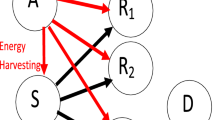
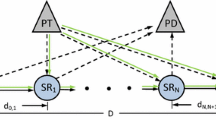
Abstract
This article derives the packet error probability (PEP) of different relay selection techniques for cognitive radio networks (CRN). The power of secondary source and relays is adaptive to not cause high interference to primary receiver \(P_R\). Secondary nodes harvest energy from radio frequency signals to be able to communicate. CRN with secondary nodes transmitting with adaptive power was already studied in the literature. However, in all previous studies, secondary nodes use their own batteries to transmit. The main motivation of our paper is to study CRN with energy harvesting and adaptive transmit power (ATP). We derive new expressions of PEP and throughput for CRN with energy harvesting and ATP. Our results are valid for opportunistic relaying, partial relay selection and reactive relay selection. Our main contribution is to optimize harvesting duration to maximize the system throughput.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amini, M. R., Mahdavi, M., & Omidi, M. J. (2018). Discrete-time Markov chain analysis of energy efficiency in a CR network regarding primary and secondary traffic with primary user returns. IEEE Access, 6, 22305–22323.
Amini, M. R., Mahdavi, M., & Omidi, M. J. (2018). Maximizing dynamic access energy efficiency in multiuser CRNs with primary user return. IEEE Systems Journal, pp. 1–12
Haykin, S. (2005). Cognitive radio: Brain-empowered wireless communications. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 23, 201–220.
Ibrahim, N. S., Sali, A., Mohamad, M. H., & Hashim, S. J. (2015). Outage performance in relay-assisted overlay cognitive radio networks. In IEEE 12th Malaysia international conference on communications (MICC).
Zhan, J., Liu, Y., Tang, X., & Chen, Q. (2018). Relaying protocols for buffer-aided energy harvesting wireless cooperative networks. IET Networks Year, 7(3), 109–118.
Xiuping, W., Feng, Y., & Tian, Z. (2018). The DF-AF selection relay transmission based on energy harvesting. In 2018 10th international conference on measuring technology and mechatronics automation (ICMTMA) (pp. 174–177).
Nguyen, H. T., Nguyen, S. Quang, & Hwang, W.-J. (2018). Outage probability of energy harvesting relay systems under unreliable backhaul connections. In 2018 2nd international conference on recent advances in signal processing, telecommunications and computing (SigTelCom) (pp: 19–23).
Qiu, C., Hu, Y., & Chen, Y. (2018). Lyapunov optimized cooperative communications with stochastic energy harvesting relay. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 5(2), 1323–1333.
Sui, D., Hu, F., Zhou, W., Shao, M., & Chen, M. (2018). Relay selection for radio frequency energy-harvesting wireless body area network with buffer. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 5(2), 1100–1107.
Hoang, T. M., Tran, M., Tan, N. T., & Choi, S.-G. (2018). Analysis of partial relay selection in NOMA systems with RF energy harvesting. In 2018 2nd international conference on recent advances in signal processing, telecommunications and computing (SigTelCom) (pp. 13–18).
Le, Q. N., Bao, V. N. Q., & An, B. (2018). Full-duplex distributed switch-and-stay energy harvesting selection relaying networks with imperfect CSI: Design and outage analysis. Journal of Communications and Networks, 20(1), 29–46.
Gong, J., Chen, X., & Xia, M. (2018). Transmission optimization for hybrid half/full-duplex relay with energy harvesting. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 17(5), 3046–3058.
Tang, H., Xie, X., & Chen, J. (2018). X-duplex relay with self-interference signal energy harvesting and its hybrid mode selection method. In 2018 27th wireless and optical communication conference (WOCC) (pp. 1–6).
Chiu, H.-C., & Huang, W.-J. (2018). Precoding design in two-way cooperative system with energy harvesting relay. In 2018 27th wireless and optical communication conference (WOCC) (pp. 1–5).
Gurjar, D. S., Singh, U., & Upadhyay, P. K. (2018). Energy harvesting in hybrid two-way relaying with direct link under Nakagami-m fading. In 2018 IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC) (pp. 1–6).
Singh, K., Ku, M.-L., Lin, J.-C., & Ratnarajah, T. (2018). Toward optimal power control and transfer for energy harvesting amplify-and-forward relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 17, 4971–4986.
Wu, Y., Qian, L., Huang, L., & Shen, X. (2018). Optimal relay selection and power control for energy-harvesting wireless relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2(2), 471–481.
Fan, R., Atapattu, S., Chen, W., Zhang, Y., & Evans, J. (2018). Throughput maximization for multi-hop decode-and-forward relay network with wireless energy harvesting. IEEE Access, 6, 24582–24595.
Huang, Y., Wang, J., Zhang, P., & Wu, Q. (2018). Performance analysis of energy harvesting multi-antenna relay networks with different antenna selection schemes. IEEE Access, 6, 5654–5665.
Babaei, M., Aygölü, Ü., & Basar, E. (2018). BER analysis of dual-hop relaying with energy harvesting in Nakagami-m fading channel. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 99, 1–1.
Kalluri, T., Peer, M., Bohara, V. A., da Costa, D. B., & Dias, U. S. (2018). Cooperative spectrum sharing-based relaying protocols with wireless energy harvesting cognitive user. IET Communications, 12(7), 838–847. IET Journals and Magazines.
