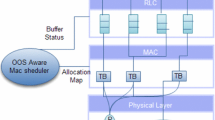
Abstract
Overhead resource elements (REs) in Long Term Evolution (LTE) networks are used for some control, signaling and synchronization tasks at both the Physical level and Media Access Control sub-level. Accurately computing all the overhead REs is necessary to achieve an efficient system design, which is difficult because LTE is a complex standard that contains a large number of implementation flexibilities and system configurations. The number of such REs depends on both the system configurations and services demanded. Aiming at exploring the influence of overhead on LTE downlink performance, we first parametrize each system configuration—including parameters corresponding to enhancement techniques such as Adaptive Modulation and Coding and Multi-Antenna Transmissions techniques—and those of the resource allocation mechanisms (which depend on users’ services). Second, using such parametrization, we model all overheads for synchronization, controlling and signaling operations in LTE Physical Downlink Shared/Control Channels. This allows for dynamically computing the useful REs (by subtracting the overhead REs from the total ones), both per Transmission Time Interval (TTI) and per frame (and hence, the corresponding bit rates). Our data rate-based performance model is able to accurately compute: (1) the real, exact system data rate or “throughput” (instead of approximations); and (2) the maximum number of simultaneous multi-service users per TTI that is able to support (called here “capacity”). Aiming at understanding the impact of each overhead mechanism, we have carried out a variety of simulations, including different service provision scenarios, such as multi-user with multi-application. The simulation results prove our starting hypothesis that the influence of overhead on LTE performance should not be neglected. The parametrized and dynamic model quantifies to what extent throughput and capacity are modified by overhead—under a combination of system configurations and services, and may provide these performance metrics, throughput and capacity, as inputs to planning, dimensioning and optimization specialized tools.














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
As will be shown, an UE may be configured to receive one or two TBs (and hence one or two codewords) in a single transmission interval. We postpone this to a later part of this paper, where it will be better understood.
References
Ericsson. (2016). Ericsson Mobility Report. On the pulse of the networked society. Technical report, https://www.ericsson.com/assets/local/mobility-report/documents/2016/ericsson-mobility-report-november-2016.pdf
GSA. GSM/3G Stats. Fast Facts. Q1 2015 mobile subscriptions. Technical report, Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA). http://www.gsacom.com/, 2015.
Albreem, M. A. M., & Ismail, N. A. H. B. (2016). A review: detection techniques for LTE system. Telecommunication Systems, 63(2), 153–168.
Ta, T., & Baras, J. S. (2015). Exploiting diversity of usage to enhance user equipment energy efficiency in LTE networks. Telecommunication Systems, 59(1), 5–23.
Sas, B., Bernal-Mor, E., Spaey, K., Pla, V., Blondia, C., & Martinez-Bauset, J. (2014). Modelling the time-varying cell capacity in LTE networks. Telecommunication Systems, 55(2), 299–313.
Li, X., Toseef, U., Dulas, D., Bigos, W., Görg, C., Timm-Giel, A., et al. (2013). Dimensioning of the LTE access network. Telecommunication Systems, 52(4), 2637–2654.
Ericsson. (2015). Ericsson Mobility Report. On the pulse of the networked society. Technical Report 1, Ericsson. http://www.ericsson.com/res/docs/2015/ericsson-mobility-report-june-2015.pdf
Hagos, D. H. (2016). The performance of network-controlled mobile data offloading from LTE to WiFi networks. Telecommunication Systems, 61(4), 675–694. doi:10.1007/s11235-015-0061-2.
Maia, A. M., Vieira, D., de Castro, M. F., & Ghamri-Doudane, Y. (2016). A fair QoS-aware dynamic LTE scheduler for machine-to-machine communication. Computer Communications, 89–90, 75–86.
Adibi, S., Mobasher, A., & Tofigh, T. (2014). LTE networking: extending the reach for sensors in mHealth applications. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 25(7), 692–706.
Brown, J., & Khan, J. Y. (2013). Key performance aspects of an LTE FDD based smart grid communications network. Computer Communications, 36(5), 551–561.
Salman, M. I., Ng, C. K., Noordin, N. K., Ali, B. M., & Sali, A. (2015). A self-configured link adaptation for green LTE downlink transmission. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 26(2), 258–275.
Abdulkafi, A. A., Chieng, D., Kiong, T. S., Ting, A., Koh, J., & Ghaleb, A. M. (2014). Energy-aware load adaptive framework for LTE heterogeneous network. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 25(9), 943–953.
