Abstract
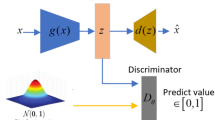
We propose a real-time RGB-based pipeline for object detection and 6D pose estimation. Our novel 3D orientation estimation is based on a variant of the Denoising Autoencoder that is trained on simulated views of a 3D model using Domain Randomization. This so-called Augmented Autoencoder has several advantages over existing methods: It does not require real, pose-annotated training data, generalizes to various test sensors and inherently handles object and view symmetries. Instead of learning an explicit mapping from input images to object poses, it provides an implicit representation of object orientations defined by samples in a latent space. Our pipeline achieves state-of-the-art performance on the T-LESS dataset both in the RGB and RGB-D domain. We also evaluate on the LineMOD dataset where we can compete with other synthetically trained approaches. We further increase performance by correcting 3D orientation estimates to account for perspective errors when the object deviates from the image center and show extended results. Our code is available here https://github.com/DLR-RM/AugmentedAutoencoder.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balntas, V., Doumanoglou, A., Sahin, C., Sock, J., Kouskouridas, R., & Kim, T. K. (2017). Pose guided RGB-D feature learning for 3D object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 3856–3864).
Bousmalis, K., Irpan, A., Wohlhart, P., Bai, Y., Kelcey, M., Kalakrishnan, M., Downs, L., Ibarz, J., Pastor, P., Konolige, K., et al. (2017a). Using simulation and domain adaptation to improve efficiency of deep robotic grasping. arXiv preprint arXiv:170907857.
Bousmalis, K., Silberman, N., Dohan, D., Erhan, D., & Krishnan, D. (2017b). Unsupervised pixel-level domain adaptation with generative adversarial networks. In The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (Vol. 1, p. 7).
Brachmann, E., Michel, F., Krull, A., Ying Yang, M., Gumhold, S., et al. (2016). Uncertainty-driven 6D pose estimation of objects and scenes from a single RGB image. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 3364–3372).
Chen, Y., & Medioni, G. (1992). Object modelling by registration of multiple range images. Image and Vision Computing, 10(3), 145–155.
Csurka, G. (2017). Domain adaptation for visual applications: A comprehensive survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:170205374.
Drost, B., Ulrich, M., Navab, N., & Ilic, S. (2010). Model globally, match locally: Efficient and robust 3D object recognition. In 2010 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, IEEE (pp. 998–1005).
Everingham, M., Van Gool, L., Williams, C. K. I., Winn, J., & Zisserman, A. (2012). The PASCAL visual object classes challenge 2012 (VOC2012) results. http://host.robots.ox.ac.uk/pascal/VOC/voc2012/results/index.html.
Glorot, X., & Bengio, Y. (2010). Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In Proceedings of the thirteenth international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics (pp. 249–256).
Hinterstoisser, S., Benhimane, S., Lepetit, V., Fua, P., & Navab, N. (2008). Simultaneous recognition and homography extraction of local patches with a simple linear classifier. In Proceedings of the British machine conference (pp. 1–10).
Hinterstoisser, S., Holzer, S., Cagniart, C., Ilic, S., Konolige, K., Navab, N., & Lepetit, V. (2011). Multimodal templates for real-time detection of texture-less objects in heavily cluttered scenes. In 2011 IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), IEEE (pp. 858–865).
Hinterstoisser, S., Cagniart, C., Ilic, S., Sturm, P., Navab, N., Fua, P., et al. (2012a). Gradient response maps for real-time detection of textureless objects. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 34(5), 876–888.
Hinterstoisser, S., Lepetit, V., Ilic, S., Holzer, S., Bradski, G., Konolige, K., & Navab, N. (2012b) Model based training, detection and pose estimation of texture-less 3D objects in heavily cluttered scenes. In Asian conference on computer vision, Springer (pp 548–562)
Hinterstoisser, S., Lepetit, V., Rajkumar, N., & Konolige, K. (2016) Going further with point pair features. In European conference on computer vision, Springer (pp. 834–848)
Hinterstoisser, S., Lepetit, V., Wohlhart, P., & Konolige, K. (2017) On pre-trained image features and synthetic images for deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:171010710.
Hodan, T. (2017). SIXD Challenge 2017. http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/sixd/challenge_2017/. Accessed 7 Oct 2019.
Hodaň, T., Matas, J., & Obdržálek, Š. (2016). On evaluation of 6D object pose estimation. In European conference on computer vision, Springer (pp. 606–619).
Hodaň, T., Haluza, P., Obdržálek, Š., Matas, J., Lourakis, M., & Zabulis, X. (2017). T-LESS: An RGB-D dataset for 6D pose estimation of texture-less objects. In IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV).
Hodan, T., Michel, F., Brachmann, E., Kehl, W., GlentBuch, A., Kraft, D., Drost, B., Vidal, J., Ihrke, S., Zabulis, X., et al. (2018) Bop: Benchmark for 6D object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 19–34).
Hodan, T., Vineet, V., Gal, R., Shalev, E., Hanzelka, J., Connell, T., Urbina, P., Sinha, S. N., & Guenter, B. K. (2019) Photorealistic image synthesis for object instance detection. arXiv:1902.03334.
Howard, A. G., Zhu, M., Chen, B., Kalenichenko, D., Wang, W., Weyand, T., Andreetto, M., & Adam, H. (2017). Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:170404861.
Kehl, W., Milletari, F., Tombari, F., Ilic, S., & Navab, N. (2016). Deep learning of local RGB-D patches for 3D object detection and 6D pose estimation. In European conference on computer vision, Springer (pp. 205–220).
