Abstract
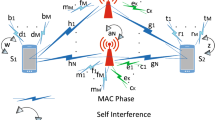
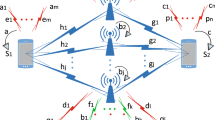
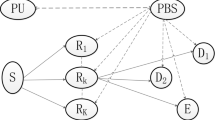
This study seeks an answer for the impact of the co-channel interference on the leakage rate of illegitimate relay-assisted power-domain non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) networks. The power-domain NOMA-based uni-/bi-directional information exchange through an illegitimate half-/full-duplex relay is adopted in the system model. Moreover, a limited number of co-channel interferers and friendly jammers are affected by the illegitimate relay in the network. Extensive computer simulations, analytical, and asymptotic results reveal that as the illegitimate relay is affected by a limited number of friendly jammers and co-channel interferers, its achievable rate cannot be enhanced and saturates at high signal-to-noise ratio. Results also show that the co-channel interference causes system coding gain losses on the users’ outage performance. In addition, the illegitimate relay remains active between \(-\,10\) and 25 dB for uni-/bi-directional information exchange. After 25 dB, the illegitimate relay saturates and experiences outages. Additionally, the order of decoding also impacts the illegitimate relay’s performance.














Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Saito, Y., Kishiyama, Y., Benjebbour, A., Nakamura, T., Li, A., & Higuchi, K. (2013). Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) for cellular future radio access. In 2013 IEEE 77th vehicular technology conference (VTC spring) (pp. 1–5).
Ding, Z., Liu, Y., Choi, J., Sun, Q., Elkashlan, M., Chih-Lin, I., & Poor, H. V. (2017). Application of non-orthogonal multiple access in LTE and 5G networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(2), 185–191.
Ozduran, V., Cioffi, J. M., & Yarman, S. B. (2013). Opportunistic source-pair selection (OSPS) method for multiuser bi-directional wireless relaying networks. In 2013 IEEE 14th workshop on signal process. advances in wireless communications (SPAWC) (pp. 565–569).
Cover, T. M. (1975). Some advances in broadcast channels. In Advances in Communication Theory. San Francisco. (pp. 229–260). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-010904-3.50011-7.
Ozduran, V., Huda Mahmood, N., & Nomikos, N. (2022). Performance analysis of power-domain non-orthogonal multiple access for full-duplex two-way relaying. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 33(7), e4487.
Daemen, J., & Rijmen, V. (1999). AES proposal: Rijndael.
Rivest, R., Shamir, A., & Adleman, L. (1978). A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. Communications of the ACM, 21, 120–126.
Wyner, A. D. (1975). The wire-tap channel. Bell System Technical Journal, 54(8), 1355–1387.
Sun, L., Zhang, T., Li, Y., & Niu, H. (2012). Performance study of two-hop amplify-and-forward systems with untrustworthy relay nodes. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 61(8), 3801–3807.
Duy, T. T., Duong, T. Q., Thanh, T. L., & Bao, V. N. Q. (2015). Secrecy performance analysis with relay selection methods under impact of co-channel interference. IET Communications, 9(11), 1427–1435.
El-Malek, A. H. A., Salhab, A. M., & Zummo, S. A. (2015) Optimal power allocation for enhancing physical layer security in opportunistic relay networks in the presence of co-channel interference. In 2015 IEEE global communications conference (GLOBECOM) (pp. 1–6).
Vahidian, S., Aissa, S., & Hatamnia, S. (2015). Relay selection for security-constrained cooperative communication in the presence of eavesdropper’s overhearing and interference. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 4(6), 577–580.
Hu, W., Li, Z., Li, H., Si, J., & Huang, H. (2017). SRT analysis of relay selection in the presence of multiple co-channel interferers. IET Communications, 11(6), 809–816.
Renna, F., Laurenti, N., & Poor, H. V. (2012). Physical-layer secrecy for OFDM transmissions over fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 7(4), 1354–1367.
