Abstract
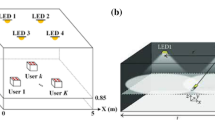
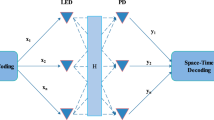
The exponential rise in wireless communication demands and allied applications have revitalized academia-industries to develop an efficient and potential solution. Furthermore, the high-pace increasing scarcity of radio spectrum has also alarmed researchers to achieve better Quality of Service (QoS) centric solution. To meet such demands Visible Light Communication (VLC) systems have gained global attention; however, up surging high rate, range and reliability (3R) needs demand better performance. Towards these goals, Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) based VLC systems is an efficient approach; though its efficacy under Multiple Users (MU) conditions remains least explored. Enabling MIMO-MU based VLC can achieve 3R objectives effectively; however, factors like multipath attenuation, interferences and varied impairment-affects makes classical approached confined. The MIMO-MU VLC systems require robust error, noise or interference resilient transmission even under adverse conditions such as non-linear LED, multipath attenuation and interference. Towards these objectives, in this paper a highly robust MIMO-MU VLC system is developed that incorporates an augmented MIMO channel design and combined pre-coding and post equalization schemes. To alleviate major interference probability in MIMO-MU environment, proposed model incorporates time (delay)-multiplexing based data transmission followed by signal adaptive precoding and Volterra Kernel based Hybrid-equalizer. This approach enables interference and noise removal as well as LED non-linearity handling under MIMO-MU VLC communication. The use of a Volterra Kernel based Decision Feedback Equalization with both linear as well as non-linear equalization enables proposed VLC system to exhibit low Bit Error Rate with low modulation index and taps, that optimizes trade-off between performance as well as complexity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cisco, San Jose, CA, USA. (2012). Cisco service provider Wi-Fi: A platform for business innovation and revenue generation. Available http://www.cisco.com/en/US/solutions/collateral/ns341/ns524/ns673/solution-overview-c22-642482.html/. Accessed January 16, 2016.
Kashani, M. A., Safari, M., & Uysal, M. (2013). Optimal relay placement and diversity analysis of relay-assisted free-space optical communication systems. IEEE/OSA Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 5(1), 37–47.
Karimi, M., & Uysal, M. (2012). Novel adaptive transmission algorithms for free-space optical links. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 60(12), 3808–3815.
Kashani, M. A., Rad, M. M., Safari, M., & Uysal, M. (2012). All-optical amplify and-forward relaying system for atmospheric channels. IEEE Communications Letters, 16(10), 1684–1687.
Burchardt, H., Serafimovski, N., Tsonev, D., Videv, S., & Haas, H. (2014). VLC: Beyond point-to-point communication. IEEE Communications Magazine, 52(7), 98–105.
Shao, S., Khreishah, A., & Khalil, I. (2016). Joint link scheduling and brightness control for greening VLC-based indoor access networks. IEEE/OSA Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 8(3), 148–161.
Armstrong, J. (2013). Optical domain digital-to-analog converter for visible light communications using led arrays [invited]. Photonics Research, 1(2), 92–95.
Jovicic, A., Li, J., & Richardson, T. (2013). Visible light communication: Opportunities, challenges and the path to market. IEEE Communications Magazine, 51(12), 26–32.
Pathak, P. H., Feng, X., Hu, P., & Mohapatra, P. (2015). Visible light communication, networking, and sensing: A survey, potential and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 17(4), 2047–2077.
Barry, J. R., Kahn, J. M., Krause, W. J., Lee, E. A., & Messerschmitt, D. G. (1993). Simulation of multipath impulse response for wireless optical channels. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 11(3), 367–379.
Lopez-Hermandez, F. J., & Betancor, M. J. (1997). DUSTIN: Algorithm for calculation of impulse response on IR wireless indoor channels. Electronics Letters, 33(21), 1804–1806.
Carruthers, J. B., & Kannan, P. (2002). Iterative site-based modeling for wireless infrared channels. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 50(5), 759–765.
Lopez-Hernandez, F. J., Perez-Jimeniz, R., & Santamaria, A. (1998). Monte Carlo calculation of impulse response on diffuse IR wireless indoor channels. Electronics Letters, 34(12), 1260–1262.
Lopez-Hernandez, F. J., Perez-Jimenez, R., & Santamaria, A. (1998). Modified Monte Carlo scheme for high efficiency simulation of the impulse response on diffuse IR wireless indoor channels. Electronics Letters, 34(19), 1819–1820.
Lopez-Hernandez, F. J., Perez-Jimenez, R., & Santamaria, A. (2000). Ray tracing algorithms for fast calculation of the channel impulse response on diffuse IR wireless indoor channels. Optical Engineering, 39(10), 2775–2780.
