Abstract
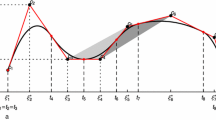
We present a new shape representation technique for a planar shape using overlapping quadratic splines. The technique refines the shape by iteratively updating each spline to reduce the cost associated with C 1 discontinuity. It consists of a series of affine commutative linear operators, producing a smooth bandpass frequency response. The primary purpose of the technique is to remove minute high-curvature points while preserving salient ones. We compare the performance of the technique against those that are based on either linear splines, cubic splines, or wavelets. We consider three criteria: sensitivity of detecting salient high-curvature points, Hausdorff distance between the representation and the original shape, and computation time. The results show that the proposed technique is highly effective in preserving salient high curvature points with a relatively small Hausdorff distance and a computational cost.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Alpert, B. (1993). A class of bases in l for the sparse representation of integral operators. SIAM Journal of Mathematical Analysis, 24, 246–262.
Asada, H., & Brady, M. (1986). The curvature primal sketch. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 8(1), 2–14.
Attneave, F. (1954). Some information aspects of visual perception. Psychological Review, 61(3), 183–193.
Belongie, S., Malik, J., & Puzicha, J. (2002). Shape matching and object recognition using shape contexts. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 24(4), 509–522.
Bengtsson, A., & Eklundh, J. (1991). Shape representation by multiscale contour approximation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 13(1), 85–93.
Bookstein, F. (1989). Principal warps: Thin-plate splines and the decomposition of deformations. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 11(6), 567–585.
Cham, T., & Cipolla, R. (1999). Automated b-spline curve representation incorporating mdl and error-minimizing control point insertion strategies. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 21(1), 49–53.
Charpiat, G., Faugeras, O., & Keriven, R. (2005). Approximations of shape metrics and application to shape warping and empirical shape statistics. Foundations of Computational Mathematics, 5(1), 1–58.
Chuang, G. C. H., & Kuo, C. C. J. (1996). Wavelet descriptor of planar curves: theory and applications. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 5(1), 56–70.
Cootes, T., Taylor, C., Cooper, D., & Graham, J. (1995). Active shape models: Their training and application. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 61(1), 38–59.
Cremers, D., Tischhauser, F., Weickert, J., & Schnorr, C. (2002). Diffusion snakes: Introducing statistical shape knowledge into the Mumford-shah functional. International Journal of Computer Vision, 50(3), 295–313.
Dambreville, S., Rathi, Y., & Tannenbaum, A. (2008). A framework for image segmentation using shape models and kernel space shape priors. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 30(8), 1385–1399.
de Boor, C. (1978). A practical guide to splines. New York: Springer.
Dessimoz, J. (1979). Curve smoothing for improved feature extraction from digitized pictures. Signal Processing, 1, 205–210.
Donoho, D. (1995). Denoising by soft-thresholding. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 41(3), 613–627.
Elder, J. H., & Zucker, S. W. (1996). Computing contour closure. In Proc. 4th European conference on computer vision (pp. 399–412). Cambridge, UK.
Elder, J., & Zucker, S. (1998). Local scale control for edge detection and blur estimation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 20(7), 699–716.
Fuchs, H., Kedem, Z., & Uselton, S. (1977). Optimal surface reconstructions from planar contours. Communications of the ACM, 20(10), 693–702.
Geronimo, J. S., Hardin, D. P., & Massopust, P. R. (1994). Fractal functions and wavelet expansions based on several scaling functions. Journal of Approximation Theory, 78, 373–401.
Getz, N. H. (1992). http://www.inversioninc.com/wavelet.html.
Jang, B., & Chin, R. (1998). Morphological scale space for 2d shape smoothing. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 70(2), 121–141.
Kass, M., Witkin, A., & Terzopoulos, D. (1988). Snakes: Active contour models. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1(4), 321–331.
Kendall, D. (1984). Shape manifolds, procrustean metrics, and complex projective spaces. Bulletin of London Mathematical Society, 16, 81–121.