Xie, D., Lai, X., Lei, X., & Fan, L. (2018). Cognitive multiuser energy harvesting decode-and-forward relaying system with direct links. IEEE Access, 6, 5596–5606.
Yan, Z., Chen, S., Zhang, X., & Liu, H.-Li. (2018). Outage performance analysis of wireless energy harvesting relay-assisted random underlay cognitive networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal pp. 1–1.
Nhat, T. T., Duy, T. T., Bao, V. N. Q. (2018). Performance evaluation of cooperative relay networks with one full-energy relay and one energy harvesting relay. In 2018 2nd international conference on recent advances in signal processing, telecommunications and computing (SigTelCom) (pp. 7–12).
Vo, V. N., Nguyen, T. G., So-In, C., Baig, Z. A., & Sanguanpong, S. (2018). Secrecy outage performance analysis for energy harvesting sensor networks with a jammer using relay selection strategy. IEEE Access, 6, 23406–23419.
Behdad, Z., Mahdavi, M., & Razmi, N. (2018). A new relay policy in RF energy harvesting for IoT networks-a cooperative network approach. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, (Early Access) pp. 1–1.
Yao, R., Lu, Y., Tsiftsis, T. A., Qi, N., Mekkawy, T., & Xu, F. (2018). Secrecy rate-optimum energy splitting for an untrusted and energy harvesting relay network. IEEE Access, 6, 19238–19246.
Yin, C., Nguyen, H. T., Kundu, C., Kaleem, Z., Garcia-Palacios, E., & Duong, T. Q. (2018). Secure energy harvesting relay networks with unreliable backhaul connections. IEEE Access, 6, 12074–12084.
Lei, H., Xu, M., Ansari, I. S., Pan, G., Qaraqe, K. A., & Alouini, M.-S. (2017). On secure underlay MIMO cognitive radio networks with energy harvesting and transmit antenna selection. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, (Early Access) pp. 192–203.
Ho-Van, K., & Do-Dac, T. (2018). Performance analysis of jamming technique in energy harvesting cognitive radio networks. Springer Telecommunication Systems, Published online 7 June 2018.
Huu, P. N., & Ho-Van, K. (2018). Bidirectional relaying with energy harvesting capable relay: Outage analysis for Nakagami-m fading. Springer Telecommunication Systems, Published online 13 March 2018.
Bayrakdar, M. E., & Calhan, A. (2018). Artificial bee colony-based spectrum handoff algorithm in wireless cognitive radio networks. International Journal of Communication Systems, 31(5), e3495.
Bayrakdar, M. E., & Calhan, A. (2017). Non-preemptive queueing model of spectrum handoff scheme based on prioritized data traffic in cognitive wireless networks. ETRI Journal, 39(4), 558–569.
Hasna, M. O., & Alouini, M.-S. (2004). Harmonic mean and end-to-end performance of transmission systems with relays. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 52(1), 130–135.
Krikidis, I., Thompson, J., McLaughlin, S., & Goertz, N. (2008). Amplify and for- ward with partial relay selection. IEEE Communications Letters, 12(4), 237–238.
Boujemaa, H. (2010). Exact symbol error probability of cooperative systems with partial relay selection. European Transactions on Telecom, 21, 79–85.
Hussain, S. I., Alouini, M. S., Qaraqe, K., & Hasna, M. (2012). Reactive relay selection in underlay cognitive networks with fixed gain relays. In IEEE ICC.
Xi, Y., Burr, A., Wei, J. B., & Grace, D. (2011). A general upper bound to evaluate packet error rate over quasi-static fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(5), 1373–1377.
Gradshteyn, I. S., & Ryzhik, I. M. (1994). Table of integrals, series and products (5th ed.). San Diego, CA: Academic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix A
The CDF of \(E_S\) is expressed as
Assuming that \(g_{AS}\) and \(g_{SP_{R}}\) are independent, we deduce
\(|g_{AS}|^2\) and \(|g_{SP_{R}}|^{2}\) follow an exponential distribution with mean \(E(|g_{AS}|^2)=\frac{1}{\alpha _{AS}}\) and \(E(|g_{SP_R}|^2)=\frac{1}{\alpha _{SP_R}}\). Therefore, we have
Appendix B
The SNR at \(R_k\) is the product of two random variables \(E_S\) and \(\frac{|h_{SR_k}|^2}{N_0}\).
Let \(X=\frac{|h_{SR_k}|^2}{N_0}\), the CDF of SNR at relay \(R_k\) is given by
where \(f_X(v)\) is the PDF of \(X=\frac{|h_{SR_k}|^2}{N_0}\):
where \(\alpha _{SR_k}=\frac{1}{E(|g_{SR_k}|^2)}\).
Using the expression of CDF of \(E_S\) provided in “Appendix A”, we can write
We deduce
We use the following result [39]
to write the CDF of SNR as
Appendix C
We use the following result [39]
where \(W_{\mu ,\nu }(x)\) is the Whittaker function.
where the two integrals are evaluated numerically using MATLAB.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halima, N.B., Boujemâa, H. Energy harvesting with adaptive transmit power for cognitive radio networks. Telecommun Syst 72, 41–52 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-019-00548-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-019-00548-w