Pollock, T. S., Abhayapala, T. D., & Kennedy, R. A. (2003). Introducing space into MIMO capacity calculations. Telecommunication Systems, 24(2–4), 415–436.
Sharma, R., Kumari, A. C., Aggarwal, M., & Ahuja, S. (2018). Optimal LED deployment for mobile indoor visible light communication system: Performance analysis. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 83, 427–432.
Miao, P., Wu, L., & Chen, Z. (2018). An anti-noise modem for visible light communication systems using the improved M-ary position phase shift keying. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 85, 126–133.
Chun, H., Chiang, C., & O’Brien, D. (2012). Visible light communication using OLEDs: Illumination and channel modeling. In Proceedings of the international workshop on optical wireless communications (pp. 1–3).
Nguyen H. Q., et al. (2010). A MATLAB-based simulation program for indoor visible light communication system. In Proceedings of CSNDSP (pp. 537–540).
Komine, T., & Nakagawa, M. (2004). Performance evaluation on visible-light wireless communication system using white LED lightings. In Proceedings. 9th IEEE symposium on computers and communications (Vol. 1, pp. 258–263).
Long, S., Khalighi, M. A., Wolf, M., Bourennane, S., & Ghassemlooy, Z. (2014). Channel characterization for indoor visible light communications. In Proceedings of IWOW (pp. 75–79).
Lee, K., Park, H., & Barry, J. R. (2011). Indoor channel characteristics for visible light communications. IEEE Communications Letters, 15(2), 217–219.
Safari, M. (2016). MIMO free-space optical communication (pp. 231–253). Cham: Springer.
Navidpour, S. M., Uysal, M., & Kavehrad, M. (2007). BER performance of free-space optical transmission with spatial diversity. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 6(8), 2813–2819.
Popoola, W. O., Poves, E., & Haas, H. (2012). Spatial pulse position modulation for optical communications. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 30(18), 2948–2954.
Zhu, Y.-J., Liang, W.-F., Zhang, J.-K., & Zhang, Y.-Y. (2015). Space-collaborative constellation designsfor MIMO indoor visible light communications. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 27(15), 1667–1670.
Nuwanpriya, A., Ho, S.-W., & Chen, C. S. (2015). Indoor MIMO visible light communications: Novel angle diversity receivers for mobile users. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 33(9), 1780–1792.
Fath, T., & Haas, H. (2013). Performance comparison of MIMO techniques for optical wireless communications in indoor environments. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 61(2), 733–742.
Marshoud, H., Dawoud, D., Kapinas, V. M., Karagiannidis, G. K., Muhaidat, S., & Sharif, B. (2015). MU-MIMO precoding for VLC with imperfect CSI. In Proceedings of the IEEE 4th international workshop on optical wireless communications (IWOW) (pp. 93–97).
Hong, Y., Chen, J., Wang, Z., & Yu, C. (2013). Performance of a precoding MIMO system for decentralized multiuser indoor visible light communications. IEEE Photonics Journal, 5(4), 7800211.
Chen, J., Ma, N., Hong, Y., & Yu, C. (2014). On the performance of MU-MIMO indoor visible light communication system based on THP algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on communications in China (ICCC) (pp. 136–140).
IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks-part 15.7: Short-range wireless optical communication using visible light. IEEE Standard 802.15.7-2011, 2011 (pp. 1–309).
Masouros, C., & Alsusa, E. (2009). Dynamic linear precoding for the exploitation of known interference in MIMO broadcast systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(3), 1396–1404.
Masouros, C. (2011). Correlation rotation linear precoding for MIMO broadcast communications. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 59(1), 252–262.
Marshoud, H., Sofotasios, P. C., Muhaidat, S., Sharif, B. S., & Karagiannidis, G. K. (2018). Optical adaptive precoding for visible light communications. IEEE Access, 6, 22121–22130.
Hsu, C. W., Chow, C. W., Lu, Y. I., Liu, Y. L., & Yeh, C. H. (2016) Demonstration of high speed imaging 3 × 3 MIMO-OFDM visible light communication system. In Proceedings of the IEEE photonics conference, USA, 2016, paper WP27.
Burton, A., Le Hoa, M., Ghassemlooy, Z., Bentley, E., & Botella, C. (2014). Experimental demonstration of 50-Mb/s visible light communications using 4 by 4 MIMO. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 26(9), 945–948.
Azhar, A. H., Tran, T. A., & O’Brien, D. (2013). A gigabit/s indoor wireless transmission using MIMO-OFDM visible-light communications. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 25(2), 171–174.
