Abstract
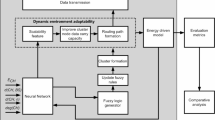
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) enable seamless data gathering and communication, facilitating efficient and real-time decision-making in IoT monitoring applications. However, the energy required to maintain communication in WSN-based IoT networks poses significant challenges, such as packet loss, packet drop, and rapid energy depletion. These issues reduce network life and performance, increasing the risk of delayed packet delivery. To address these challenges, this work presents a novel energy-efficient distributed neuro-fuzzy routing model executed in two stages to enhance communication efficiency and energy management in WSN-based IoT applications. In the first stage, nodes with high energy levels are predicted using a fusion of distributed learning with neural networks and fuzzy logic. In the second stage, clustering and routing are performed based on the predicted eligible nodes, incorporating thresholds for energy and distance with two combined metrics. The cluster head (CH) combined metric optimizes cluster head selection, while the next-hop combined metric facilitates efficient multi-hop communication. Extensive simulation results demonstrate that the proposed model significantly enhances network lifetime compared to EANFR, RBFNN T2F, and TTDFP by 9.48%, 25%, and 31.5%, respectively.













Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availibility statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Abbreviations
- ACK:
-
Acknowledgment
- ADV:
-
Advertisement
- ANFIS:
-
Adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system
- BS:
-
Base station
- CH:
-
Cluster head
- CCHs:
-
Candidate cluster heads
- DNN:
-
Deep neural network
- EANFR:
-
Energy-aware neuro fuzzy routing
- EEDC:
-
Energy efficient dynamic clustering
- FedAVG:
-
Federated average
- FND, HND, LND:
-
First node died, half node died, last node died
- LEACH:
-
Low energy adaptive clustering hierarchical
- SEP:
-
Stable election protocol
- I-SEP:
-
Improved stable election protocol
- GA:
-
Genetics algorithm
- MF:
-
Membership function
- NN:
-
Neural network
- NFL:
-
Neuro-fuzzy learning
- PDR:
-
Packet delivery ratio
- RBFNN:
-
Radial basis function neural network
- RFCM-GA:
-
Rough fuzzy c means and genetic algorithm
- ReLU:
-
Rectified linear unit
- T2F:
-
Type 2 fuzzy
- TTDFP:
-
Two tier distributed fuzzy protocol
References
Lazarescu, M. T. (2013). Design of a WSN platform for long-term environmental monitoring for IoT applications. IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, 3(1), 45–54. https://doi.org/10.1109/JETCAS.2013.2243032
Shafique, T., Gantassi, R., Soliman, A.-H., Amjad, A., Hui, Z.-Q., & Choi, Y. (2023). A review of energy hole mitigating techniques in multi-hop many to one communication and its significance in IoT oriented smart city infrastructure. IEEE Access, 11, 121340–121367. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3327311
Naeem, M. K., Patwary, M., & Abdel-Maguid, M. (2017). Universal and dynamic clustering scheme for energy constrained cooperative wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access, 5, 12318–12337. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2655345
Cengiz, K., & Dag, T. (2018). Energy aware multi-hop routing protocol for WSNs. IEEE Access, 6, 2622–2633. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2784542
Khalil, R. A., Saeed, N., Masood, M., Fard, Y. M., Alouini, M.-S., & Al-Naffouri, T. Y. (2021). Deep learning in the industrial internet of things: Potentials, challenges, and emerging applications. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(14), 11016–11040. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3051414
El Mokadem, R., Ben Maissa, Y., & El Akkaoui, Z. (2023). Federated learning for energy constrained devices: A systematic mapping study. Cluster Comput, 26, 1685–1708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-022-03763-4
Ni, J., Zhang, K., Lin, X., & Shen, X. (2018). Securing fog computing for Internet of Things applications: Challenges and solutions. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 20(1), 601–628. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2017.2762345
Mertens, J. S., Galluccio, L., & Morabito, G. (2022). MGM-4-FL: Combining federated learning and model gossiping in WSNs. Computer Networks, 214, 109144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2022.109144
Gamal, M., Mekky, N. E., Soliman, H. H., & Hikal, N. A. (2022). Enhancing the lifetime of wireless sensor networks using fuzzy logic LEACH technique-based particle swarm optimization. IEEE Access, 10, 36935–36948. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3163254
Heinzelman, W. B., Chandrakasan, A. P., & Balakrishnan, H. (2002). An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 1(4), 660–670. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2002.804190
Wang, M.-Y., Ding, J., Chen, W.-P., & Guan, W.-Q. (2015). SEARCH: A stochastic election approach for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 19(3), 443–446. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2015.2391100
Behera, T. M., Mohapatra, S. K., Samal, U. C., Khan, M. S., Daneshmand, M., & Gandomi, A. H. (2020). I-SEP: An improved routing protocol for heterogeneous WSN for IoT-based environmental monitoring. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(1), 710–717. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2019.2940988
Sert, S. A., Alchihabi, A., & Yazici, A. (2018). A two-tier distributed fuzzy logic based protocol for efficient data aggregation in multihop wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 26(6), 3615–3629. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2841369
