Abstract
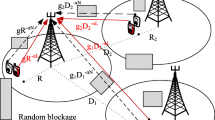
Due to the spectrum scarcity in conventional celluar frequency bands, millimeter wave (mmWave) frequency bands are attracting increasing attention as a promising candidate for future wireless cellular communication networks. The performance analysis in terms of coverage and rate of mmWave network is a crucial aspect and has been received an increasing interest in recent literature. However, the impact of LoS/NLoS propagation and outage on the coverage probability and rate of the mmWave network is yet to be completely understood. In this paper, we analyze the performance of mmWave networks considering (a) only Non Line-of-Sight (NLoS) environment and (b) both NLoS and LoS propagation. In particular, we compare the coverage and rate performances of mmWave networks with a more practical blockage model that encompasses an outage state, standard path loss function,and directional beamforming which is implemented using number of antennas and scanning angle at the transmitter and receiver. Further, for more practical and precise analysis, we assume that channel amplitudes are Nakgami-m distributed with different fading parameters for NLoS and LoS communication links. Also, different from existing works, the user association with a BS is assumed with a LoS/NLoS path with the smallest pathloss. Our numerical results depict that the presence of an outage state in blockage model decreases the performance of mmWave network. Also, we show the presence of LoS propagation increases the performance of network at the small average cell radius. Further, the impact of variable number of transmit antennas, scanning angle, and antenna radiation efficiency on the network performance is also addressed.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
CISCO. (2014). Cisco visual networking index: Global mobile data traffic forecast update (2013–2018).
Rappaport, T. S., Heath, R. W, Jr., Daniels, R. C., & Murdock, J. N. (2014). Millimeter wave wireless communication. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Pi, Z., & Khan, F. (2011). An introduction to millimeter-wave mobile broadband systems. IEEE Communications Magazine, 49(6), 101–107.
Rappaport, T. S., Sun, S., Mayzus, R., Zhao, H., Azar, Y., Wang, K., et al. (2013). Millimeter wave mobile communications for 5G cellular: It will work!. IEEE Access, 1, 335–349.
Rangan, S., Rappaport, T. S., & Erkip, E. (2014). Millimeter-wave cellular wireless networks: Potentials and challenges. Proceedings of the IEEE, 102(3), 366–385.
Doan, C. H., Emami, S., Sobel, D. A., Niknejad, A. M., & Brodersen, R. W. (2004). Design considerations for 60 GHz cmos radios. IEEE Communications Magazine, 42(12), 132–140.
Gutierrez, F., Agarwal, S., Parrish, K., & Rappaport, T. S. (2009). On-chip integrated antenna structures in CMOS for 60 GHz WPAN systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 27(8), 1367–1378.
Rappaport, T. S., Murdock, J. N., & Gutierrez, F. (2011). State of the art in 60-GHz integrated circuits and systems for wireless communications. Proceedings of the IEEE, 99(8), 1390–1436.
Akdeniz, M. R., Liu, Y., Samimi, M. K., Sun, S., Rangan, S., Rappaport, T. S., et al. (2014). Millimeter wave channel modeling and cellular capacity evaluation. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 32(6), 1164–1179.
Ghosh, A., Thomas, T. A., Cudak, M. C., Ratasuk, R., Moorut, P., Vook, F. W., et al. (2014). Millimeter-Wave enhanced local area systems: A high-data-rate approach for future wireless networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 32(6), 1152–1163.
Andrews, J. G., Baccelli, F., & Ganti, R. K. (2011). A tractable approach to coverage and rate in cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 59(11), 3122–3134.
Bai, Tianyang, & Heath, R. W. (2015). Coverage and rate analysis for millimeter-wave cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 14(2), 1100–1114.
Singh, S., Kulkarni, M. N., Ghosh, A., & Andrews, J. G. (2015). Tractable model for rate in self-backhauled millimeter wave cellular networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 33(10), 2196–2211.
Thomas, T. A., & Vook, F. W. (2014). System level modeling and performance of an outdoor mmWave local area access system. In IEEE international symposium on personal indoor and mobile radio communication (pp. 187–191).
Kulkarni, M. N., Singh, S., & Andrews, J. G. (2014). Coverage and rate trends in dense urban mmWave cellular networks. In Global communications conference (GLOBECOM), 2014 (pp. 3809–3814). IEEE
Andrews, J. G., Bai, T., Kulkarni, M. N., Alkhateeb, A., Gupta, A. K., & Heath, R. W. (2017). Modelling and analyzing millimeter wave cellular systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 65(1), 403–430.
Bai, T., Vaze, R., & Heath, R. W. (2014). Analysis of blockage effects on urban cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(9), 5070–5083.
Galiotto, C., Pratas, N.K., Marchetti, N., & Doyle, L. (2015). A stochastic geometry framework for LoS/NLoS propagation in dense small cell networks. In IEEE international conference on communications (ICC), 2015 , London (pp. 2851–2856).
Mailloux, R. J. (1994). Phased array antenna handbook. Boston, MA: Artech House.
Baccelli, F., & Blaszczyszyn, B. (2009). Stochastic geometry and wireless networks (Vol. I)., Theory Breda: Now Publishers.
Andrews, J. G., Gupta, A. K., Dhillon, H. S. A primer on cellular network analysis using stochastic geometry. Submitted to IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials. arXiv:1604.03183.
Haenggi, M. (2005). On distances in uniformly random networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 51(10), 3584–3586.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korrai, P., Rao, K.D. Performance analysis of downlink mmWave networks under LoS/NLoS propagation with blockage and directional beamforming. Telecommun Syst 72, 53–68 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-019-00547-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-019-00547-x