Kilian, M., Mitra, N. J., & Pottmann, H. (2007). Geometric modeling in shape space. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 26(3), 64.
Kimia, B., & Siddiqi, K. (1996). Geometric heat-equation and nonlinear diffusion of shapes and images. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 64(3), 305–322.
Kubota, T. (2003). Contextual and non-combinatorial approach to feature extraction. In A. Rangarajan, M. A. T. Figueiredo, & J. Zerubia (Eds.), 4th international workshop on energy minimization methods in computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 467–482). Lisbon, Portugal.
Laurentini, A. (1994). The visual hull concept for silhouette-based image understanding. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 16(2), 150–162.
Lindeberg, T. (1998). Feature detection with automatic scale selection. International Journal of Computer Vision, 30(2), 79–116.
Lu, F., & Milios, E. E. (1994). Optimal spline fitting to planar shape. Signal Processing, 37, 129–140.
Marr, D. (1982). Vision. San Francisco: Freeman.
Michor, P., & Mumford, D. (2006). Riemannian geometries on spaces of plane curves. Journal of European Mathematical Society, 8, 1–48.
Mio, W., Srivastava, A., & Joshi, S. (2007). On shape of plane elastic curves. International Journal of Computer Vision, 73(3), 307–324.
Mokhtarian, F., & Mackworth, A. (1986). Scale based description and recognition of planar curves and two-dimensional shapes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 8(1), 34–43.
Mokhtarian, F., Abbasi, S., & Kittler, J. (1996). Efficient and robust retrieval by shape content through curvature scale space. In Proc. international workshop on image databases and multimedia search (pp. 35–42). Amsterdam, Netherlands.
Nonato, L. G., Cuadros-Vargas, A. J., Minghim, R., & Oliveira, M. C. F. D. (2005). Beta-connection: Generating a family of models from planar cross sections. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 24(4), 1239–1258.
Paglieroni, D. W., & Jain, A. K. (1988). Control point transforms for shape representation and measurement. Computer Vision, Graphics and Image Processing, 42, 87–111.
Precioso, F., Barlaud, M., Blu, T., & Unser, M. (2005). Robust real-time segmentation of images and videos using a smooth-spline snake-based algorithm. IEEE Transaction on Image Processing, 14(7), 910–924.
Rattarangsi, A., & Chin, R. (1992). Scale-based detection of corners of planar curves. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 14(4), 430–449.
Richardson, T., & Wang, S. (2006). Open-curve shape correspondence without endpoint correspondence. In Proc. international conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI) (Vol. I, pp. 17–24). Copenhagen, Denmark.
Sebastian, T., Klein, P., & Kimia, B. (2003). On aligning curves. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 25(1), 116–124.
Sharon, E., Brandt, A., & Basri, R. (2000). Completion energies and scale. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 22(10), 1117–1131.
Sundaramoorthi, G., Yezzi, A. Jr., & Mennucci, A. (2007). Sobolev active contours. International Journal of Computer Vision, 73(3), 345–366.
Teh, C., & Chin, R. (1989). On the detection of dominant points on digital curve. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 11(8), 859–872.
Wang, S., Kubota, T., & Richardson, T. (2004). Shape correspondence through landmark sliding (pp. I: 143–150).
Wang, S., Kubota, T., Siskind, J., & Wang, J. (2005). Salient closed boundary extraction with ratio contour. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 27(4), 546–561.
Witkin, A. (1983). Scale-space filtering. In Proc. 8th int’l joint conf. artificial intelligence (pp. 1019–1022).
Younes, L. (1998). Computable elastic distances between shapes. SIAM Journal of Applied Mathematics, 58, 565–586.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubota, T. A Shape Representation with Elastic Quadratic Polynomials—Preservation of High Curvature Points under Noisy Conditions. Int J Comput Vis 82, 133–155 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-008-0192-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-008-0192-y