Abstract
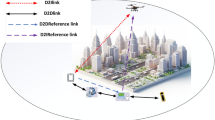
Device-to-Device (D2D) relayed communication helps in extending the coverage range of cellular networks. Relay devices support multi-hop D2D communication where two devices are out of the direct D2D range. However, identifying suitable fixed relays in a network is a complex problem that needs a more efficient solution. Relay-assisted communication may also fail due to the non-cooperative nature of the users (draining battery energy for supporting other devices). This paper proposes a UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle)-assisted multi-hop D2D communication scheme that serves more out-of-direct-range D2D users using the dynamic location of the UAVs (drones). Dynamic location of UAVs solves the connectivity issues with many users. We aim at maximizing the achievable throughput of the D2D users for both uplink (users to UAVs) and downlink (UAVs to users) channels simultaneously. An optimization problem is formulated for maximizing throughput subject to interference, power, and bandwidth constraints. The UAV trajectories are predicted for serving the multi-hop D2D users in the system using Neural Network (NN), and thereafter, a novel resource assignment scheme, named Dual Optimal Channel Allocation (DOCA), is proposed. DOCA optimally allocates resource blocks (RBs) for both uplink and downlink channels and ensures that the overall interference caused by resource sharing between cellular and D2D users is minimal. The spectrum efficiency has been achieved by resource sharing between cellular and D2D users. An association matrix is obtained that indicates potential resource-sharing partners of D2D and cellular users. Finally, we show the performance of the proposed technique with regard to throughput improvement, buffer requirement, and churn rate of the system.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Jameel, F., Hamid, Z., Jabeen, F., Zeadally, S., & Javed, M. A. (2018). A survey of device-to-device communications: Research issues and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 20(3), 2133–2168. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2018.2828120
Barik, P. K., Singhal, C., Datta, R. (2017). Throughput enhancement using d2d based relay-assisted communication in cellular networks. In 2017 IEEE 28th annual international symposium on personal, indoor, and mobile radio communications (PIMRC) (pp. 1–6). https://doi.org/10.1109/PIMRC.2017.8292340
Abualola, H., Otrok, H., Barada, H., Al-Qutayri, M., & Al-Hammadi, Y. (2021). Matching game theoretical model for stable relay selection in a UAV-assisted internet of vehicles. Vehicular Communications, 27, 100290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vehcom.2020.100290
Zhong, X., Guo, Y., Li, N., & Chen, Y. (2020). Joint optimization of relay deployment, channel allocation, and relay assignment for UAVs-aided D2D networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 28(2), 804–817. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNET.2020.2970744
Nguyen, M.-N., Nguyen, L. D., Duong, T. Q., & Tuan, H. D. (2019). Real-time optimal resource allocation for embedded UAV communication systems. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 8(1), 225–228. https://doi.org/10.1109/LWC.2018.2867775
Ji, J., Zhu, K., Niyato, D., & Wang, R. (2021). Joint trajectory design and resource allocation for secure transmission in cache-enabled UAV-relaying networks with d2d communications. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(3), 1557–1571. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.3013647
Zhang, S., Zhang, H., He, Q., Bian, K., & Song, L. (2018). Joint trajectory and power optimization for UAV relay networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 22(1), 161–164. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2763135
Liu, X., Lai, B., Lin, B., & Leung, V. C. M. (2022). Joint communication and trajectory optimization for multi-UAV enabled mobile internet of vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 23(9), 15354–15366. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2022.3140357
Na, Z., Liu, Y., Shi, J., Liu, C., & Gao, Z. (2021). UAV-supported clustered NOMA for 6G-enabled internet of things: Trajectory planning and resource allocation. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(20), 15041–15048. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.3004432
Wang, J., Na, Z., & Liu, X. (2021). Collaborative design of multi-UAV trajectory and resource scheduling for 6G-enabled internet of things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(20), 15096–15106. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.3031622