Sun, Y., Ng, D. W. K., & Schober, R. (2017). Resource allocation for secure full-duplex OFDMA radio systems: (Invited paper). In 2017 IEEE 18th international workshop on signal processing advances in wireless communications (SPAWC) (pp. 1–5).
Ozduran, V. (2018). Physical layer security of multi-user full-duplex one-way wireless relaying network. In 2018 Advances in wireless and optical communications (RTUWO) (pp. 17–22).
Ozduran, V. (2019). Secrecy analysis of multi-user half/full-duplex wireless bi-directional relaying network. Balkan Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 7, 342–354.
Romero-Zurita, N., Ghogho, M., & McLernon, D. (2011). Physical layer security of MIMO-OFDM systems by beamforming and artificial noise generation. Physical Communication, 4(4), 313–321.
Chen, J., Yang, L., & Alouini, M. (2018). Physical layer security for cooperative NOMA systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67(5), 4645–4649.
Yu, C., Ko, H., Peng, X., Xie, W., & Zhu, P. (2019). Jammer-aided secure communications for cooperative NOMA systems. IEEE Communications Letters, 23(11), 1935–1939.
Abbasi, O., & Ebrahimi, A. (2017). Secrecy analysis of a NOMA system with full duplex and half duplex relay. In 2017 Iran workshop on communication and information theory (IWCIT) (pp. 1–6).
Wang, Z., & Peng, Z. (2019). Secrecy performance analysis of relay selection in cooperative NOMA systems. IEEE Access, 7, 86274–86287.
Yu, C., Ko, H., Peng, X., & Xie, W. (2019). Secrecy outage performance analysis for cooperative NOMA over Nakagami-\(m\) channel. IEEE Access, 7, 79866–79876.
Zheng, B., Wen, M., Wang, C., Wang, X., Chen, F., Tang, J., & Ji, F. (2018). Secure NOMA based two-way relay networks using artificial noise and full duplex. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 36(7), 1426–1440.
Lei, H., Yang, Z., Park, K., Ansari, I. S., Pan, G., & Alouini, M. (2019). On physical layer security of multiple-relay assisted NOMA systems. In 2019 IEEE international conference on communications workshops (ICC workshops) (pp. 1–6).
ElHalawany, B. M., Ruby, R., Riihonen, T., & Wu, K. (2018). Performance of cooperative NOMA systems under passive eavesdropping. In 2018 IEEE global communications conference (GLOBECOM) (pp. 1–6).
Li, A. (2019). Enhancing the physical layer security of cooperative NOMA system. In 2019 IEEE 3rd information technology, networking, electronic and automation control conference (ITNEC) (pp. 2194–2198).
Abolpour, M., Mirmohseni, M., & Aref, M. R. (2019). Outage performance in secure cooperative NOMA. In 2019 Iran workshop on communication and information theory (IWCIT) (pp. 1–6).
Zaghdoud, N., Alouane, W. H., Boujemaa, H., Mnaouer, A. B., & Touati, F. (2019). Secrecy performance of AF relaying in cooperative NOMA over Rician channel. In2019 15th international wireless communications mobile computing conference (IWCMC) (pp. 805–810).
Lv, L., Jiang, H., Ding, Z., Yang, L., & Chen, J. (2019). Exploiting adaptive jamming in secure cooperative NOMA with an untrusted relay. In ICC 2019—2019 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC) (pp. 1–6).
Zheng, B., Wen, M., Chen, F., Tang, J., & Ji, F. (2018). Secure NOMA based full-duplex two-way relay networks with artificial noise against eavesdropping. In 2018 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC) (pp. 1–6).
Feng, Y., Yang, Z., & Yan, S. (2017). Non-orthogonal multiple access and artificial-noise aided secure transmission in FD relay networks. In 2017 IEEE Globecom workshops (GC wkshps) (pp. 1–6).
Zaghdoud, N., Alouane, W. H., Boujemaa, H., & Touati, F. (2019). Secure performance of AF and DF relaying in cooperative NOMA systems. In 2019 19th international conference on sciences and techniques of automatic control and computer engineering (STA) (pp. 614–619).