Hong, Y., Chen, J., & Yu, C. (2014). Performance improvement of the pre-coded multi-user MIMO indoor visible light communication system. In 2014 9th international symposium on communication systems, networks & digital sign (CSNDSP), Manchester (pp. 314–318).
Zhong, Q., Fan, Y., & Liu, S. (2018). Performance comparison of MU-MIMO schemes for indoor visible light communication systems. Optics Communications, 420, 110–115.
Ma, H., Lampe, L., & Hranilovic, S. (2015). Coordinated broadcasting for multiuser indoor visible light communication systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 63(9), 3313–3324.
Komine, T., & Nakagawa, M. (2004). Fundamental analysis for visible-light communication system using LED lights. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 50(1), 100–107.
Kasper, B. L. (1982). Equalization of multimode optical fiber systems. Bell System Technical Journal, 61(7), 1367–1388.
Rappaport, T. S. (2002). Wireless communications: Principles and practice (2nd ed.). Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall PTR.
Cossu, G., Khalid, A. M., Choudhury, P., Corsini, R., & Ciaramella, E. (2012). 3.4 Gbit/s visible optical wireless transmission based on RGB LED. Optics Express, 20(26), B501–B506.
Wang, Y., Huang, X., Tao, L., Shi, J., & Chi, N. (2015). 4.5-Gb/s RGB-LED based WDM visible light communication system employing CAP modulation and RLS based adaptive equalization. Optics Express, 23(10), 13627–13633.
Wang, Y., Huang, X., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., & Chi, N. (2014). Enhanced performance of visible light communication employing 512QAM N-SC-FDE and DD-LMS. Optics Express, 22(13), 15328–15334.
Qian, H., Yao, S., Cai, S., & Zhou, T. (2014). Adaptive post distortion for nonlinear LEDs in visible light communications. IEEE Photonics Journal, 6(4), 1–8.
Li, J., Huang, Z., Liu, X., & Ji, Y. (2015). Hybrid time-frequency domain equalization for LED nonlinearity mitigation in OFDM-based VLC systems. Optics Express, 23(1), 611–619.
Wang, Y., Tao, L., Huang, X., Shi, J., & Chi, N. (2015). Enhanced performance of a high speed WDM CAP64 VLC system employing Volterra series based nonlinear equalizer. IEEE Photonics Journal, 7(3), 1–7.
Schetzen, M. (1980). The Volterra and Wiener theories of nonlinear systems (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Agrawal, G. P. (2001). Nonlinear fiber optics (3rd ed.). London: Academic Press.
Haykin, S. S. (2005). Adaptive filter theory. Pearson Education India.
Wu, H., Tierno, J. A., Pepeljugoski, P., Schaub, J., Gowda, S., Kash, J. A., et al. (2003). Integrated transversal equalizers in high-speed fiber-optic systems. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(12), 2131–2137.
Sewter, J., & Carusone, A.C. (2005). A 40 Gb/s transversal filter in 0.18/spl mu/m CMOS using distributed amplifiers. In IEEE custom integrated circuits conference (pp. 417–420).
Aharonovich, M., & Arnon, S. (2005). Performance improvement of optical wireless communication through fog with a decision feedback equalizer. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 22(8), 1646–1654.
Ardalan, S. (1986). Floating-point error analysis of recursive least-squares and least-mean-squares adaptive filters. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 33(12), 1192–1208.
Lin, J.-Y., & Wei, C.-H. (1995). Adaptive nonlinear decision feedback equalization with channel estimation and timing recovery in digital magnetic recording systems. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and SystemsII: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 42(3), 196–206.
Agarossi, L., Bellini, S., Bregoli, F., & Migliorati, P. (1998). Equalization of nonlinear optical channels. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on communications (Vol. 2, pp. 662–667).
Amendola, D., Cordeschi, N., Shojafar, M., Abate, V., & De Rango, F. (2014). Performance evaluation of a multi-frame persistent neighbor discovery strategy based on sift-distribution in DTN RFID networks. In International symposium on performance evaluation of computer and telecommunication systems (SPECTS 2014) (pp. 647–653). IEEE.
Wang, Y., Tao, L., Huang, X., Shi, J., & Chi, N. (2015). 8-Gb/s RGBY LED-based WDM VLC system employing high-order CAP modulation and hybrid post equalizer. IEEE Photonics Journal, 7(6), 1–7.
Maiti, d, & Brandt-Pearce, M. (2015). Modified nonlinear decision feedback equalizer for long-haul fiber-optic communications. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 33(18), 3763–3772.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, T., Balani, W. A robust pre-coding and hybrid equalization assisted MIMO-MU visible light communication system for QoS centric indoor communication. Telecommun Syst 72, 457–470 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-019-00581-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-019-00581-9