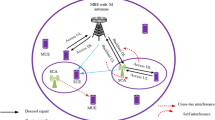
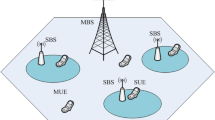
Abstract
Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) communication is a potential strategy for overcoming the limits of classic orthogonal multiple access schemes, and it can improve possible rates. In contrast, MIMO–NOMA improves them even more due to multiple antenna diversity advantages. On the other hand, future wireless communication will rely on heterogeneous networks (HetNets), which allow many wireless access networks to coexist hierarchically. However, channel reciprocity is invalid because of the shorter channel coherence time in 5G and 6G communications. As a result, channel estimation through an uplink (UL) pilot no longer holds for downlink (DL) transmission. To address this issue, a statistical beamforming approach is proposed that does not consider channel reciprocity for channel estimation. Consequently, the proposed method saves the pilot transmission overhead required for channel estimation resulting in increased spectral efficiency. To achieve this, we propose to employ the characterization of the ratio of the indefinite quadratic form (IQF) to obtain a closed-form formula for the outage probability in MIMO–NOMA HetNets. The analytical expression obtained is then utilized to design optimal beamforming weights using the genetic algorithm (GA) that solves a constrained multi-objective optimization task. In summary, advantages of our proposed method are (1) it provides spectral efficient method of beamforming, (2) it derives an exact characterization of outage probability in MIMO–NOMA HetNets in closed form, and (3) it develops a GA based optimization solution that solves a constrained multi-objective optimization task simulation results presented validate the theoretical analysis and show supremacy of the proposed method over classical statistical method.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Availability of data and material
There is no data associated with this manuscript.
Code Availability
Code can be made available on request.
References
Kadir, M. I., Sugiura, S., Zhang, J., Chen, S., & Hanzo, L. (2012). OFDMA/SC-FDMA aided space-time shift keying for dispersive multiuser scenarios. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 62(1), 408–414. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2012.2220794
Rehman, S. U., Hussain, A., Hussain, F., & Mannan, M. A. (2020). A comprehensive study: 5G wireless networks and emerging technologies. In International Electrical Engineering Conference (IEEC) (Vol. 5, pp. 25–32).
Sari, H., Vanhaverbeke, F., & Moeneclaey, M. (2000). Multiple access using two sets of orthogonal signal waveforms. IEEE Communications Letters, 4(1), 4–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/4234.823531
Jungnickel, V., Manolakis, K., Zirwas, W., Panzner, B., Braun, V., Lossow, M., & Svensson, T. (2014). The role of small cells, coordinated multipoint, and massive MIMO in 5G. IEEE Communications Magazine, 52(5), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2014.6815892
Saito, Y., Kishiyama, Y., Benjebbour, A., Nakamura, T., Li, A., & Higuchi, K. (2013). Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) for cellular future radio access. In 2013 IEEE 77th vehicular technology conference (VTC Spring) (pp. 1–5). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/VTCSpring.2013.6692652
Shin, W., Vaezi, M., Lee, B., Love, D. J., Lee, J., & Poor, H. V. (2017). Non-orthogonal multiple access in multi-cell networks: Theory, performance, and practical challenges. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(10), 176–183. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2017.1601065
Ali, S., Hossain, E., & Kim, D. I. (2016). Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) for downlink multiuser MIMO systems: User clustering, beamforming, and power allocation. IEEE Access, 5, 565–577. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2646183
Shaikh, M. A., Manzar, A., Moinuddin, M., Rehman, S. U., & Mustafa, H. (2022). Semi-blind beamforming in beam space MIMO NOMA for mmWave communications. IEEE Access, 10, 120426–120435. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3222399
Rehman, S. U., Ahmad, J., Manzar, A., & Moinuddin, M. (2023). Beamforming techniques for MIMO–NOMA for 5G and beyond 5G: Research gaps and future directions. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing,. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02517-w
Rehman, S. U., Ahmad, J., Manzar, A., & Moinuddin, M. (2022). Outage probability and ergodic capacity analysis of MIMO-NOMA heterogeneous network for 5G system. Journal of Independent Studies and Research Computing, 20(2), 15–23. https://doi.org/10.31645/JISRC.22.20.2.3
Zhao, J., Liu, Y., Chai, K. K., Nallanathan, A., Chen, Y., & Han, Z. (2017). Spectrum allocation and power control for non-orthogonal multiple access in HetNets. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 16(9), 5825–5837. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2017.2716921
Wu, Y., & Qian, L. P. (2017). Energy-efficient NOMA-enabled traffic offloading via dual-connectivity in small-cell networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 21(7), 1605–1608. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2685384
Ali, M. S., Hossain, E., Al-Dweik, A., & Kim, D. I. (2018). Downlink power allocation for CoMP-NOMA in multi-cell networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 66(9), 3982–3998. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2831206
Chen, C., Cai, W., Cheng, X., Yang, L., & Jin, Y. (2017). Low complexity beamforming and user selection schemes for 5G MIMO–NOMA systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 35(12), 2708–2722. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2017.2727229
Chinnadurai, S., Selvaprabhu, P., Jeong, Y., Sarker, A. L., Hai, H., Duan, W., & Lee, M. H. (2017). User clustering and robust beamforming design in multicell MIMO-NOMA system for 5G communications. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 78, 181–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2017.05.021
Liu, S., & Zhang, C. (2016). Non-orthogonal multiple access in a downlink multiuser beamforming system with limited CSI feedback. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2016, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-016-0735-9
Cui, J., Ding, Z., & Fan, P. (2017). Power minimization strategies in downlink MIMO-NOMA systems. In 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) (pp. 1–6). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICC.2017.7996398
