Abstract
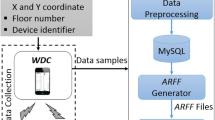
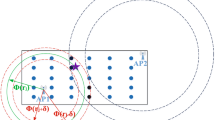
Indoor localization has attracted significant demand in diverse smart building applications like automated energy management, patient tracking in hospitals, industrial indoor navigation, etc. Most of the proposals use Wi-Fi access points to construct indoor localization systems and in such systems, the fundamental task is to deploy access points correctly. The existing literature has employed additional access points or related hardware to improve localization accuracy, which in turn results in expensive installation and maintenance costs. Our objective is to optimize deployment by modifying the positions of already existing access points without using any additional hardware. To achieve this, we propose a reverse multilateration based access point positioning framework that has three phases: the first phase uses multivariate regression to predict the coordinates of the target location based on received signal strength indicator values collected from multiple access points; the second phase identifies the misplaced access points using the cumulative error by distance ratio; and the third phase computes the new positions of access points through reverse multilateration. Experiments show that the proposal generates 888 correct predictions out of 960 data points, thereby improving the prediction accuracy by 4.79% when compared with existing methods.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Cillis, F., et al. (2020). hybrid indoor positioning system for first responders. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 50(2), 468–479. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2017.2772821
Zhao, Y., Xu, J., Wu, J., Hao, J., & Qian, H. (2020). Enhancing camera-based multimodal indoor localization with device-free movement measurement using WiFi. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(2), 1024–1038. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2019.2948605
Ding, H., Zheng, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2016). AP weighted multiple matching nearest neighbors approach for fingerprint-based indoor localization. In 2016 Fourth international conference on ubiquitous positioning, indoor navigation and location based services (UPINLBS) (pp. 218–222). https://doi.org/10.1109/UPINLBS.2016.7809974
Pichaimani, V., & Varma, M. (2021). Positioning of WiFi devices for indoor floor planning using principal featured Kohonen deep structure. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02326-y
Wen, K., Seow, C. K., & Tan, S. Y. (2020). An indoor localization and tracking system using successive weighted RSS projection. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 19(9), 1620–1624. https://doi.org/10.1109/LAWP.2020.3011993
Shang, F., Su, W., Wang, Q., Gao, H., & Fu, Q. (2014). A location estimation algorithm based on rssi vector similarity degree. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/371350
Dinh, T.-M.T., Duong, N.-S., & Sandrasegaran, K. (2020). Smartphone-based indoor positioning using BLE iBeacon and reliable lightweight fingerprint map. IEEE Sensors Journal, 20(17), 10283–10294. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.2989411
Akl, R., Pasupathy, K., & Haidar, M. (2011). Anchor nodes placement for effective passive localization. In 2011 International conference on selected topics in mobile and wireless networking (iCOST) (pp. 127–132). https://doi.org/10.1109/iCOST.2011.6085823
Karakaya, S., & Ocak, H. (2020). Low Cost easy-to-install indoor positioning system. Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems, 100, 131–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-020-01193-1
Li, S., Deng, Z., Liu, Y., & Hu, E. (2020). A novel simultaneous calibration and localization algorithm framework for indoor scenarios. IEEE Access, 8, 180100–180112. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3027859
Yan, X., Luo, Q., Yang, Y., Liu, S., Li, H., & Hu, C. (2019). ITL-MEPOSA: improved trilateration localization with minimum uncertainty propagation and optimized selection of anchor nodes for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access, 7, 53136–53146. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2911032
Yang, Z., & Liu, Y. (2008). Quality of trilateration: Confidence based iterative localization. In 2008 the 28th international conference on distributed computing systems (pp. 446–453). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDCS.2008.59
Sasiwat, Y., et al. (2019). Human movement effects on the performance of the RSSI-based trilateration method: Adaptive filters for distance compensation. Journal of Reliable Intelligent Environments., 6, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40860-019-00094-x
Mantilla-Gaviria, I. A., Leonardi, M., Galati, G., et al. (2015). Localization algorithms for multilateration (MLAT) systems in airport surface surveillance. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 9, 1549–1558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-013-0608-1
João Paulo Marques, P. G., et al. (2021). A cost-effective trilateration-based radio localization algorithm using machine learning and sequential least-square programming optimization. Computer Communications, 177, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2021.06.005
Baek, S. H., et al. (2019). The trilateration-based BLE Beacon system for analyzing user-identified space usage of new ways of working offices. Building and Environment, 149, 264–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2018.12.030
Mass-Sanchez, J., Vargas-Rosales, C., Ruiz-Ibarra, E., Garcia-Berumen, A., & Espinoza-Ruiz, A. (2020). Localization based on probabilistic multilateration approach for mobile wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access, 8, 54994–55011. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2978495
He, S., & Chan, S.-H.G. (2017). INTRI: Contour-based trilateration for indoor fingerprint-based localization. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 16(6), 1676–1690. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2016.2604810
Liao, L., Chen, W., Zhang, C., Zhang, L., Xuan, D., & Jia, W. (2011). Two birds with one stone: Wireless access point deployment for both coverage and localization. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 60(5), 2239–2252. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2011.2109405
Lee, J.-H., & Shin, B.-S. (2017). SensDeploy: Efficient sensor deployment strategy for real-time localization. Human-Centric Computing and Information Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13673-017-0117-2
