Abstract
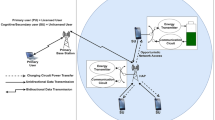
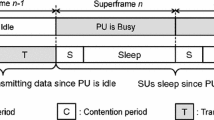
Efficient energy transfer is crucial for a green base station with limited energy to replenish the energy of stand-alone devices in the Internet of Things (IoT). Cognitive radio (CR) is critical to satisfying the spectrum requirement for IoT devices. This paper proposes two wireless charging policies, namely, charging in residual multi-frame time and charging one energy unit at a time, for the random access multiple access control on CR-based green-energy networks. The novelty of the policies is to send wireless energy at appropriate timing and duration. Event-driven simulations are conducted to study the performances of the policies. Simulation results show that the two policies significantly yield high energy efficiency, and maintain throughput and quality-of services. Besides, the policy of charging one energy unit at a time outperforms the policy of charging in residual multi-frame time.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Chettri, L., & Bera, R. (2020). A comprehensive survey on Internet of Things (IoT) towards 5G wireless systems. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(1), 16–32.
Sharma, S. K., & Wang, X. (2020). Towards massive machine type communications in ultra-dense cellular IoT networks: Current issues and machine learning-assisted solutions. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 22(1), 426–471.
Stoyanova, M., Nikoloudakis, Y., Panagiotakis, S., Pallis, E., & Markakis, E. K. (2020). A survey on the Internet of Things (IoT) forensics: Challenges, approaches, and open issues. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 22(2), 1191–1221.
Xia, N., Chen, H.-H., & Yang, C.-S. (2018). Radio resource management in machine-to-machine communications—A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 20(1), 791–828.
Ali, A., Hamouda, W., & Uysal, M. (2015). Next generation M2M cellular networks: Challenges and practical considerations. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(9), 18–24.
Awin, F. A., Alginahi, Y. M., Abdel-Raheem, E., & Tepe, K. (2019). Technical issues on cognitive radio-based Internet of Things systems: A survey. IEEE Access, 7, 97887–97908.
Ahmad, W. S. H. M. W., et al. (2020). 5G technology: Towards dynamic spectrum sharing using cognitive radio networks. IEEE Access, 8, 14460–14488.
Rawat, P., Singh, K. D., & Bonnin, J. M. (2016). Cognitive radio for M2M and Internet of Things: A survey. Computer Communications, 94(15), 1–29.
Khan, A. A., Rehmani, M. H., & Rachedi, A. (2017). Cognitive radio based Internet of Things: Applications, architectures, spectrum related functionalities, and future research directions. IEEE Wireless Communications, 24(3), 17–25.
Aijaz, A., & Aghvami, A.-H. (2015). PRMA-based cognitive machine-to-machine communications in smart grid networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 64(8), 3608–3623.
Aijaz, A., & Aghvami, A.-H. (2015). Cognitive machine-to-machine communications for Internet-of-Things: A protocol stack perspective. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2(2), 103–112.
Singh, R. P., Sangwan, A., & Godara, K. (2019). Modified-PRMA MAC protocol for cognitive radio networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 107, 869–885.
Lu, X., Wang, P., Niyato, D., Kim, D. I., & Han, Z. (2016). Wireless charging technologies: Fundamentals, standards, and network applications. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 18(2), 1413–1452.
Ku, M.-L., Li, W., Chen, Y., & Liu, K. J. R. (2016). Advances in energy harvesting communications: Past, present, and future challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 18(2), 1384–1412.
Soyata, T., Copeland, L., & Heinzelman, W. (2016). RF energy harvesting for embedded systems: A survey of tradeoffs and methodology. IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazine, 16(1), 22–57.
Ren, J., et al. (2018). RF energy harvesting and transfer in cognitive radio sensor networks: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Communications Magazine, 56(1), 104–110.
Mohjazi, L., Dianati, M., Karagiannidis, G. K., Muhaidat, S., & Al-Qutayri, M. (2015). RF-powered cognitive radio networks: Technical challenges and limitations. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(4), 94–100.
Liu, X., & Ansari, N. (2019). Toward green IoT: Energy solutions and key challenges. IEEE Communications Magazine, 57(3), 104–110.
Liu, X., & Ansari, N. (2019). Profit-driven user association and smart grid energy transfer in green cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 68(10), 10111–10120.
Liu, B., Wang, J., Ma, S., Zhou, F., Ma, Y., & Lu, G. (2019). Energy efficient cooperation in mobile edge computing-enabled cognitive radio networks. IEEE Access, 7, 45382–45394.