Cao, Y., Tang, J., Zhao, N., Chen, Y., Zhang, X. Y., Jin, M., & Alouini, M. (2019). Full-duplex relay assisted secure transmission for NOMA networks. In 2019 IEEE/CIC international conference on communications in China (ICCC) (pp. 596–601).
Liu, F., Li, J., Li, S., & Liu, Y. (2018). Physical layer security of full-duplex two-way AF relaying networks with optimal relay selection. In 2018 IEEE Globecom workshops (GC wkshps) (pp. 1–6).
Arafa, A., Shin, W., Vaezi, M., & Poor, H. V. (2020). Secure relaying in non-orthogonal multiple access: Trusted and untrusted scenarios. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 15, 210–222.
Xiang, Z., Yang, W., Pan, G., Cai, Y., & Sun, X. (2019). Secure transmission in non-orthogonal multiple access networks with an untrusted relay. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 8(3), 905–908.
Xiang, Z., Yang, W., Cai, Y., Ding, Z., & Song, Y. (2020). Secure transmission design in HARQ assisted cognitive NOMA networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 15, 2528–2541.
Khan, W. U., Liu, J., Jameel, F., Khan, M. T. R., Ahmed, S. H., & Jäntti, R. (2020). Secure backscatter communications in multi-cell NOMA networks: Enabling link security for massive IoT networks. In IEEE INFOCOM 2020-IEEE conference on computer communications workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS) (pp. 213–218).
Khan, W. U., Jameel, F., Li, X., Bilal, M., & Tsiftsis, T. A. (2021). Joint spectrum and energy optimization of NOMA-enabled small-cell networks with QoS guarantee. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 70(8), 8337–8342.
Ozduran, V. (2020). Leakage rate analysis with imperfect channel state information for cooperative non-orthogonal multiple access networks. International Journal of Communication Systems, 33(9), e4387.
Sun, Y., Ding, Z., Dai, X., & Karagiannidis, G. K. (2018). A feasibility study on network NOMA. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 66(9), 4303–4317.
Tse, D., & Viswanath, P. (2005). Fundamentals of wireless communications. Cambridge University Press.
Ikki, S. S., & Aissa, S. (2012). Performance analysis of two-way amplify-and-forward relaying in the presence of co-channel interferences. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 60(4), 933–939.
Zou, Y., Wang, X., Shen, W., & Hanzo, L. (2014). Security versus reliability analysis of opportunistic relaying. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 63(6), 2653–2661.
Gradshteyn, I. S., & Ryzhik, I. M. (2007). Tables of integrals, series and products (7th ed.). Elsevier Inc.
Ibrahim, D. H., Hassan, E. S., & El-Dolil, S. A. (2014). Improving physical layer security in two-way cooperative networks with multiple eavesdroppers. In 2014 9th international conference on informatics and systems (pp. ORDS–8–ORDS–13).
Ozduran, V., Soleimani-Nasab, E., & Yarman, B. S. (2016). Opportunistic source-pair selection for multi-user two-way AF wireless relaying networks. IET Communications, 10(16), 2106–2118.
Ozduran, V., Yarman, B. S., & Cioffi, J. M. (2019). Opportunistic source-pair selection method with imperfect channel state information for multiuser bi-directional relaying networks. IET Communications, 13(7), 905–917.
Jimenez Rodriguez, L., Tran, N. H., & Le-Ngoc, T. (2014). Performance of full-duplex AF relaying in the presence of residual self-interference. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 32(9), 1752–1764.
Khan, W. U., Lagunas, E., Mahmood, A., Ali, Z., Chatzinotas, S., & Ottersten, B. (2022). Integration of NOMA with reflecting intelligent surfaces: A multi-cell optimization with SIC decoding errors. [Online]. Available: arXiv:2205.03248
Khan, W. U., Lagunas, E., Ali, Z., Javed, M. A., Ahmed, M., Chatzinotas, S., Ottersten, B., & Popovski, P. (2022). Opportunities for physical layer security in UAV communication enhanced with intelligent reflective surfaces. [Online]. Available: arXiv:2203.16907
Papoulis, A., & Pillai, U. (2001). Probability, random variables and stochastic processes (4th ed., p. 11). McGraw-Hill.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix A: Proof of Proposition 1
Revisiting (2) and also considering the logarithm properties, below expressions can be achieved.