Nasser, A., Muta, O., Elsabrouty, M., & Gacanin, H. (2019). Interference mitigation and power allocation scheme for downlink MIMO-NOMA HetNet. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 68(7), 6805–6816. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2019.2918336
Nasser, A., Muta, O., & Elsabrouty, M. (2019). Cross-tier interference management scheme for downlink mMIMIO-NOMA HetNet. In 2019 IEEE 89th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Spring) (pp. 1–5). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/VTCSpring.2019.8746524
Jain, P., & Gupta, A. (2022). Performance analysis of massive MIMO millimeter wave NOMA HetNet. In 2022 International Conference on Emerging Smart Computing and Informatics (ESCI) (pp. 1–5). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ESCI53509.2022.9758313
Al-Naffouri, T. Y., Moinuddin, M., Ajeeb, N., Hassibi, B., & Moustakas, A. L. (2016). On the distribution of indefinite quadratic forms in Gaussian random variables. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 64(1), 153–165. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCOMM.2015.2496592
Hassan, A. K., Moinuddin, M., Al-Saggaf, U. M., & Al-Naffouri, T. Y. (2017). Performance analysis of beamforming in MU-MIMO systems for Rayleigh fading channels. IEEE Access, 5, 3709–3720. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2682791
Hassan, A. K., Moinuddin, M., Al-Saggaf, U. M., Aldayel, O., Davidson, T. N., & Al-Naffouri, T. Y. (2020). Performance analysis and joint statistical beamformer design for multi-user MIMO systems. IEEE Communications Letters, 24(10), 2152–2156. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3001556
Aljohani, A. J., & Moinuddin, M. (2021). Statistical beamforming techniques for power domain NOMA system. Electronics, 10(24), 3064. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10243064
Mursia, P., Atzeni, I., Gesbert, D., & Cottatellucci, L. (2018). Covariance shaping for massive MIMO systems. In 2018 IEEE global communications conference (GLOBECOM) (pp. 1-6). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8647861
Al-Naffouri, T. Y. (2009). Scaling of the minimum of iid random variables. Signal Processing, 89(9), 1830–1834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2009.02.012
Li, J., Sun, G., Wang, A., Zheng, X., Chen, Z., Liang, S., & Liu, Y. (2023). Multi-objective sparse synthesis optimization of concentric circular antenna array via hybrid evolutionary computation approach. Expert Systems with Applications. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120771
Zerovnik, J. (2015). Heuristics for NP-hard optimization problems—Simpler is better!? Logistics, Supply Chain, Sustainability and Global Challenges, 6(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1515/jlst-2015-0006
Nigar, N., Shahzad, M. K., Islam, S., & Oki, O., & Lukose, J. M. (2023). Multi-objective dynamic software project scheduling: A novel approach to handle employeeś addition. IEEE Access, 11, 39792–39806. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3265716
Beasley, D., Bull, D. R., & Martin, R. R. (1993). An overview of genetic algorithms: Part 1 fundamentals. University Computing, 15(2), 58–69.
Beasley, D., Bull, D. R., & Martin, R. R. (1993). An overview of genetic algorithms: Part 2 research topics. University Computing, 15(4), 170–181.
Man, K. F., Tang, K. S., & Kwong, S. (1996). Genetic algorithms: Concepts and applications [in engineering design]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 43(5), 519–534. https://doi.org/10.1109/41.538609
Kennedy, J. & Eberhart, R. (1995). Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of ICNN’95 - international conference on neural networks, Perth, WA, Australia (Vol. 4), (pp. 1942–1948). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
Shami, T. M., El-Saleh, A. A., Alswaitti, M., Al-Tashi, Q., Summakieh, M. A., & Mirjalili, S. (2022). Particle swarm optimization: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access, 10, 10031–10061. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3142859
Dorigo, M., & Gambardella, L. M. (1997). Ant colony system: A cooperative learning approach to the traveling salesman problem. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 1(1), 53–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.585892
Dorigo, M., Birattari, M., & Stutzle, T. (2006). Ant colony optimization. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 1(4), 28–39. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCI.2006.329691
Ansell, D. W. (2010). Antenna performance optimisation using evolutionary algorithms. PhD dissertation, department of aerospace, power & sensors, Cranfield University, UK. https://dspace.lib.cranfield.ac.uk/handle/1826/4661
Truong, V., & Truong, & Nayyar, A. (2023). System performance and optimization in NOMA mobile edge computing surveillance network using GA and PSO. Computer Networks, 223, 109575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2023.109575
Shao, K., Fu, H., & Wang, B. (2023). An efficient combination of genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization for scheduling data-intensive tasks in heterogeneous cloud computing. Electronics, 12(16), 3450. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163450
Deng, D., Fan, L., Lei, X., Tan, W., & Xie, D. (2017). Joint user and relay selection for cooperative NOMA networks. IEEE Access, 5, 20220–20227. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2751503
Abbas, Q., Zeb, S., Hassan, S. A., Mumtaz, R., & Zaidi, S. A. R. (2020). Joint optimization of age of information and energy efficiency in IoT networks. In 2020 IEEE 91st vehicular technology conference (VTC2020-Spring) (pp. 1–5). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/VTC2020-Spring48590.2020.9129207
Acknowledgements
The Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Abdulaziz University (KAU), Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, has funded this project, under Grant No. (KEP-MSc: 63-135-1443).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SUR and JA have implemented the main idea and prepared the manuscript text. AM and MM have conceptualized the idea of the proposed method and designed the algorithm for the proposed system. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflict of interest for the submitted work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rehman, S.U., Ahmad, J., Manzar, A. et al. Performance analysis and design of semi-blind beamforming for downlink MIMO–NOMA heterogeneous network. Telecommun Syst 85, 551–562 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-023-01098-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-023-01098-y