Memon, I., Chen, L., Majid, A., Lv, M., Hussain, I., & Chen, G. (2015). Travel recommendation using geo-tagged photos in social media for tourist. Wireless Personal Communications, 80(4), 1347–1362.
Memon, I. (2015). Authentication user’s privacy: An integrating location privacy protection algorithm for secure moving objects in location based services. Wireless Personal Communications, 82(3), 1585–1600.
Domenic, M. K., Wang, Y., Zhang, F., Memon, I., & Gustav, Y. H. (2013). Preserving users’ privacy for continuous query services in road networks. In 2013 6th international conference on Information management, innovation management and industrial engineering (ICIII), Vol. 1, pp. 352–355. IEEE.
Gustav, Y. H., Wang, Y., Domenic, M. K., Zhang, F., & Memon, I. (2013). Velocity similarity anonymization for continuous query location based services. In 2013 international conference on computational problem-solving (ICCP), pp. 433–436. IEEE.
Memon, I., & Arain, Q. A. (2017). Dynamic path privacy protection framework for continuous query service over road networks. World Wide Web, 20(4), 639–672. doi:10.1007/s11280-016-0403-3.
Arain, Q. A., Uqaili, M. A., Deng, Z., Memon, I., Jiao, J., Shaikh, M. A., Zubedi, A., Ashraf, A., & Arain, U. A. (2016). Clustering based energy efficient and communication protocol for multiple mix-zones over road networks. Wireless Personal Communications. doi:10.1007/s11277-016-3900-x.
Arain, Q. A., Zhongliang, D., Memon, I., Arain, S., Shaikh, F. K., Zubedi, A., Unar, M.A., Ashraf, A., & Shaikh, R. (2016). Privacy preserving dynamic pseudonym-based multiple mix-zones authentication protocol over road networks. Wireless Personal Communications. doi:10.1007/s11277-016-3906-4.
Akhtar, R., Leng, S., Memon, I., Ali, M., & Zhang, L. (2015). Architecture of hybrid mobile social networks for efficient content delivery. Wireless Personal Communications, 80(1), 85–96.
Holma, H., & Toskala, A. (2010). WCDMA for UMTS: HSPA evolution and LTE. New York: Wiley.
Papathanasiou, C., Dimitriou, N., & Tassiulas, L. (2013). Dynamic radio resource and interference management for MIMO-OFDMA mobile broadband wireless access systems. Computer Networks, 57(1), 3–16.
Li, J., Wu, X., & Laroia, R. (2013). OFDMA mobile broadband communications: A systems approach. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Cox, C., & Cox, B. (2014). An Introduction to LTE: LTE, LTE-Advanced, SAE, VoLTE and 4G Mobile Communications. New York: Wiley.
Dahlman, E., Parkvall, S., & Skold, J. (2013). 4G: LTE/LTE-advanced for mobile broadband. Cambridge: Academic Press.
Dahlman, E., Parkvall, S., Skold, J., & Beming, P. (2010). 3G evolution: HSPA and LTE for mobile broadband. Cambridge: Academic Press.
GSMA. The Mobile Economy 2015. Technical report, https://www.gsmamobileeconomy.com (2015).
Miller, M. (2015). The Internet of Things: How smart TVs, smart cars, smart homes, and smart cities are changing the world. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Education.
Chakrabarty, S. & Engels, D. W. (2016). A secure IoT architecture for Smart Cities. In 2016 13th IEEE annual consumer communications & networking conference (CCNC), pp. 812–813. IEEE.
Albino, V., Berardi, U., & Dangelico, R. M. (2015). Smart cities: Definitions, dimensions, performance, and initiatives. Journal of Urban Technology, 22(1), 3–21.
Ericsson. (2016). Stockholm tops Ericsson Networked Society City Index 2016. Technical report, Ericsson. http://hugin.info/1061/R/2021689/751081.pdf.
Ericsson. (2016). Laying the foundations for a smart, sustainable city. Technical report, Ericsson, White paper Uen 284 23-3277. https://www.ericsson.com/res/docs/whitepapers/wp-smart-cities.pdf.
Ericsson. (2015). Ericsson Mobility Report. On the pulse of the net- worked society. Technical Report 1. Technical report, Ericsson, available on http://www.ericsson.com/res/docs/2015/ericsson-mobility-report-june- 2015.pdf.
del Arco-Vega, M. A., Cuadra, L., Portilla-Figueras, J. A., & Salcedo-Sanz, S. (2017). Near-optimal user assignment in LTE mobile networks with evolutionary computing. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 28(6), e3132-n/a. doi:10.1002/ett.3132.