Zheng, Y., Liu, J., Sheng, M., Han, S., Shi, Y., & Valaee, S. (2021). Toward practical access point deployment for angle-of-arrival based localization. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 69(3), 2002–2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3042267
Zhou, B., Tu, W., Mai, K., Xue, W., Ma, W., & Li, Q. (2020). A novel access point placement method for WiFi fingerprinting considering existing aps. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 9(11), 1799–1802. https://doi.org/10.1109/LWC.2020.2981793
Jia, M., Khattak, S. B. A., Guo, Q., Gu, X., & Lin, Y. (2020). Access point optimization for reliable indoor localization systems. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 69(4), 1424–1436. https://doi.org/10.1109/TR.2019.2955748
Tong, X., Wang, H., Liu, X., & Qu, W. (2021). MapFi: Autonomous mapping of Wi-Fi infrastructure for indoor localization. In IEEE transactions on mobile computing. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2021.3108155
Sheng, M., Zheng, Y., Liu, J., Valaee, S., & Li, J. (2020). Accurate indoor localization assisted with optimizing array orientations and receiver positions. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 69(1), 509–521. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2019.2951022
Njima, W., Chafii, M., Nimr, A., & Fettweis, G. (2020). Deep learning based data recovery for localization. IEEE Access, 8, 175741–175752. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3026615
Li, Y., Hu, X., Zhuang, Y., Gao, Z., Zhang, P., & El-Sheimy, N. (2020). Deep reinforcement learning (DRL): Another perspective for unsupervised wireless localization. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(7), 6279–6287. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2019.2957778
Hu, J., Liu, D., Yan, Z., & Liu, H. (2019). Experimental analysis on weight K-nearest neighbor indoor fingerprint positioning. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(1), 891–897. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2018.2864607
Hoang, M. T., Yuen, B., Dong, X., Lu, T., Westendorp, R., & Reddy, K. (2019). Recurrent neural networks for accurate RSSI indoor localization. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(6), 10639–10651. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2019.2940368
Yim, J. (2008). Introducing a decision tree-based indoor positioning technique. Expert Systems with Applications., 34(2), 1296–1302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2006.12.028
Wang, L., Zhou, H., Jiang, G., & Zheng, B. (2015). WiFi-based self-adaptive matching and preprocessing WKNN algorithm. Signal Processing, 31(9), 1067–1074.
Varma, P. S., & Anand, V. (2022). Intelligent scanning period dilation based Wi-Fi fingerprinting for energy efficient indoor positioning in IoT applications. The Journal of Supercomputing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-022-04980-9
Nessa, A., Adhikari, B., Hussain, F., & Fernando, X. N. (2020). A survey of machine learning for indoor positioning. IEEE Access, 8, 214945–214965. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3039271
Tao, Y., & Ganz, A. (2020). Simulation framework for evaluation of indoor navigation systems. IEEE Access, 8, 20028–20042. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2968435
Varma, P. S., & Anand, V. (2022). Fault-tolerant indoor localization based on speed conscious recurrent neural network using Kullback–Leibler divergence. Peer-to-Peer Network Application, 15(3), 1370–1384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-022-01301-y
Singla, A., Padakandla, S., & Bhatnagar, S. (2021). Memory-based deep reinforcement learning for obstacle avoidance in UAV with limited environment knowledge. EEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 22(1), 107–118. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2019.2954952
Li, P., Yang, X., Yin, Y., Gao, S., & Niu, Q. (2020). Smartphone-based indoor localization with integrated fingerprint signal. IEEE Access, 8, 33178–33187. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2974038
Anand, V., Agrawal, P., Varma, P.S., Pandey, S., & Kumar, S. (2021). Azimuth tree-based self-organizing protocol for internet of things. In Proceedings of fifth international congress on information and communication technology. Advances in intelligent systems and computing (Vol. 1184, pp. 342–356), Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5859-7_34
Varma, P. S., & Anand, V. (2021). Indoor localization for IoT applications: Review, challenges and manual site survey approach. IEEE Bombay Section Signature Conference (IBSSC), 2021, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/IBSSC53889.2021.9673236
Huang, P., Zhao, H., Liu, W., & Jiang, D. (2021). MAPS: Indoor localization algorithm based on multiple AP selection. Mobile Networks and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-019-01411-7
Labinghisa, B., & Lee, D. (2021). Neural network-based indoor localization system with enhanced virtual access points. The Journal of Supercomputing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03272-4
Gu, F., Valaee, S., Khoshelham, K., Shang, J., & Zhang, R. (2020). Landmark graph-based indoor localization. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(9), 8343–8355. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.2989501
Varma, P. S., & Anand, V. (2021). Random forest learning based indoor localization as an IoT service for smart buildings. Wireless Personal Communications, 117, 3209–3227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07977-w
Kanrar, S., Dawar, K., & Pundir, A. (2020). Pedestrian localisation in the typical indoor environments. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 79, 27833–27866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09291-w
Jeong, J., Yeon, S., Kim, T., et al. (2018). SALA: Smartphone-assisted localization algorithm for positioning indoor IoT devices. Wireless Networks, 24, 27–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1309-9
Zhang, X., He, F., Chen, Q., et al. (2022). A differentially private indoor localization scheme with fusion of WiFi and bluetooth fingerprints in edge computing. Neural Computing and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06815-9
Zhang, M., Jia, J., Chen, J., et al. (2021). Real-time indoor localization using smartphone magnetic with LSTM networks. Neural Computing and Applications, 33, 10093–10110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-05774-5
Funding
No funding was received for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Varma, P.S., Anand, V. ReMAPP: reverse multilateration based access point positioning using multivariate regression for indoor localization in smart buildings. Telecommun Syst 83, 303–322 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-023-01021-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-023-01021-5