of different planar geometries of antenna arrays for isoflux radiation is presented in this paper. This synthesis considers the reduction of the side lobe level and the isoflux radiation requirements for Geostationary Earth Orbit satellites. The behavior of the radiation is studied in three geometries of two-dimensional antenna arrays such as uniform planar arrays, aperiodic planar arrays (APA) and concentric ring arrays (CRA). The well-known methods of genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization are utilized for the optimization problem. In this way, the designs of APA and CRA presented in this paper could provide an acceptable solution for reducing the antenna hardware and simplifying the power feeding even more than results presented previously in the literature.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stutzman, W. L., & Thiele, G. A. (1998). Antenna theory and design (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Gavish, B. (1997). LEO/MEO systems—global mobile communication systems. Telecommunication Systems, 8, 99–141.
Gavish, B., & Kalvenes, J. (1997). The impact of intersatellite communication links on LEOS performance. Telecommunication Systems, 8, 159–190.
McMahon, G., Sugden, G., & Septiawan, R. (2003). Class dependent traffic allocation in a LEO satellite network. Telecommunication Systems, 22, 241–266.
Russo, P., d’Ippolito, A., Ferrarotti, A., & Ruggieri, M. (1997). A C/I advantageous satellite system configuration for land mobile applications. Telecommunication Systems, 8, 319–340.
Sandau, R., Roeser, H.-P., & Valenzuela, A. (2010). Small satellite missions for earth observation: New developments and trends. Berlin: Springer.
Hay, S. G., Bateman, D. G., Bird, T. S., & Cooray, F. R. (1999). Simple Ka band Earth coverage antennas for LEO satellites. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Symposium, 1, 708–711.
Ravanelli, R., Iannicelli, C., Baldecchi, N., & Franchini, F. Multi-objective optimization of an isoflux antenna for LEO satellite down-handling link. Sentinel GMES ESA program.
Jin, J., Wang, H. L., Zhu, W. M., & Liu, Y. Z. (2006). Array patterns synthesizing using genetic algorithm. Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium, 2, 64–68.
Aerts, W., & Vandenbosch, G. A. E. (2004). Optimal inter-element spacing in linear array antennas and its application in satellite communications. In: Proceedings of the 34th European microwave conference.
Koleck, T. (2003). Active antenna coverage synthesis for GEO satellite using genetic algorithm. Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, 1, 142–144.
Morabito, A. F., Lagana, A. R., & Isernia, T. (2010). On the optimal synthesis of ring symmetric shaped patterns by means of uniformly spaced planar arrays. Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, 20, 33–48.
Vigano, M. C., Toso, G., Angeletti, P., Lager, I. E., Yarovoy, A., & Caratelli, D. (2010). Sparse antenna array for earth coverage satellite applications. In: Proceedings of the Fourth European Conference on Antennas and Propagation.
Unz, H. (1960). Linear arrays with arbitrarily distributed elements. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 8(2), 222–223.
Chen, K., Yun, X., He, Z., & Han, C. (2007). Synthesis of sparse planar arrays using modified real genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans on Antennas and Propagation, 55, 1067–1073.
Wang, Q., Yao, M., & You, H. (2008). Application of genetic algorithm optimization in the low profile phased array antenna for satellite communication on the move. In: Proceedings of the Second International symposium on the intelligent information technology application, (pp. 649–652).
Son, S. H., Park, U. H., Jeon, S. I., & Kim, C. J. (2004). Low sidelobe design by position perturbation in mobile array antenna for satellite communications. Vehicular Technology Conference, 1(13), 10.
Maffett, A. L. (1962). Array factors with nonuniform spacing parameter. IRE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 10, 131–136.
Reyna, A., Panduro, M. A., & del Rio-Bocio, C. (2012). Design of aperiodic planar arrays for isoflux radiation in GEO satellites by applying evolutionary optimization. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(8), 6872–6878.
Harrington, R. (1961). Sidelobe reduction by nonuniform element spacing. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 9, 187–192.
Reyna, Alberto, Panduro, Marco A., & del Rio, Carlos. (2011). Design of concentric ring antenna arrays for isoflux radiation in GEO satellites. IEICE Electronics Express, 8(7), 484–490.
Mandal, D., Ghoshal, S. P., & Bhattacharjee, A. K. (2011). Optimized radii and excitations with concentric circular antenna array for maximum sidelobe level reduction using wavelet mutation based particle swarm optimization techniques. Telecommunication Systems, 47, 1–11, 2011, doi:10.1007/s11235-011-9482-8.
Biller, L., & Friedman, G. (1973). Optimization of radiation patterns for an array of concentric ring sources. IEEE Transactions Audio Electroacoustic, 21(1), 57–61.
Haupt, Randy L. (2008). Optimized element spacing for low sidelobe concentric ring arrays. IEEE Transactions on Antenna and Propagation, 56(1), 266–268.
Bulatsyk, O. O., Katsenelenbaum, B. Z., Yu Topolyuk, P., & Voitovich, N. N. (2010). Phase optimization problems: Applications in wave field theory. Weinheim: Wiley.
Rahmat-Samii, Y., & Michielssen, E. (1999). Electromagnetic optimisation by genetic algorithms. New York: Wiley.
Robinson, J., & Rahmat-Samii, Y. (2004). Particle swarm optimization in electromagnetics. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 52, 397–407.
Haupt, R. L. (1993). Thinned arrays using genetic algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 41(2), 993–999.
Sherman, K. N. (2002). Phased array shaped multi-beam optimization for LEO satellite communications using a genetic algorithm. In: Proceedings 2000 IEEE International Conference on Phased Array Systems and Technology.
Eberhart, R. C., & Shi, Y. (2001). Particle swarm optimization: Developments, applications and resources. In: Proceedings Congress Evolutionary Computation, (pp. 81–86).
Reyna, A., & Panduro, M. A. (2008). Optimization of a scannable pattern for uniform planar antenna arrays to minimize the side lobe level. Journals of Electromagnetics Waves and Applications, 22(16), 2241–2250.
Reyna, A., & Panduro, M. A. (2010). Design of steerable concentric rings array using rotation properties and evolutionary optimization. In: Proceedings of the Fourth European Conference on Antennas and Propagation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
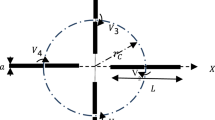
Since the Fig. 1, trigonometric math functions are defined as:
Besides, consider the canonical implicit equation of an ellipse as follows:
Then, the math calculation for the prescribed radiation pattern \(R_{s}(\theta )\) is obtained by substituting Eqs. (2) and (3) in (1).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reyna, A., Panduro, M.A., del Rio-Bocio, C. et al. Design of different planar geometries of antenna arrays for isoflux radiation in GEO satellites. Telecommun Syst 65, 269–279 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-016-0227-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-016-0227-6