Li, Y., Baccelli, F., Andrews, J. G., Novlan, T. D., & Zhang, J. C. (2016). Modeling and analyzing the coexistence of WI-FI and LTE in unlicensed spectrum. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 15(9), 6310–6326.
Stasiak, M., Glabowski, M., Wisniewski, A., & Zwierzykowski, P. (2010). Modelling and dimensioning of mobile wireless networks: From GSM to LTE. New York: Wiley.
Challita, U., Dawy, Z., Turkiyyah, G., & Naoum-Sawaya, J. (2016). A chance constrained approach for LTE cellular network planning under uncertainty. Computer Communications, 73, 34–45.
Siomina, I., & Yuan, D. (2012). Analysis of cell load coupling for LTE network planning and optimization. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 11(6), 2287–2297.
Majewski, K., & Koonert M. (2010). Conservative cell load approximation for radio networks with Shannon channels and its application to LTE network planning. In 2010 sixth advanced international conference on telecommunications (AICT), pp. 219–225. IEEE.
Anchora, L., Mezzavilla, M., Badia, L., & Zorzi, M. (2012). A performance evaluation tool for spectrum sharing in multi-operator LTE networks. Computer Communications, 35(18), 2218–2226.
Yang, K., Martin, S., & Yahiya, T. A. (2015). LTE uplink interference aware resource allocation. Computer Communications, 66, 45–53.
Xenakis, D., Passas, N., & Verikoukis, C. (2012). An energy-centric handover decision algorithm for the integrated LTE macrocell-femtocell network. Computer Communications, 35(14), 1684–1694.
Sesia, S., Toufik, I., & Baker, M. (2009). LTE: The UMTS long term evolution. New York: Wiley Online Library.
Ali, S. G. A., Baba, M. D., Mansor, M. A., & Abdullah, L. M. (2014). An IMS signalling module for LTE-based femtocell networks. In 2014 IEEE 5th control and system graduate research colloquium (ICSGRC), pp. 247–252. IEEE.
Ali, S. G. A., Baba, M. D., Mansor, M. A., & Abdullah, L. M. (2014). SIP based IMS registration signalling for LTE-based femtocell networks. In 2014 IEEE 5th control and system graduate research colloquium (ICSGRC), pp. 25–30. IEEE.
Rinne, M., & Tirkkonen, O. (2010). LTE, the radio technology path towards 4G. Computer Communications, 33(16), 1894–1906.
Rezaei, F., Hempel, M., & Sharif, H. (2011). LTE PHY performance analysis under 3GPP standards parameters. In 2011 IEEE 16th international workshop on computer aided modeling and design of communication links and networks (CAMAD), pp. 102–106. IEEE.
Cui, D. (2009). LTE peak rates analysis. In 18th annual wireless and optical communications conference, 2009. WOCC 2009, pp. 1–3. IEEE.
Srikanth, S., Pandian, P., & Fernando, X. (2012). Orthogonal frequency division multiple access in WiMAX and LTE: A comparison. Communications Magazine, IEEE, 50(9), 153–161.
Astély, D., Dahlman, E., Furuskar, A., Jading, Y., Lindström, M., & Parkvall, S. (2009). LTE: the evolution of mobile broadband. IEEE Communications Magazine, 47(4), 44–51.
Ahmadzadeh, A. M., Sanchez-García, J. E., Saavedra-Moreno, B., Portilla-Figueras, A., & Salcedo-Sanz, S. (2012). Capacity estimation algorithm for simultaneous support of multi-class traffic services in Mobile WiMAX. Computer Communications, 35(1), 109–119.
Siomina, I., Furuskar, A., & Fodor, G. (2009). A mathematical framework for statistical QoS and capacity studies in OFDM networks. In 2009 IEEE 20th international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications, pp. 2772–2776. IEEE.
Jang, J., & Lee, K. B. (2003). Transmit power adaptation for multiuser OFDM systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 21(2), 171–178.
Stańczak, S., Feistel, A., Wiczanowski, M., & Boche, H. (2010). Utility-based power control with QoS support. Wireless Networks, 16(6), 1691–1705.
Wiczanowski, M., Boche, H., & Stanczak, S. (2009). An algorithm for optimal resource allocation in cellular networks with elastic traffic. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 57(1), 41–44.