Note that \(f\gamma _{x}\left( \gamma \right) =\frac{1}{P _{s}^{1}\Omega _{h}}e^{-\gamma \left( \frac{1}{P _{s}^{1}\Omega _{h}}\right) }\). Also note that sum of M independent and identically distributed (i.i.d) exponentially distributed RVs follows the Gamma distribution [44]. As such, the PDF expressions of \(\gamma _{F}\) and \(\gamma _{J}\) can be written as: \(f_{\gamma _{F}}\left( \gamma _{F}\right) =\left( \frac{1}{P _{J}\Omega _{f_{j}}}\right) ^{N}\frac{\gamma _{F}^{N-1}}{(N-1)!}e^{-\frac{\gamma _{F}}{P _{F}\Omega _{f_{k}}}}\) and \(f_{\gamma _{J}}\left( \gamma _{J}\right) =\left( \frac{1}{P _{J}\Omega _{m_{j}}}\right) ^{M}\frac{\gamma _{J}^{M-1}}{(M-1)!}e^{-\frac{\gamma _{J}}{P _{J}\Omega _{m_{j}}}}\) [53]. In this regard, substituting \(f_{\gamma _{F}}\left( \gamma _{F}\right) \) and \(f_{\gamma _{J}}\left( \gamma _{J}\right) \) into (56) and solving the integrals with the help of [46, Eq. (3.310.11)] and [46, Eq. (3.351.3)], the final CDF expression can be obtained as in (17). Likewise, following the similar methodologies as in (56), the other CDFs, \(F_{{\text {LR}_{\text {x}_{1}}}}^{\mathrm{HD(OWR)}}\), \(F_{{\text {LR}_{\text {x}_{2}}}}^\mathrm{FD(OWR)}\), \(F_{{\text {LR}_{\text {x}_{1}}}}^{\mathrm{FD(OWR)}}\), \(F_{\text {LR}_{\text {x}_{2}}}^{\mathrm{HD(TWR)}}\), \(F_{{\text {LR}_{\text {y}_{2}}}}^{\mathrm{HD(TWR)}}\), \(F_{{\text {LR}_{\text {x}_{1}}}}^{\mathrm{HD(TWR)}}\), \(F_{{\text {LR}_{\text {y}_{1}}}}^\mathrm{HD(TWR)}\), \(F_{{\text {LR}_{\text {x}_{2}}}}^{\mathrm{FD(TWR)}}\), \(F_{\text {LR}_{\text {y}_{2}}}^{\mathrm{FD(TWR)}}\), \(F_{{\text {LR}_{\text {x}_{1}}}}^{\mathrm{FD(TWR)}}\), and \(F_{{\text {LR}_{\text {y}_{1}}}}^{\mathrm{FD(TWR)}}\) can be calculated as in (18), (19), (20), (21), (22), (23), (24), (25), (26), (27), and (28), respectively.
Appendix B: Proof of Proposition 2
Utilizing (2) and the intercept probability formulation, which is \(P _{r}\left[ C_{e}> R\right] \) [45, Eq. (5)], and also logarithm properties, following results can be obtained.
Substituting \(f_{\gamma _{F}}\left( \gamma _{F}\right) \) and \(f_{\gamma _{J}}\left( \gamma _{J}\right) \) into (57) and utilizing [46, Eq. (3.310.11)] and [46, Eq. (3.351.3)] for solving the integral expressions, the final CDF can be achieved as in (29). Note that considering the methodology as in (57), the other related CDFs, presented in Proposition 2, can be obtained.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ozduran, V., Nomikos, N. On the leakage-rate performance of untrusted relay-aided NOMA under co-channel interference. Telecommun Syst 85, 67–86 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-023-01071-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-023-01071-9