Fodor, G., Dahlman, E., Mildh, G., Parkvall, S., Reider, N., Miklós, G., & Turányi, Z. (2012). Design aspects of network assisted device-to-device communications. IEEE Communications Magazine, 50(3), 170–177. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2012.6163598
Asadi, A., Wang, Q., & Mancuso, V. (2014). A survey on device-to-device communication in cellular networks. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 16(4), 1801–1819. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2014.2319555
Sun, J., Zhang, Z., Xing, C., & Xiao, H. (2018). Uplink resource allocation for relay-aided device-to-device communication. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 19(12), 3883–3892. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2017.2788562
Bansod, R., Shastry, A., Kumar, B., & Mishra, P. K. (2018). Ga-based resource allocation scheme for D2D communication for 5G networks. In International conference on inventive research in computing applications (ICIRCA) (vol. 2018, pp. 748–752). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIRCA.2018.8597186
Tseng, H. -W., Yu, Y. -J., Wu, B. -S., Kuo, C. -F., & Chen, P. -S. (2017). A resource allocation scheme for device-to-device communication over ultra-dense 5G cellular networks. In International conference on applied system innovation (ICASI) (vol. 2017, pp. 80–83). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASI.2017.7988351
Chen, Y., Ai, B., Niu, Y., He, R., Zhong, Z., & Han, Z. (2019). Resource allocation for device-to-device communications in multi-cell multi-band heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 68(5), 4760–4773. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2019.2903858
Zhang, H., Liao, Y., & Song, L. (2017). D2D-U: Device-to-device communications in unlicensed bands for 5G system. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 16(6), 3507–3519. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2017.2683479
Lin, X., Li, J., Baldemair, R., Cheng, J.-F.T., Parkvall, S., Larsson, D. C., Koorapaty, H., Frenne, M., Falahati, S., Grovlen, A., & Werner, K. (2019). 5G new radio: Unveiling the essentials of the next generation wireless access technology. IEEE Communications Standards Magazine, 3(3), 30–37. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOMSTD.001.1800036
Mishra, P. K., Kumar, A., & Pandey, S. (2017). Minimum interference based resource allocation method in two-hop D2D communication for 5G cellular networks. In International conference on intelligent sustainable systems (ICISS) (vol. 2017, pp. 1191–1196). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISS1.2017.8389375
Klaine, P. V., Imran, M. A., Onireti, O., & Souza, R. D. (2017). A survey of machine learning techniques applied to self-organizing cellular networks. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 19(4), 2392–2431. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2017.2727878
Chen, M., Challita, U., Saad, W., Yin, C., & Debbah, M. (2019). Artificial neural networks-based machine learning for wireless networks: A tutorial. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 21(4), 3039–3071. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2019.2926625
Lee, W., Kim, M., & Cho, D. (2019). Deep learning based transmit power control in underlaid device-to-device communication. IEEE Systems Journal, 13(3), 2551–2554. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2018.2870483
Najla, M., Gesbert, D., Becvar, Z., & Mach, P. (2019). Machine learning for power control in D2D communication based on cellular channel gains. In: IEEE Globecom workshops (GC Wkshps) (vol. 2019, pp. 1–6). https://doi.org/10.1109/GCWkshps45667.2019.9024549
Akoush, S., Sameh, A. (2007). Bayesian learning of neural networks for mobile user position prediction. In 2007 16th international conference on computer communications and networks (pp. 1234–1239). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCN.2007.4317989
Quintero, A. (2005). A user pattern learning strategy for managing users’ mobility in UMTS networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 4(6), 552–566. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2005.75
Stoyanova, M., & Mahonen, P. (2007). A next-move prediction algorithm for implementation of selective reservation concept in wireless networks. In 2007 IEEE 18th international symposium on personal. Indoor and mobile radio communications (pp. 1–5). https://doi.org/10.1109/PIMRC.2007.4394861
Vukovic, M., Lovrek, I., Jevtic, D. (2007). Predicting user movement for advanced location-aware services. In 2007 15th international conference on software, telecommunications and computer networks (pp. 1–5). https://doi.org/10.1109/SOFTCOM.2007.4446120
Premchaisawatt, S., Ruangchaijatupon, N. (2014). Enhancing indoor positioning based on partitioning cascade machine learning models. In 2014 11th international conference on electrical engineering/electronics, computer, telecommunications and information technology (ECTI-CON) (pp. 1–5). https://doi.org/10.1109/ECTICon.2014.6839831
