Abstract
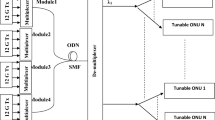
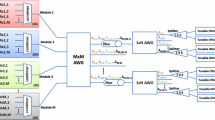
This paper reviews various energy efficient approaches in existence and proposes a Hybrid WDM–TDM PON architecture that allows the adaptive bandwidth allocation mechanism to reduce central office power consumption with acceptable performance. Our proposed architecture allows sending two signals, one broadband and other narrowband to each optical networking unit so an appropriate signal can be utilized according to the traffic demand. In case of very low traffic, only narrowband signal is used and a significant amount of energy consumption and OPEX is reduced. By using \(2\times \hbox {N}\) power splitter and interleaver, proposed architecture provides broadcasting at both broadband and narrowband signal depending on the required link rate. This further reduces energy consumption and OPEX by avoiding the transmission of same signal from multiple sources. Offered data rates to the optical distribution networks (ODNs) may also be varied by doubling the wavelength spacing of remote node AWG so that two contiguous wavelengths can be transmitted at each port or ODN. This provides the geographical dynamic bandwidth allocation. Proposed architecture also support simultaneous transmission of both broadband and narrowband signals to the ODN to provide bandwidth scalability and network extensibility for supporting future access network in terms of new users and data rates. As two signals are reaching to any ODN, resiliency against OLT TRx and line card failure is also achieved. The performance of the proposed design is verified by simulation results in terms of bit error rate and receiver sensitivity to demonstrate its feasibility for the next-generation optical access network.















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Lee, C., Sorin, W., & Kim, B. (2006). Fiber to the home using a PON infrastructure. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 24(12), 4568–4583.
Indre, R. M., Pesic, J., & Roberts, J. (2014). POPI: A passive optical pod interconnect for high performance data centers. In 2014 International conference on optical network design and modeling (pp. 84–89), Stockholm.
Ni, W., Huang, C., Liu, Y. L., Li, W., Leong, K. W., & Wu, J. (2014). POXN: A new passive optical cross-connection network for low-cost power-efficient datacenters. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 32(8), 1482–1500.
Kazovsky, L., Shaw, W., Gutierrez, D., Cheng, N., & Wong, S. (2007). Next-generation optical access networks. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 25(11), 3428–3442.
Gong, X., Guo, L., Liu, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2015). System performance analysis of time-division-multiplexing passive optical network using directly modulated lasers or colorless optical network units. Optical Engineering, 54(5), 056110.
Luo, Y., Zhou, X., Effenberger, F., Yan, X., Peng, G., Qian, Y., et al. (2013). Time- and wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network (TWDM-PON) for next-generation PON Stage 2 (NG-PON2). Journal of Lightwave Technology, 31(4), 587–593.
Yuang, M., Hsu, D., Tien, P., Chen, H., Wei, C., Chen, S., et al. (2013). An energy and cost efficient WDM/OFDMA PON system: Design and demonstration. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 31(16), 2809–2816.
Garg, A. K., & Janyani, V. (2015). Power budget improvement in energy efficient long reach hybrid passive optical network. In 2015 International conference on microwave and photonics (ICMAP) (pp. 1–2), Dhanbad.
Banerjee, A., Park, Y., Clarke, F., Song, H., Yang, S., Kramer, G., et al. (2005). Wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network (WDM-PON) technologies for broadband access: A review [Invited]. Journal of Optical Networking, 4(11), 737–758.
Effenberger, F., Cleary, D., Haran, O., Kramer, G., Li, R. D., Oron, M., et al. (2007). An introduction to PON technologies. IEEE Communications Magazine, 45(3), 17–25.
Garg, A. K., & Janyani, V. (2015). Identification of cost and energy efficient multiplexing techniques for LR-PON for different network scenario. In IEEE workshop on recent advances in photonics (WRAP) (pp. 1–4). IISc Bangalore: IEEE.
Skubic, B., Betou, E., Ayhan, T., & Dahlfort, S. (2012). Energy-efficient next-generation optical access networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 50, 122–127.
Song, J., Yang, C., Zhang, Q., Ma, Z., Huang, X., et al. (2015). Energy efficiency evaluation of tree-topology 10 gigabit ethernet passive optical network and ring-topology time- and wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network. Optical Engineering, 54(9), 090502.
Feng, H., Chae, C., Tran, A. V., & Nirmalathas, A. (2011). Cost-effective introduction and energy-efficient operation of long-reach WDM/TDM PON systems. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 29(21), 3135–3143.
Kani, J., Shimazu, S., Yoshimoto, N., & Hadama, H. (2011). Energy efficient optical access network technologies. In OFC/NFOEC (pp. 1–3).
Dixit, A., Lannoo, B., Das, G., Colle, D., Pickavet, M., & Demeester, P. (2013). Flexible TDMA/WDMA passive optical network: Energy efficient next-generation optical access solution. Optical Switching and Networking, 10(4), 491–506.
