Abstract
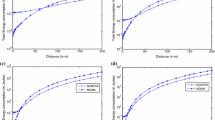
This paper proposes the use of quadrature space shift keying (QSSK) modulation for wireless sensor networks (WSNs). QSSK is a multiple input multiple output communication protocol that attracted substantial interest due to several promised inherent advantages. It has been shown in literature that QSSK scheme achieves high spectral efficiency with low average error probability, high energy efficiency, and very simple transmitter and receiver architectures. Hence, its use in WSNs is very promising to ameliorate the major limitations of such networks. The performance of a WSN with QSSK modulation and in the presence of co-channel interference is studied in this paper. A closed form expression for the average pair wise error probability is derived and used to obtain a tight upper bound on the overall average bit error ratio. Obtained results verified the superiority of QSSK scheme as compared to traditional modulation techniques especially for high spectral efficiency.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Arampatzis, T., Lygeros, J., & Manesis, S. (2005). A survey of applications of wireless sensors and wireless sensor networks. In IEEE International symposium on, mediterrean conference on control and automation intelligent control.
Borges, L. M., Velez, F. J., & Lebres, A. S. (2014). Survey on the characterization and classification of wireless sensor network applications. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, vol. 16(no. 4), 1860–1890.
Althunibat, S., Antonopoulos, A., Karatsakli, E., Granelli, F., & Verikoukis, C. (2016). Countering intelligent-dependent malicious nodes in target detection wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 16(23), 8627–8639.
Akyildiz, I. F., Su, W., Sankarasubramaniam, Y., & Cayirci, E. (2002). Wireless sensor networks: A survey. Computer Networks, 38(4), 393–422.
Abbasi, A. A., & Younis, M. (2007). A survey on clustering algorithms for wireless sensor networks. Computer Communications, 30(14), 2826–2841.
Polastre, J., Szewczyk, R., & Culler, D. (2005). Telos: Enabling ultra-low power wireless research. In Fourth International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, IPSN 2005 (pp. 364–369).
XBOW MICA2 Mote Specifications. http://www.xbow.com.
Yu, Y., Krishnamachari, B., & Prasanna, V. K. (2004). Energy-latency tradeoffs for data gathering in wireless sensor networks. IEEE INFOCOM, 2004. doi:10.1109/INFCOM.2004.1354498.
Son, D., Krishnamachari, B., & Heidemann, J. (2006). Experimental study of concurrent transmission in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 4th international conference on Embedded networked sensor systems. ACM.
Bagaa, M., Challal, Y., Ksentini, A., Derhab, A., & Badache, N. (2014). Data aggregation scheduling algorithms in wireless sensor networks: Solutions and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, vol. 16(no. 3), 1339–1368.
Gao, S., Qian, L., & Vaman, D. R. (2008). Distributed energy efficient spectrum access in wireless cognitive radio sensor networks. In IEEE Wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC).
Shojafar, M., Abolfazli, S., Mostafaei, H., & Singhal, M. (2015). Improving channel assignment in multi-radio wireless mesh networks with learning automata. Wireless Personal Communications, 82(1), 61–80.
Zhu, J., Song, Y., Jiang, D., & Song, H. (2016). Multi-armed bandit channel access scheme with cognitive radio technology in wireless sensor networks for the internet of things. IEEE Access, 4, 4609–4617.
Chiwewe, T. M., & Hancke, G. P. (2012). A distributed topology control technique for low interference and energy efficiency in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 8(1), 11–19.
Kumar, S., Sharma, A., & Raghuvanshi, S. S. (2011). Energy efficient scheduling algorithm with interference reduction for wireless sensor networks. In International conference on computational intelligence and communication networks, Gwalior, (pp. 328–332).
Liang, S., Ge, Y., Jiang, S., & Tan, H. P. (2014). A lightweight and robust interference mitigation scheme for wireless body sensor networks in realistic environments. In IEEE Wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), Istanbul, (pp. 1697–1702).
Razi, A., & Abedi, A. (2011). Interference reduction in Wireless Passive Sensor Networks using directional antennas. In 4th Annual caneus fly by wireless workshop, Montreal, QC (pp. 1–4).
Pantazis, N. A., Nikolidakis, S. A., & Vergados, D. D. (2013). Energy-efficient routing protocols in wireless sensor networks: A survey. IEEE Communications surveys and tutorials, 15(2), 551–591.
Althunibat, S., Abu-Al-Aish, A., Shehab, W. F. A., & Alsawalmeh, W. H. (2016). Auction-based data gathering scheme for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 20(6), 1223–1226.
Yetgin, H., Cheung, K. T. K., El-Hajjar, M., & Hanzo, L. H. (2017). A survey of network lifetime maximization techniques in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, vol. 19(no. 2), 828–854.
Mesleh, R., Ikki, S. S., & Aggoune, H. M. (2015). Quadrature spatial modulation. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 64(6), 2738–2742.
Basar, E. (2016). Index modulation techniques for 5G wireless networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 54(no. 7), 168–175.
Jeganathan, J., Ghrayeb, A., Szczecinski, L., & Ceron, A. (2009). Space shift keying modulation for MIMO channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(7), 3692–3703.
Mesleh, R. Y., Haas, H., Sinanovic, S., Ahn, C. W., & Yun, S. (2008). Spatial modulation. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 57(4), 2228–2241.
Mesleh, R., Ikki, S. S., & Aggoune, H. M. (2017). Quadrature spatial modulation-performance analysis and impact of imperfect channel knowledge. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 28, e2905. doi:10.1002/ett.2905.
Badarneh, O. S., & Mesleh, R. (2016). A comprehensive framework for quadrature spatial modulation in generalized fading scenarios. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 64(7), 2961–2970.
Ikki, S. S., & Mesleh, R. (2012). A general framework for performance analysis of space shift keying (SSK) modulation in the presence of gaussian imperfect estimations. IEEE Communications Letters, 16(2), 228–230.
Khalifeh, A., Al-Agtash, S., Tanash, R., & AlQudah, M., (2016). Deploying agents for monitoring and notification of wireless sensor networks. In 2016 IEEE 28th International conference on tools with artificial intelligence (ICTAI), San Jose, CA, (pp. 754–757).
Akyildiz, I. F., & Wang, Xudong. (2005). A survey on wireless mesh networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 43(9), S23–S30.
Benyamina, D., Hafid, A., & Gendreau, M. (2012). Wireless mesh networks design? A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 14(2), 299–310.
Craig, J. W. (1991). A new, simple and exact result for calculating the probability of error for two-dimensional signal constellations. In MILCOM 91 - Conference record, McLean, VA, (vol. 2, pp. 571–575).
Turin, G. L. (1960). The characteristic function of Hermitian quadratic forms in complex normal variables. Biometrika, 47(1/2), 199–201.
Proakis, J. G. (1995). Digital communications. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), under the SPS Grant G4936 (Hybrid Sensor Network for Emergency Critical Scenarios).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Althunibat, S., Khalifeh, A. & Mesleh, R. On the performance of wireless sensor networks with QSSK modulation in the presence of co-channel interference. Telecommun Syst 68, 105–113 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-017-0382-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-017-0382-4