Capka, J., & Boutaba, R. (2004). Mobility prediction in wireless networks using neural networks. In J. Vicente & D. Hutchison (Eds.), Management of multimedia networks and services (pp. 320–333). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
Sharma, S. K., & Wang, X. (2020). Toward massive machine type communications in ultra-dense cellular IoT networks: Current issues and machine learning-assisted solutions. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 22(1), 426–471. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2019.2916177
Balevi, E., & Gitlin, R. D. (2017). Unsupervised machine learning in 5G networks for low latency communications. In 2017 IEEE 36th international performance computing and communications conference (IPCCC) (vol. 2017, pp. 1–2). https://doi.org/10.1109/PCCC.2017.8280492
Deb, S., & Monogioudis, P. (2015). Learning-based uplink interference management in 4G LTE cellular systems. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 23(2), 398–411. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNET.2014.2300448
Sandhir, P., & Mitchell, K. (2008). A neural network demand prediction scheme for resource allocation in cellular wireless systems. In 2008 IEEE region 5 conference (pp. 1–6). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPSD.2008.4562719
Fazio, P., De Rango, F., & Selvaggi, I. (2010). A novel passive bandwidth reservation algorithm based on neural networks path prediction in wireless environments. In Proceedings of the 2010 international symposium on performance evaluation of computer and telecommunication systems (SPECTS ’10) (pp. 38–43).
Zang, Y., Ni, F., Feng, Z., Cui, S., & Ding, Z. (2015). Wavelet transform processing for cellular traffic prediction in machine learning networks. In IEEE China summit and international conference on signal and information processing (ChinaSIP) (vol. 2015, pp. 458–462). https://doi.org/10.1109/ChinaSIP.2015.7230444
Railean, I., Stolojescu, C., Moga, S., & Lenca, P. (2010). Wimax traffic forecasting based on neural networks in wavelet domain. In 4th international conference on research challenges in information science (RCIS) (vol. 2010, pp. 36–40). https://doi.org/10.1109/RCIS.2010.5507338
Chen, X., Mériaux, F., & Valentin, S. (2013). Predicting a user’s next cell with supervised learning based on channel states. In 2013 IEEE 14th workshop on signal processing advances in wireless communications (SPAWC) (pp. 36–40). https://doi.org/10.1109/SPAWC.2013.6612007
Zoha, A., Saeed, A., Imran, A., Imran, M., & Abu-Dayya, A. (2016). A learning-based approach for autonomous outage detection and coverage optimization. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 27, 439–450. https://doi.org/10.1002/ett.2971
Feng, V.-S., & Chang, S. Y. (2012). Determination of wireless networks parameters through parallel hierarchical support vector machines. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 23(3), 505–512. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2011.156
3GPP TS 38.101-1 version 15.3.0, 5G;NR; user equipment (UE) radio transmission and reception; part 2: Range 1 standalone.
3GPP TS 38.901, 5G. (2017). Study on channel model for frequencies from 0.5 to 100 GHz, technical specification (TS), 3rd generation partnership project (3GPP), version 14.0.0, release 14.
Bertsekas, D. (2009). Convex optimization theory. Athena Scientific.
ChinaPage. (2018). China mobile user gemographics. https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/chinapage/china-mobile-user-gemographics
Zhou, K., Gui, J., & Xiong, N. (2017). Improving cellular downlink throughput by multi-hop relay-assisted outband D2D communications. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2017, 1499–1687. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-017-0998-9
Liu, J., Wu, G., Xiao, S., Zhou, X., Li, G. Y., Guo, S., & Li, S. (2019). Joint power allocation and user scheduling for device-to-device-enabled heterogeneous networks with non-orthogonal multiple access. IEEE Access, 7, 62657–62671. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2916921
Funding
There are no funding agencies for this publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Pradip Kumar Barik and Ashu Dayal Chaurasiya wrote the main manuscript. Simulation was done by Pradip Kumar Barik and Ashu Dayal Chaurasiya. Pradip Kumar Barik prepared the figures and tables in the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Barik, P.K., Chaurasiya, A.D. & Datta, R. DOCA: a UAV-assisted multi-hop D2D resource allocation scheme for 5G and beyond using machine learning. Telecommun Syst 87, 465–482 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-024-01186-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-024-01186-7