Tadokoro, M., Kubo, R., Nishihara, S., Yamada, T., & Nakamura, H. (2012). Adaptive bandwidth aggregation mechanisms using a shared wavelength for energy-efficient WDM/TDM-PON (pp. 87–88).
Garg, A. K., & Janyani, V. (2016). WDM-PON network for simultaneous upstream transmission with ONU interconnection capability. In The international conference on fiber optics and photonics (PHOTONICS 2016), India Tu4A.13.
Garg, A. K., & Janyani, V. (2016). Overall/subgroup ONU intercommunication based on two stage flexible PON network. In The international conference on fiber optics and photonics (PHOTONICS 2016), India W3A.1.
Cheng, N., Gao, J. H., Xu, C., et al. (2014). Flexible TWDM PON system with pluggable optical transceiver modules. Optical Express, 22(2), 2079–2091.
Cheng, N. (2015). Flexible TWDM PON with WDM overlay for converged services. Optical Fiber Technology, 26, 21–30.
Yuan, Y., Lu, P., Rodrigues, J., & Zhu, Z. (2013). Improving energy-efficiency of HFC networks with a master-slave linecard configuration. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on communications (ICC) (pp. 4159–4163).
Zhu, Z. (2012). Design of energy-saving algorithms for hybrid fiber coaxial networks based on the DOCSIS 3.0 standard. IEEE/OSA Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 4(6), 449–456.
Zhu, Z., Lu, P., Rodrigues, J., & Wen, Y. (2013). Energy-efficient wideband cable access networks in future smart cities. IEEE Communications Magazine, 51(6), 94–100.
Lu, P., Yuan, Y., Yang, Z., & Zhu, Z. (2013). On the performance analysis of energy-efficient upstream scheduling for hybrid fiber-coaxial networks with channel bonding. IEEE Communications Letters, 17(5), 1020–1023.
Chatterjee, B. C., Sarma, N., & Oki, E. (2015). Routing and spectrum allocation in elastic optical networks: A tutorial. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 17(3), 1776–1800.
Chatterjee, B. C., & Oki, E. (2015). Performance evaluation of spectrum allocation policies for elastic optical networks. In 2015 17th international conference on transparent optical networks (ICTON) (pp. 1–4), Budapest.
Zhang, G., Leenheer, M. De, Morea, A., & Mukherjee, B. (2013). A survey on OFDM-based elastic core optical networking. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 15(1), 65–87.
Zhang, G., Leenheer, M. De, & Mukherjee, B. (2012). Optical traffic grooming in OFDM-based elastic optical networks [Invited]. IEEE/OSA Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 4(11), B17–B25.
Bock, C., Prat, J., & Walker, S. D. (2005). Hybrid WDM/TDM PON using the AWG FSR and featuring centralized light generation and dynamic bandwidth allocation. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 23(12), 3981–3988.
Zhang, J., & Ansari, N. (2009). Minimizing the arrayed waveguide grating cost and the optical cable cost in deploying WDM passive optical networks. IEEE/OSA Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 1(5), 352–365.
Maier, G., Martinelli, M., Pattavina, A., & Salvadori, E. (2000). Design and cost performance of the multistage WDM-PON access networks. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 18(2), 125–143.
Dai, J., Zhou, F., Zhang, M., & Liu, D. (2014). Electro-optical tunable arrayed waveguide grating based on liquid crystal clad waveguide. In International photonics and optoelectronics meetings, OSA Technical Digest, paper OTh4C.8.
Horn, W., Kroesen, S., Herrmann, J., Imbrock, J., & Denz, C. (2012). Electro-optical tunable waveguide Bragg gratings in lithium niobate induced by femtosecond laser writing. Optical Express, 20(24), 26922–26928.
Toyoda, S., Ooba, N., Kitoh, T., Kurihara, T., & Maruno, T. (2001). Wide tuning range and low operating power AWG-based thermo-optic wavelength tunable filter using polymer waveguides. Electronics Letters, 37(18), 1130–1132.
Yang, Y., et al. (2015). Thermo-optically tunable silicon AWG with above 600 GHz channel tunability. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 27(22), 2351–2354.
Zhang, H., Ma, C., Qin, Z., Zhang, X., Zhang, D., & Zhang, D. (2007). Thermo-optic tunable polymer arrayed waveguide grating. Optical Engineering, 46(5), 054601-1–054601-4.
Haxha, S., Rahman, B., Langley, R., Sciences, M., & Square, N. (2005). Broadband and low-driving-power LiNbO\(_3\) electrooptic modulators. Optical and Quantum Electronics, 36(14), 1205–1220.
Zhang, S., Ji, W., Li, X., Huang, K., & Yan, Z. (2016). Efficient and reliable protection mechanism in long-reach PON. IEEE/OSA Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 8(1), 23–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garg, A.K., Janyani, V. Adaptive bandwidth mechanism using dual rate OLT for energy efficient WDM–TDM passive optical network. Telecommun Syst 66, 657–670 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-017-0316-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-017-0316-1