Wiczanowski, M., Stańczak, S., & Boche, H. (2008). Providing quadratic convergence of decentralized power control in wireless networks: The method of min-max functions. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 56(8), 4053–4068.
Stańczak, S., Wiczanowski, M., & Boche, H. (2007). Distributed utility-based power control: Objectives and algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 55(10), 5058–5068.
Larmo, A., Lindstrom, M., Meyer, M., Pelletier, G., Torsner, J., & Wiemann, H. (2009). The LTE link-layer design. Communications Magazine, IEEE, 47(4), 52–59.
Zhang, Z., Zhao, Z., Guan, H., Miao, D., & Tan, Z. (2013). Study of signaling overhead caused by keep-alive messages in LTE network. In 2013 IEEE 78th vehicular technology conference (VTC Fall), pp. 1–5. IEEE.
Razavi, S. M., & Yuan, D. (2014). Reducing signaling overhead by overlapping tracking area list in LTE. In 2014 7th IFIP wireless and mobile networking conference (WMNC), pp. 1–7. IEEE.
Razavi, S. M., Yuan, D., Gunnarsson, F., & Moe, J. (2010). Exploiting tracking area list for improving signaling overhead in LTE. In 2010 IEEE 71st vehicular technology conference (VTC 2010-Spring), pp. 1–5. IEEE.
Osman, L. O. W. (2015). Optimization of Tracking Area List Design for Reducing Total Signaling Overhead in LTE Systems. Ph.D. thesis, University of Khartoum.
Mittal, P., Darwazeh, I., & Manukyan, H. (2014). Overhead estimation during intra eNB handover in 4G LTE systems. In 9th international symposium on communication systems, networks & digital signal processing (CSNDSP), pp. 960–965. IEEE.
Yang, Y., Li, P., & Wang, W. (2013). Algorithm about mobility load balance considering system overhead on LTE system. In 22nd wireless and optical communication conference (WOCC), pp. 231–235. IEEE.
Shahab, M. B. (2015). Efficient channel quality indicator reporting schemes in LTE with reduced signaling overhead. In 38th international conference on telecommunications and signal processing (TSP), pp. 123–128. IEEE.
Thainesh, J. S., Wang, N., & Tafazolli, R. (2015). Reduction of core network signalling overhead in cluster based LTE small cell networks. In IEEE 20th international workshop on computer aided modelling and design of communication links and networks (CAMAD), pp. 226–230. IEEE.
Edström, P. (2007). Overhead impacts on long-term evolution radio networks. Master’s thesis, KTH Information and Communication Technology, Stockholm.
Seo, J.-B., & Leung, V. C. M. (2012). Performance modeling and stability of semi-persistent scheduling with initial random access in LTE. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 11(12), 4446–4456.
Pratap, A., & Pati, H. M. (2015). Capacity estimation for cellular LTE using AMR codec with semi-persistent scheduling. In Intelligent computing, communication and devices, pp. 725–736. Springer.
Ding, L., Tong, F., Chen, Z., & Liu, Z. (2011). A novel MCS selection criterion for VoIP in LTE. In 7th international conference on wireless communications, networking and mobile computing (WiCOM), pp. 1–4. IEEE.
Jiang, D., Wang, H., Malkamaki, E., Tuomaala, E. (2007). Principle and performance of semi-persistent scheduling for VoIP in LTE system. In International conference on wireless communications, networking and mobile computing, 2007. WiCom 2007, pp. 2861–2864. IEEE.
3GPP. LTE; Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Multiplexing and channel coding. Technical report, ETSI, France, 2010. Technical Specification Name: 3GPP TS 36.212 version 9.2.0, Release 9.
3GPP. LTE; Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Physical layer procedures. Technical report, ETSI, France, 2010. Technical Specification Name: 3GPP TS 36.213 version 9.2.0 Release 9.
Lee, J., Han, J.-K., & Zhang, J. C. (2009). MIMO technologies in 3GPP LTE and LTE-advanced. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2009(1), 1–10.
Duplicy, J., Badic, B., Balraj, R., Ghaffar, R., Horváth, P., Kaltenberger, F., et al. (2011). MU-MIMO in LTE Systems. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2011(1), 1–13.
Li, Q., Li, G., Lee, W., Lee, M., Mazzarese, D., Clerckx, B., et al. (2010). MIMO techniques in WiMAX and LTE: A feature overview. Communications Magazine, IEEE, 48(5), 86–92.