Liu, B., Li, W., Ma, Y., Wang, J., & Lu, G. (2019). Wireless powered cognitive-based mobile edge computing with imperfect spectrum sensing. IEEE Access, 7, 80431–80442.
Zhai, C., Li, Y., Li, C., & Liu, J. (2020). Cognitive relaying with wireless energy harvesting and accumulation. IEEE Systems Journal (Early Access), 1–12.
Tayel, A. F., Rabia, S. I., El-Malek, A. H. A., & Abdelrazek, A. M. (2020). An optimal policy for hybrid channel access in cognitive radio networks with energy harvesting. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 69(10), 11253–11265.
Xu, D., & Li, Q. (2019). Resource allocation for secure communications in cooperative cognitive wireless powered communication networks. IEEE Systems Journal, 13(3), 2431–2442.
Ding, H., et al. (2017). Cognitive capacity harvesting networks: Architectural evolution towards future cognitive radio networks. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 19(3), 1902–1923.
Pejoski, S., & Hadzi-Velkov, Z. (2020). Slotted ALOHA wireless networks with RF energy harvesting in Nakagami-m fading. Ad-Hoc Networks, 107, 1–10.
Iqbal, M. S., Sadi, Y., & Coleri, S. (2020). Throughput maximization for full duplex wireless powered communication networks. In IEEE international conference on communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland (pp. 7–11).
Perera, T. D. P., Jayakody, D. N. K., Sharma, S. K., Chatzinotas, S., & Li, J. (2018). Simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT): Recent advances and future challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 20(1), 264–302.
Varshney, L. (2008). Transporting information and energy simultaneously. In Proceedings of the IEEE international symposium on information theory (pp. 1612–1616).
Zhou, X., Zhang, R., & Ho, C. K. (2013). Wireless information and power transfer: Architecture design and rate-energy tradeoff. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 61, 4754–4767.
Boshkovska, E., Ng, D., Zlatanov, N., & Schober, R. (2015). Practical non-linear energy harvesting model and resource allocation for SWIPT systems. IEEE Communications Letters, 19, 2082–2085.
Xu, J., Liu, L., & Zhang, R. (2014). Multiuser MISO beamforming for simultaneous wireless information and power transfer. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 62, 4798–4810.
Zhang, Z., Long, K., Vasilakos, A. V., & Hanzo, L. (2016). Full-duplex wireless communications: Challenges, solutions, and future research directions. Proceedings of IEEE, 104(7), 1369–1409.
Sharma, S. K., et al. (2018). Dynamic spectrum sharing in 5G wireless networks with full-duplex technology: Recent advances and research challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 20(1), 674–707.
Amjad, M., Akhtar, F., Rehmani, M. H., Reisslein, M., & Umer, T. (2017). Full-duplex communication in cognitive radio networks: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 19(4), 2158–2191.
Kolodziej, K. E., Perry, B. T., & Herd, J. S. (2019). In-band full-duplex technology: Techniques and systems survey. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 67(7), 3025–3041.
Lien, S.-Y., Chen, K.-C., & Lin, Y. (2011). Toward ubiquitous massive accesses in 3GPP machine-to-machine communications. IEEE Communications Magazine, 49(4), 66–74.
Obaidat, M. S., Nicopolitidis, P., & Zarai, F. (2015). Modeling and simulation of computer networks and systems: Methodologies and applications. Burlington: Morgan Kaufmann.
Lu, X., Wang, P., Niyato, D., Kim, D. I., & Han, A. (2014). Wireless networks with RF energy harvesting: A contemporary survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 17(2), 757–789.
Chen, X., et al. (2019). Analysis and design of an ultra-low-power Bluetooth low-energy transmitter with ring oscillator-based ADPLL and 4X frequency edge combiner. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 54(5), 1339–1350.
Ejaz, W., Naeem, M., Basharat, M., Anpalagan, A., & Kandeepan, S. (2016). Efficient wireless power transfer in software-defined wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 16(20), 7409–7420.
Naderi, M. Y., Nintanavongsa, P., & Chowdhury, K. R. (2014). RF-MAC: A medium access control protocol for re-chargeable sensor networks powered by wireless energy harvesting. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(7), 3926–3937.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tzeng, SS., Lin, YJ. Wireless energy transfer policies for cognitive radio based MAC in energy-constrained IoT networks. Telecommun Syst 77, 435–449 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-021-00771-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-021-00771-4