Rasi, D., & Deepa, S. N. (2021). Energy optimization of internet of things in wireless sensor network models using type-2 fuzzy neural systems. International Journal of Communication Systems, 34, e4967. https://doi.org/10.1002/dac.4967
Qu, Z., Xu, H., Zhao, X., Tang, H., Wang, J., & Li, B. (2021). An energy-efficient dynamic clustering protocol for event monitoring in large-scale WSN. IEEE Sensors Journal, 21(20), 23614–23625. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2021.3103384
Jeevanantham, S., & Rebekka, B. (2022). Energy-aware neuro-fuzzy routing model for WSN based-IoT. Telecommunication Systems, 81, 441–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-022-00955-6
Ali, H., Tariq, U. U., Hussain, M., Lu, L., Panneerselvam, J., & Zhai, X. (2021). ARSH-FATI: A novel metaheuristic for cluster head selection in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Systems Journal, 15(2), 2386–2397. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2020.2986811
Gong, Y., Guo, X., & Lai, G. (2023). A centralized energy-efficient clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 23(2), 1623–1634. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2022.3224180
Hemavathi, N., Meenalochani, M., & Sudha, S. (2020). Influence of received signal strength on prediction of cluster head and number of rounds. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 69(6), 3739–3749. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2019.2932652
Li, Q., Wen, Z., Wu, Z., Hu, S., Wang, N., Li, Y., Liu, X., & He, B. (2023). A survey on federated learning systems: Vision, hype and reality for data privacy and protection. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 35(4), 3347–3366. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2021.3124599
Venkatesan, C., Jeevanantham, S., & Rebekka, B. (2024). Energy-aware federated learning for AQI pollutants forecasting in edge networks. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSE.2024.3398795
Tsang, Y. P., Wu, C. H., & Dong, N. (2023). A federated-ANFIS for collaborative intrusion detection in securing decentralized autonomous organizations. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEM.2023.3304409
Jang, J.-S.R. (1993). ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 23(3), 665–685. https://doi.org/10.1109/21.256541
Zhang, L., Shi, Y., Chang, Y.-C., & Lin, C.-T. (2023). Robust fuzzy neural network with an adaptive inference engine. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2023.3241170
Li, H.-X., & Liu, Z. (2008). A probabilistic neural-fuzzy learning system for stochastic modeling. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 16(4), 898–908. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2008.917302
Guzel, M., Kok, I., Akay, D., & Ozdemir, S. (2020). ANFIS and deep learning based missing sensor data prediction in IoT. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 32(2), e5400.
Suresh, S. S., Prabhu, V., Parthasarathy, V., Senthilkumar, G., & Gundu, V. (2024). Intelligent data routing strategy based on federated deep reinforcement learning for IOT-enabled wireless sensor networks. Measurement: Sensors, 31, 101012.
Behera, T. M., Mohapatra, S. K., Samal, U. C., & Khan, M. S. (2019). Hybrid heterogeneous routing scheme for improved network performance in WSNs for animal tracking. Internet of Things, 6, 100047.
Pundir, S., Wazid, M., Singh, D. P., Das, A. K., Rodrigues, J. J. P. C., & Park, Y. (2020). Intrusion detection protocols in wireless sensor networks integrated to Internet of Things deployment: Survey AND FUTURE CHALLENGES. IEEE Access, 8, 3343–3363. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2962829
Kaur, G., Chanak, P., & Bhattacharya, M. (2021). Energy-efficient intelligent routing scheme for IoT-enabled WSNs. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(14), 11440–11449. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3051768
Olatinwo, D. D., Abu-Mahfouz, A. M., Hancke, G. P., & Myburgh, H. C. (2023). Energy efficient priority-based hybrid MAC protocol for IoT-enabled WBAN systems. IEEE Sensors Journal, 23(12), 13524–13538. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2023.3273427
Bi, H., Sun, Y., Liu, J., & Cao, L. (2022). SmartEar: Rhythm-based tap authentication using earphone in information-centric wireless sensor network. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 9(2), 885–896. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3063479
Zhang, J., Guo, S., Guo, J., Zeng, D., Zhou, J., & Zomaya, A. Y. (2023). Towards data-independent knowledge transfer in model-heterogeneous federated learning. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 72(10), 2888–2901. https://doi.org/10.1109/TC.2023.3272801
Sheikh, A. M., & Joshi, S. (2024). Improved smart energy-based routing approach for IoT networks in wireless sensor nodes. Journal of Engineering and Applied Science, 71, 103. https://doi.org/10.1186/s44147-024-00435-5
Singh, A., & Nagaraju, A. (2020). Low latency and energy efficient routing-aware network coding-based data transmission in multi-hop and multi-sink WSN. Ad Hoc Networks, 107, 102182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2020.102182
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Methodology, Software, analysis and original draft preparation were performed by SJ. The final draft of the manuscript was supervised, reviewed and edited by BR. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no Conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jeevanantham, S., Venkatesan, C. & Rebekka, B. Distributed neuro-fuzzy routing for energy-efficient IoT smart city applications in WSN. Telecommun Syst 87, 497–516 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-024-01195-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-024-01195-6