Ball, C. F., Mullner, R., Lienhart, J., & Winkler, H. (2009). Performance analysis of closed and open loop MIMO in LTE. In European wireless conference, EW 2009, pp. 260–265. IEEE.
Capozzi, F., Piro, G., Grieco, L. A., Boggia, G., & Camarda, P. (2013). Downlink packet scheduling in LTE cellular networks: Key design issues and a survey. Communications Surveys & Tutorials, IEEE, 15(2), 678–700.
Schwarz, S., Mehlfuhrer, C., & Rupp, M. (2010). Low complexity approximate maximum throughput scheduling for LTE. In 2010 conference record of the forty fourth Asilomar conference on signals, systems and computers (ASILOMAR), pp. 1563–1569. IEEE.
Kwan, R., Leung, C., & Zhang, J. (2009). Proportional fair multiuser scheduling in LTE. Signal Processing Letters, IEEE, 16(6), 461–464.
Furuskar, A., Jonsson, T., & Lundevall, M. (2008). The LTE radio interface-key characteristics and performance. In IEEE 19th international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications, PIMRC 2008, pp. 1–5. IEEE.
3GPP. LTE; Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Base Station (BS) radio transmission and reception. Technical report, ETSI, France, 2011. Technical Specification Name: 3GPP TS 36.104 version 10.2.0 Release 10.
3GPP. LTE; Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Physical layer procedures (3GPP TS 36.213 version 10.10.0 Release 10). Technical report, 3GPP, 7 2013. ETSI TS 136 213 V10.10.0 (2013-07).
3GPP. LTE; Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Physical channels and modulation. Technical report, ETSI, France, 2010. Technical Specification Name: 3GPP TS 36.211 version 9.1.0, Release 9.
Real-Wireless. (2011). 4G Capacity Gains v1.4. Technical report, OFCOM, 1.
Bhowal, A., Paradkar, T., & Purohit, N. (2015). Evaluation of extended CP and ultra-extended CP in MBSFN. In 2015 IEEE UP section conference on electrical computer and electronics (UPCON), pp. 1–6. IEEE.
3GPP. LTE; Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Physical channels and modulation (3GPP TS 36.211 version 10.0.0 Release 10). Technical report, 3GPP, 1 2011. ETSI TS 136 211 V10.0.0 (2011-01).
Elsherif, A. R., & Khairy, M. M. (2011). Adaptive primary synchronization signal detection for 3GPP Long Term Evolution. In 9th international wireless communications and mobile computing conference (IWCMC), pp. 1716–1721. IEEE.
Nasraoui, L., Atallah, L. N., & Siala, M. (2014). Robust doubly-differential primary synchronization approach for 3GPP LTE systems. In International wireless communications and mobile computing conference (IWCMC), pp. 1069–1074. IEEE.
Popović, B. M., & Berggren, F. (2008). Primary synchronization signal in E-UTRA. In IEEE 10th international symposium on spread spectrum techniques and applications, pages 426–430. IEEE.
3GPP. LTE Feasibility study for evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (UTRA) and Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN). Technical report, ETSI, France, 2009. Technical Specification Name: 3GPP TR 25.912 version 9.0.0 Release 9.
Chinipardaz, M., Rasti, M., & Nourhosseini, M. (2014). An overview of cell association in heterogeneous network: Load balancing and interference management perspective. In 7th international symposium on telecommunications (IST), pp. 1250–1256. IEEE.
Andrews, J. G., Singh, S., Ye, Q., Lin, X., & Dhillon, H. S. (2014). An overview of load balancing in HetNets: Old myths and open problems. IEEE Wireless Communications, 21(2), 18–25.
Jeffrey, G. (2013). Andrews. Seven ways that HetNets are a cellular paradigm shift. IEEE Communications Magazine, 51(3), 136–144.
Damnjanovic, A., Montojo, J., Wei, Y., Ji, T., Luo, T., Vajapeyam, M., Yoo, T., Song, O., & Malladi, D. (2011). A survey on 3GPP heterogeneous networks. IEEE Wireless Communications, 18(3), 10–21.
Acknowledgements
This work has been partially supported by the Project TIN2014-54583-C2-2-R of the Spanish Ministerial Commission of Science and Technology (MICYT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadzadeh, A.M., Cuadra, L., del Arco-Vega, M.A. et al. Influence of overhead on LTE downlink performance: a comprehensive model. Telecommun Syst 67, 485–517 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-017-0355-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-017-0355-7