Abstract
This paper proposes a new similarity measure that is invariant to global and local affine illumination changes. Unlike existing methods, its computational complexity is very low. When used for stereo correspondence estimation, its computational complexity is linear in the number of image pixels and disparity searching range. It also outperforms the current state of the art similarity measures in terms of accuracy on the Middlebury benchmark (with radiometric differences).











Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Notes
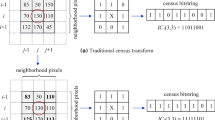
The trained patch size for Census transform is \(19 \times 19\).
References
Brown, M., Burschka, D., & Hager, G. D. (2003). Advances in computational stereo. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 25(8), 993–1008.
Chia, A., Zhuo, S., Gupta, R., Tai, Y., Cho, S., Tan, P., et al. (2011). Semantic colorization with internet images. ACM Transcation on Graphics, 30(6), 156:1–156:8.
Cox, I., Roy, S., & Hingorani, S. (1995). Dynamic histogram warping of image pairs for constant image brightness. In ICIP.
De-Maeztu, L., Mattoccia, S., Villanueva, A., & Cabeza, R. (2011). Linear stereo matching. In ICCV, Nov 2011 (pp. 1708–1715).
Ding, Y., Xiao, J., & Yu, J. (2011). Importance filtering for image retargeting. In CVPR.
Egnal, G. (2000). Mutual information as a stereo correspondence measure, Technical Report MS-CIS-00-20. Computer and Information Science, University of Pennsylvania.
Goesele, M., Snavely, N., Curless, B., Hoppe, H., & Seitz, S. (2007). Multi-view stereo for community photo collections. In ICCV.
He, K., Rhemann, C., Rother, C., Tang, X., & Sun, J. (2011) A global sampling method for alpha matting. In CVPR, June 2011 (pp. 2049–2056).
He, K., Sun, J., & Tang, X. (2011). Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 33(12), 2341–2353.
He, K., Sun, J., & Tang, X. (2013). Guided image filtering. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 35(6), 1397–1409.
Heo, Y., Lee, K., & Lee, S. (2009). Mutual information-based stereo matching combined with sift descriptor in log-chromaticity color space. In CVPR, 2009 (pp. 445–452).
Heo, Y., Lee, K., & Lee, S. (2011). Robust stereo matching using adaptive normalized cross-correlation. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 33(4), 807–822.
Heo, Y., Lee, K., & Lee, S. (2013). Joint depth map and color consistency estimation for stereo images with different illuminations and cameras. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 35(5), 1094–1106.
Hestenes, M., & Stiefel, D. (1952). Methods of conjugate gradients for solving linear systems. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 49, 409–436.
Hirschmuller, H. (2008). Stereo processing by semiglobal matching and mutual information. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 30(2), 328–341.
Hirschmuller, H., & Scharstein, D. (2009). Evaluation of stereo matching costs on images with radiometric differences. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 31(9), 1582–1599.
Hosni, A., Rhemann, C., Bleyer, M., Rother, C., & Gelautz, M. (2013). Fast cost-volume filtering for visual correspondence and beyond. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 35(2), 504–511.
Kim, J., Kolmogorov, V., & Zabih, R. (2003). Visual correspondence using energy minimization and mutual information. In ICCV.
Klaus, A., Sormann, M., & Karner, K. (2006). Segment-based stereo matching using belief propagation and a self-adapting dissimilarity measure. In ICPR, 2006 (pp. 15–18).
Levin, A., Lischinski, D., & Weiss, Y. (2008). A closed-form solution to natural image matting. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 30(2), 228–242.
Scharstein, D., & Szeliski, R. (2002a) Middlebury stereo datasets. http://vision.middlebury.edu/stereo/data/.
Scharstein, D., & Szeliski, R. (2002b). A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. International Journal of Computer Vision, 47, 7–42.
Snavely, N., Seitz, S. M., & Szeliski, R. (2006). Photo tourism: Exploring photo collections in 3d. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 25(3), 835–846.
Wang, L., & Yang, R. (2011). Global stereo matching leveraged by sparse ground control points. In CVPR, June 2011 (pp. 3033–3040).
Wang, L., Yang, R., & Davis, J. (2007). Brdf invariant stereo using light transport constancy. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 29(9), 1616–1626.
Yang, Q., Wang, L., & Ahuja, N. (2010) A constant-space belief propagation algorithm for stereo matching. In CVPR, 2010 (pp. 1458–1465).
Yang, Q., Wang, L., Yang, R., Stewenius, H., & Nister, D. (2009). Stereo matching with color-weighted correlation, hierachical belief propagation and occlusion handling. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 31(3), 492–504.
Yang, Q. (2015). Stereo matching using tree filtering. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 37(4), 834–846.
Yoon, K.-J., & Kweon, I.-S. (2006). Adaptive support-weight approach for correspondence search. IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 28(4), 650–656.
Zabih, R., & Woodfill, J. (1994). Non-parametric local transforms for computing visual correspondence. In ECCV, 1994 (pp. 151–158).
Zhu, S., Zhang, L., & Jin, H. (2012). A locally linear regression model for boundary preserving regularization in stereo matching. In Proceedings of the 12th European conference on computer vision—Volume Part V, ser. ECCV’12 (pp. 101–115). Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Zomet, A., & Peleg, S. (2002). Multi-sensor super resolution. In WACV.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Research Grants Council of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, China (Project No. CityU 21201914).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Masatoshi Okutomi.
Appendix
Appendix
1.1 Appendix 1: Derivation of Eq. 12
The matching cost measured from two corresponding pixels p and \(p'\) in two grayscale images \(I_L\) and \(I_R\) is:
1.2 Appendix 2: Derivation of Eq. 22
Similar to Eq. 4, we can extend Eq. 20 for color images as follows:
\(\tilde{\mathcal {X}}\) is defined in Eq. 21, and
and
The linear system presented in Eq. 28 can be rewritten as:
where
and
1.3 Appendix 3: Derivation of Eq. 23
The matching cost for color images is:
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Yang, Q., Tang, J. et al. Linear Time Illumination Invariant Stereo Matching. Int J Comput Vis 119, 179–193 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-016-0886-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-016-0886-5