Kehl, W., Manhardt, F., Tombari, F., Ilic, S., & Navab, N. (2017) SSD-6D: Making RGB-based 3D detection and 6D pose estimation great again. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 1521–1529)
Kingma, D., & Ba, J. (2014) Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:14126980.
Lin, T. Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ramanan, D., Dollár, P., & Zitnick, C. L. (2014) Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In European conference on computer vision, Springer (pp. 740–755).
Lin, T. Y., Goyal, P., Girshick, R., He, K., & Dollár, P. (2017). Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 2980–2988).
Liu, W., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Szegedy, C., Reed, S., Fu, C. Y., & Berg, A. C. (2016) SSD: Single shot multibox detector. In European conference on computer vision, Springer (pp. 21–37).
Mahendran, S., Ali, H., & Vidal, R. (2017). 3D pose regression using convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:170805628.
Manhardt, F., Kehl, W., Navab, N., & Tombari, F. (2018). Deep model-based 6D pose refinement in RGB. In The European conference on computer vision (ECCV)
Matthey, L., Higgins, I., Hassabis, D., & Lerchner, A. (2017). dsprites: Disentanglement testing Sprites dataset. https://github.com/deepmind/dsprites-dataset/.
Mitash, C., Bekris, K. E., & Boularias, A. (2017). A self-supervised learning system for object detection using physics simulation and multi-view pose estimation. In 2017 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), IEEE (pp. 545–551).
Movshovitz-Attias, Y., Kanade, T., & Sheikh, Y. (2016). How useful is photo-realistic rendering for visual learning? In European conference on computer vision, Springer (pp. 202–217).
Phong, B. T. (1975). Illumination for computer generated pictures. Communications of the ACM, 18(6), 311–317.
Rad, M., & Lepetit, V. (2017). BB8: A scalable, accurate, robust to partial occlusion method for predicting the 3D poses of challenging objects without using depth. arXiv preprint arXiv:170310896.
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., & Sun, J. (2015). Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 91–99).
Richter, S. R., Vineet, V., Roth, S., & Koltun, V. (2016). Playing for data: Ground truth from computer games. In European conference on computer vision, Springer (pp. 102–118).
Rumelhart, D. E., Hinton, G. E., & Williams, R. J. (1985). Learning internal representations by error propagation. Technical report, California University, San Diego, La Jolla, Institute for Cognitive Science.
Saxena, A., Driemeyer, J., & Ng, A. Y. (2009). Learning 3D object orientation from images. In IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, 2009. ICRA’09. IEEE (pp. 794–800).
Shrivastava, A., Pfister, T., Tuzel, O., Susskind, J., Wang, W., & Webb, R. (2017). Learning from simulated and unsupervised images through adversarial training. In 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), IEEE (pp. 2242–2251)
Su, H., Qi, C. R., Li, Y., & Guibas, L. J. (2015). Render for CNN: Viewpoint estimation in images using CNNs trained with rendered 3D model views. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 2686–2694).
Sundermeyer, M., Marton, Z. C., Durner, M., Brucker, M., & Triebel, R. (2018). Implicit 3D orientation learning for 6D object detection from RGB images. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 699–715).
Tekin, B., Sinha, S. N., & Fua, P. (2017). Real-time seamless single shot 6D object pose prediction. arXiv preprint arXiv:171108848.
Tobin, J., Fong, R., Ray, A., Schneider, J., Zaremba, W., & Abbeel, P. (2017). Domain randomization for transferring deep neural networks from simulation to the real world. In 2017 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), IEEE (pp. 23–30).
Tremblay, J., To, T., Sundaralingam, B., Xiang, Y., Fox, D., & Birchfield, S. (2018). Deep object pose estimation for semantic robotic grasping of household objects. In Conference on robot learning (pp. 306–316)
Ulrich, M., Wiedemann, C., & Steger, C. (2009). CAD-based recognition of 3D objects in monocular images. ICRA, 9, 1191–1198.
Vidal, J., Lin, C. Y., & Martí, R. (2018) 6D pose estimation using an improved method based on point pair features. arXiv preprint arXiv:180208516.
Vincent, P., Larochelle, H., Lajoie, I., Bengio, Y., & Manzagol, P. A. (2010). Stacked denoising autoencoders: Learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 11(Dec), 3371–3408.
Wohlhart, P., & Lepetit, V. (2015). Learning descriptors for object recognition and 3D pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 3109–3118).
Wu, Z., Shen, C., & Hengel, A. (2016). Bridging category-level and instance-level semantic image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:160506885.
Xiang, Y., Schmidt, T., Narayanan, V., & Fox, D. (2017). Posecnn: A convolutional neural network for 6D object pose estimation in cluttered scenes. arXiv preprint arXiv:171100199.
Zakharov, S., Shugurov, I., & Ilic, S. (2019). DPOD: Dense 6D pose object detector in RGB images. arXiv preprint arXiv:190211020.
Zhang, Z. (1994). Iterative point matching for registration of free-form curves and surfaces. International Journal of Computer Vision, 13(2), 119–152.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Ingo Kossyk, Dimitri Henkel and Max Denninger for helpful discussions. We also thank the reviewers for their useful comments.
Funding
Funding was provided by German Aerospace Center (DLR) and Robert Bosch GmbH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Yair Weiss.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundermeyer, M., Marton, ZC., Durner, M. et al. Augmented Autoencoders: Implicit 3D Orientation Learning for 6D Object Detection. Int J Comput Vis 128, 714–729 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-019-01243-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-019-01243-8